
Concept explainers
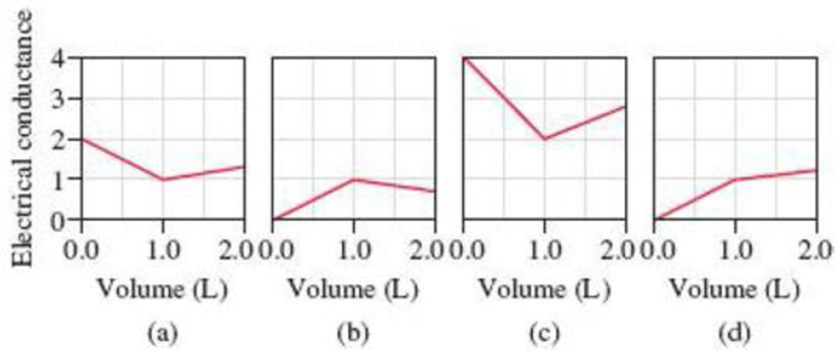
Because the acid-base and precipitation reactions discussed in this chapter all involve ionic species, their progress can be monitored by measuring the electrical conductance of the solution. Match each of the following reactions with one of the diagrams shown here. The electrical conductance is shown in arbitrary units. Explain the significance of the point at which the slope changes in each diagram.
(1) A 1.0 M KOH solution is added to 1.0 L of 1.0 M HC2H3O2.
(2) A 1.0 M NaOH solution is added to 1.0 L of 1.0 M HCl.
(3) A 1.0 M BaCl2 solution is added to 1.0 L of 1.0 M K2SO4.
(4) A 1.0 M NaCl solution is added to 1.0 L of 1.0 M AgNO3.
(5) A 1.0 M HC2H3O2 solution is added to 1.0 L of 1.0 M NH3.
(a)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance, when
Answer to Problem 9.168QP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data
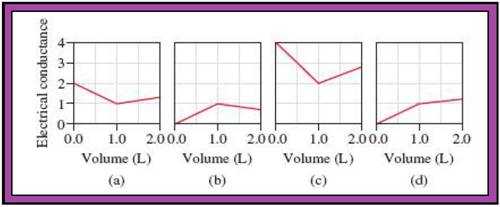
Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
If Conductance unit of
(b)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance when,
Answer to Problem 9.168QP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data

Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
(c)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance when,
Answer to Problem 9.168QP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data

Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
(d)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance, when
Answer to Problem 9.168QP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data

Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
(e)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance, when
Answer to Problem 9.168QP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data

Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
Match the calculated conductance unit of each reaction in given diagrams in Fig.1.
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Student Solutions Manual For Chemistry: Atoms First
- The Behavior of Substances in Water Part 1: a Ammonia, NH3, is a weak electrolyte. It forms ions in solution by reacting with water molecules to form the ammonium ion and hydroxide ion. Write the balanced chemical reaction for this process, including state symbols. b From everyday experience you are probably aware that table sugar (sucrose), C12H22O11, is soluble in water. When sucrose dissolves in water, it doesnt form ions through any reaction with water. It just dissolves without forming ions, so it is a nonelectrolyte. Write the chemical equation for the dissolving of sucrose in water. c Both NH3 and C12H22O11 are soluble molecular compounds, yet they behave differently in aqueous solution. Briefly explain why one is a weak electrolyte and the other is a nonelectrolyte. d Hydrochloric acid, HCl, is a molecular compound that is a strong electrolyte. Write the chemical reaction of HCl with water. e Compare the ammonia reaction with that of hydrochloric acid. Why are both of these substances considered electrolytes? f Explain why HCl is a strong electrolyte and ammonia is a weak electrolyte. g Classify each of the following substances as either ionic or molecular. KCl NH3 CO2 MgBr2 HCl Ca(OH)2 PbS HC2H3O2 h For those compounds above that you classified as ionic, use the solubility rules to determine which are soluble. i The majority of ionic substances are solids at room temperature. Describe what you would observe if you placed a soluble ionic compound and an insoluble ionic compound in separate beakers of water. j Write the chemical equation(s), including state symbols, for what happens when each soluble ionic compound that you identified above is placed in water. Are these substances reacting with water when they are added to water? k How would you classify the soluble ionic compounds: strong electrolyte, weak electrolyte, or nonelectrolyte? Explain your answer. l Sodium chloride, NaCl, is a strong electrolyte, as is hydroiodic acid, HI. Write the chemical equations for what happens when these substances are added to water. m Are NaCl and HI strong electrolytes because they have similar behavior in aqueous solution? If not, describe, using words and equations, the different chemical process that takes place in each case. Part 2: You have two hypothetical molecular compounds, AX and AY. AX is a strong electrolyte and AY is a weak electrolyte. The compounds undergo the following chemical reactions when added to water. AX(aq)+H2O(l)AH2O+(aq)+X(aq)AY(aq)+H2O(l)AH2O+(aq)+Y(aq) a Explain how the relative amounts of AX(aq) and AY(aq) would compare if you had a beaker of water with AX and a beaker of water with AY. b How would the relative amounts of X(aq) and Y(aq) in the two beakers compare? Be sure to explain your answer.arrow_forwardAn aqueous sample is known to contain either Mg2+ or Ba2+ ions. Treatment of the sample with Na2CO3 produces a precipitate, but treatment with ammonium sulfate does not. Use the solubility rules (see Table 4.1) to determine which cation is present.arrow_forwardConsider the following generic equation OH(aq)+HB(aq) B(aq)+H2OFor which of the following pairs would this be the correct prototype equation for the acid-base reaction in solution? If it is not correct, write the proper equation for the acid-base reaction between the pair. (a) hydrochloric acid and pyridine, C5H5N (b) sulfuric acid and rubidium hydroxide (c) potassium hydroxide and hydrofluoric acid (d) ammonia and hydriodic acid (e) strontium hydroxide and hydrocyanic acidarrow_forward
- Write the net ionic equation for the reaction, if any, that occurs on mixing (a) solutions of sodium hydroxide and magnesium chloride. (b) solutions of sodium nitrate and magnesium bromide. (c) magnesium metal and a solution of hydrochloric acid to produce magnesium chloride and hydrogen. Magnesium metal reacting with HCl.arrow_forwardA metal, M, was converted to the sulfate, M2(SO4)3. Then a solution of the sulfate was treated with barium chloride to give barium sulfate crystals, which were filtered off. M2(SO4)3(aq)+3BaCl2(aq)2MCl3(aq)+3BaSO4(s) If 1.200 g of the metal gave 6.026 g of barium sulfate, what is the atomic weight of the metal? What is the metal?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





