
Concept explainers
The following Lewis structures for (a) HCN, (b) C2H2, (c) SnO2, (d) BF3, (e) HOF, (f) HCOF, and (g) NF3 are incorrect. Explain what is wrong with each one and give a correct structure for the molecule. (Relative positions of atoms are shown correctly.)
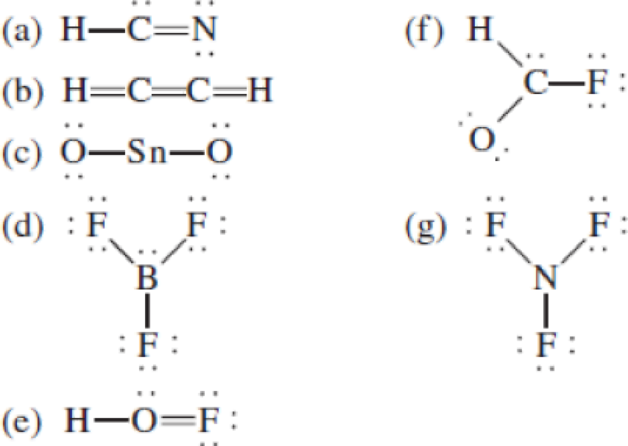
(a)
Interpretation: The Lewis structures of the molecules should be corrected with appropriate explanation.
Concept Introduction: Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Dots represent the electron position around the atoms and lines or dot pairs represent covalent bonds between atoms.
The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Answer to Problem 9.47QP
Explanation of Solution
To find: The correct Lewis structure for the given molecule.
- The given structure of the molecule is shown below.
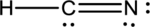
- In the given structure, the carbon contains lone pair of electrons and the bond between carbon and nitrogen is double bond. So the octets of these two atoms are not filled.
- The corrected Lewis structure of the above compound is drawn below.
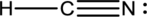
The total number of valence electrons is found to be 10, where 1 electron, 5 electrons and 4 electrons were contributed by H, C and N atoms respectively. Carbon is placed as the central atoms since its electronegativity is less than nitrogen.
The 6 electrons getting after reducing two electrons for each bond from the total valence electron are distributed on N atom to complete the octet. Sincethe octets of C atoms are not filled, a triple bond is made between C and N atoms.
(b)
Interpretation: The Lewis structures of the molecules should be corrected with appropriate explanation.
Concept Introduction: Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Dots represent the electron position around the atoms and lines or dot pairs represent covalent bonds between atoms.
The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Answer to Problem 9.47QP

Explanation of Solution
To find: The correct Lewis structure of the given molecule.
- The given structure of the molecule is below.

- In the given structure there is a double bond between hydrogen and carbon which violates the octet rule and also the bond between 2 carbon atoms is double.
- The corrected Lewis structure of the above compound is drawn below.

