
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The products expected when
Concept introduction:
An
All these reactions take place in the presence of basic compounds but in case of
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The products formed when
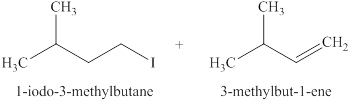
Explanation of Solution
The type of reactions those occurs when
The products that are obtained via
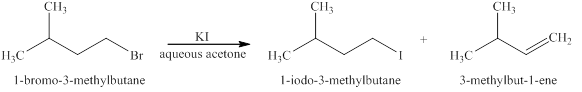
Figure 1
The
An
The products formed when
(b)
Interpretation:
The products expected when
Concept introduction:
An alkyl halide in the presence of basic compounds undergoes multiple kinds of reaction, for example,
All these reactions take place in the presence of basic compounds but in case of
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The products expected when
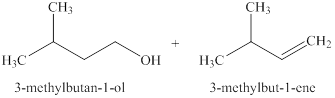
Explanation of Solution
The type of reactions which
The products that are obtained via
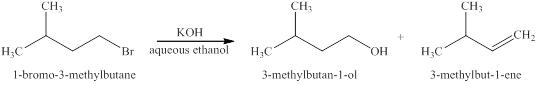
Figure 2
The
An
The products expected when
(c)
Interpretation:
The products expected when
Concept introduction:
An alkyl halide in the presence of basic compounds undergoes multiple kinds of reaction, for example,
All these reactions take place in the presence of basic compounds but in case of
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The product expected when
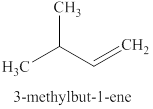
Explanation of Solution
The type of reaction which
The product that is obtained via
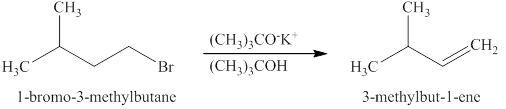
Figure 3
An
Only
The product expected when
(d)
Interpretation:
The products expected from the reaction of the product of part (c) and
Concept introduction:
An
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The products expected from the reaction of the products of part (c) and
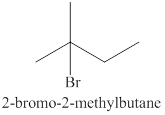
Explanation of Solution
Markonikov’s gave the rule purely on the basis of the observation of products received by him when performed the addition reaction on alkene.
Some reactions do not follow the rule because they follow the stability of the intermediate formed in the mechanism of that particular reaction.
The reaction of an alkene
In the reaction between the product of part (c) and
The products expected from the reaction of the products of part (c) and
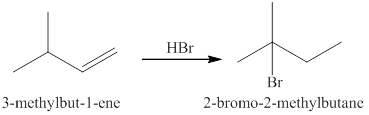
Figure 4
The products expected from the reaction of the products of part (c) and
(e)
Interpretation:
The products expected when
Concept introduction:
An alkyl halide in the presence of basic compounds undergoes multiple kinds of reaction, for example,
All these reactions take place in the presence of basic compounds but in case of
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The products expected when
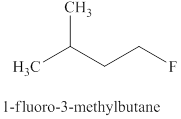
Explanation of Solution
The type of reaction which
The product for the

Figure 5
The
The fluoride ion only undergoes
The products expected when
(f)
Interpretation:
The products expected from the reaction of the product of part (c), chloroform and potassium
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The products expected from the reaction of the product of part (c), chloroform, and potassium
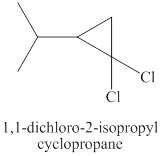
Explanation of Solution
Step-1: Take up of proton to give carbanion.
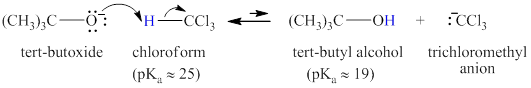
Figure 6
Step-2: Elimination of chloride ion to give carbene.
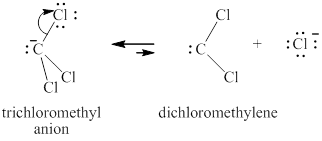
Figure 7
The carbene thus formed adds on the alkene in the leading to no change in the respective stereochemistry of substituents on alkene.
The same reaction is happening when the product of part (c) plus chloroform plus potassium
Therefore, the products expected from the reaction of the product of part (c), chloroform and potassium
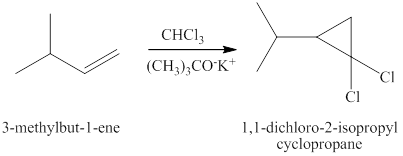
Figure 8
The products expected from the reaction of the product of part (c) chloroform and potassium
(g)
Interpretation:
The products expected from the reaction of the product of part (c) and
Concept introduction:
The reaction of an alkene with the diiodomethane in the presence of
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The products expected from the reaction of the product of part (c) and
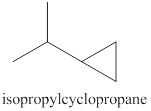
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of the product of part (c) and
The products expected from the reaction of the product of part (c) and
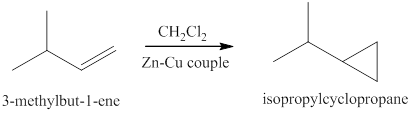
Figure 9
The products expected from the reaction of the product of part (c) and
(h)
Interpretation:
The products expected from the reaction of
Concept introduction:
The reaction of an alkyl halide with a metal like lithium leads to the formation of organolithium compounds (alkyllithium). These compounds are very sensitive to moisture or polar hydrogens reacts immediately leading to the formation of
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The products expected from the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of an alkyl halide with a metal like lithium leads to the formation of organolithium compounds (alkyllithium), which are highly susceptible to humidity or react to polar hydrogen instantly leading to the alkyl group’s formation. The same reaction is happening in this case.
The products expected from the reaction of
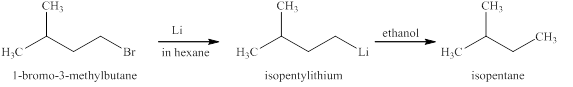
Figure 10
The products expected from the reaction of
(i)
Interpretation:
The products expected when
Concept introduction:
An alkyl halide in the presence of basic compounds undergoes multiple kinds of reaction, for example,
All these reactions take place in the presence of basic compounds but in case of
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The products expected when
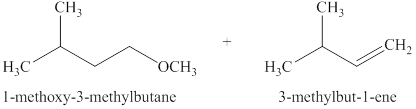
Explanation of Solution
The type of reactions that occurs when
The products that are obtained via
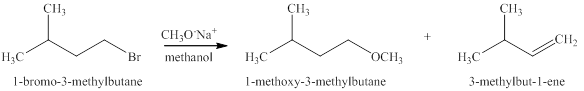
Figure 11
The
An
The products expected when
(j)
Interpretation:
The products expected from the reaction of
Concept introduction:
The reaction of an alkyl halide with a metal like magnesium in the presence of dry ether leads to the formation of
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The products expected from the reaction of
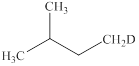
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of an alkyl halide with a metal like magnesium in the presence of dry ether results in the formation of (organometallic compounds) also known as a Grignard reagent. These compounds are very susceptible to reactions of moisture or polar hydrogen leading to the creation of alkane of the alkyl group instantly. In this case, the same reaction is occurring.
The Grignard reagent obtained in this reaction is isopentylmagnesium bromide and product obtained after treatement with heavy water is deuterated isopentane.
The products expected from the reaction of
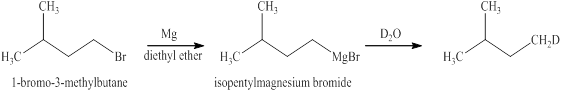
Figure 12
The products expected from the reaction of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Loose-leaf Version For Organic Chemistry
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