Each carbon atom bonded with one carbon and hydrogen atom. The total number of valence electrons found to be 10, where 1 electron, 5 electrons were contributed by each H and C atoms respectively.
Sincethere are noelectrons to distribute after reducing two electrons for each bond from the total valence electron, a triple bond is made between two C atomsto fill the octets.
(c)
Interpretation: The Lewis structures of the molecules should be corrected with appropriate explanation.
Concept Introduction: Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Dots represent the electron position around the atoms and lines or dot pairs represent covalent bonds between atoms.
The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Answer to Problem 9.47QP
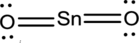
Explanation of Solution
To find: The correct Lewis structure of the given molecule.
- The given structure of the molecule is below.
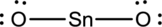
- In the given structure, tin atom does not fill the octet since the bond between tin and terminal atoms are single bond.
- The corrected Lewis structure of the above compound is drawn below.
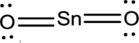
The electronegativity of tin atom is less than oxygen, so it is taken as the central atom bonded with an oxygen atom at each side. Tin atom contributes 4 and each oxygen atom contributes 6 electrons making the total number of valence electrons 16.
To obtain the remaining electrons 12, two electrons for each bond is reduced from the total number of valence electrons, which then further distributed on the terminal oxygen atoms to fill the octets.
Since the central tin atom does not complete octet, a double bond is formed between each terminal oxygen atom
(d)
Interpretation: The Lewis structures of the molecules should be corrected with appropriate explanation.
Concept Introduction: Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Dots represent the electron position around the atoms and lines or dot pairs represent covalent bonds between atoms.
The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Answer to Problem 9.47QP
Explanation of Solution
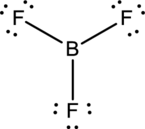
To find: The correct Lewis structure of the given molecule.
- The given structure of the molecule is below.
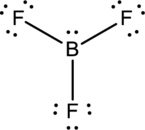
- In this structure, there is a lone pair of electron on boron atom whereas in actual structure that lone pair is no needed to fill the octet.
- The corrected Lewis structure of the above compound is drawn below.
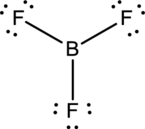
Boron atom has less electronegativity comparing to fluorine. So it is taken as the central atom with 3 terminal fluorine atoms.The boron has 4 and each fluorine atom have 7 valence electrons. Since there are 3 fluorine atoms the total valence electron of the molecule becomes 24.
The 18 electrons after reducing two electrons for each bond from the total valence electron are distributed onfluorine atom to fill the octets. So each fluorine atom gets 3 lone pairs.
(e)
Interpretation: The Lewis structures of the molecules should be corrected with appropriate explanation.
Concept Introduction: Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Dots represent the electron position around the atoms and lines or dot pairs represent covalent bonds between atoms.
The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Answer to Problem 9.47QP
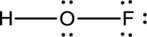
Explanation of Solution
To find: The correct Lewis structure of the given molecule
- The given structure of the molecule is below.
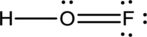
- In the given structure, there is a double bond between oxygen and fluorine which is not needed. Distributing a lone pair on oxygen is enough to fill its octet.
- The corrected Lewis structure of the above compound is drawn below.
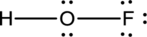
The electronegativity of oxygen atom is less than fluorine and the molecule is with hydrogen and fluorine atoms at the terminal position of oxygen.
Hydrogen, oxygen and fluorine contribute 1, 6 and 7 electrons respectively making the total number of valence electrons 14.
The 10 electrons after reducing for each bond from the total valence electron are distributed on terminal atoms, then to central oxygen atom to fill the octets.
(f)
Interpretation: The Lewis structures of the molecules should be corrected with appropriate explanation.
Concept Introduction: Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Dots represent the electron position around the atoms and lines or dot pairs represent covalent bonds between atoms.
The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Answer to Problem 9.47QP
Explanation of Solution
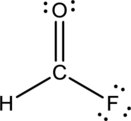
- The given structure of the molecule is below.
- Here the bond between oxygen and carbon is not given appropriately to fill the octet.
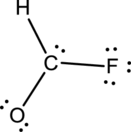
- The corrected Lewis structure of the above compound is drawn below.
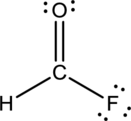
Comparing to fluorine and oxygen, carbon has the least electronegativity, so it is taken as the central atom with hydrogen, fluorine and oxygen at its terminal positions.
Hydrogen, oxygen, carbon and fluorine contribute 1, 6, 4 and 7 electrons respectively making the total number of valence electrons 18.
To fill the octets of the atoms, the 12 electrons after reducing two electrons for each bond from the total valence electron are distributed on terminal atoms.
Since the central carbon atom does not have sufficient electrons to fill the octet, a double bond is made between carbon and terminal oxygen atoms.
(g)
Interpretation: The Lewis structures of the molecules should be corrected with appropriate explanation.
Concept Introduction: Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Dots represent the electron position around the atoms and lines or dot pairs represent covalent bonds between atoms.
The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Answer to Problem 9.47QP
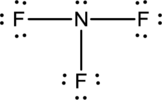
Explanation of Solution
- The given structure of the molecule is below.
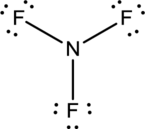
- In this structure a lone pair of electrons is missing which is sufficient to fill the octet of nitrogen.
- The corrected Lewis structure of the above compound is drawn below.
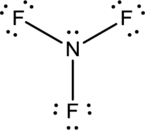
Nitrogen atom has less electronegativity comparing to fluorine. So it is taken as the central atom with 3 fluorine atoms at the terminal positions of it
The nitrogen has 5 and each fluorine atom have 7 valence electrons. Since there are 3 fluorine atoms the total number of valence electrons becomes 26.
The 20 electrons after reducing two electrons for each bond from the total valence electron are distributed on fluorine atom to fill the octets. The remaining 2 electrons are distributed to the central atom so that nitrogen fills the octet.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
CHEMISTRY 3
- The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties is called organic chemistry. Besides carbon atoms, organic compounds also can contain hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms (as well as other types of atoms). A common trait of simple organic compounds is to have Lewis structures where all atoms have a formal charge of zero. Consider the following incomplete Lewis structure for an organic compound called histidine (an amino acid), which is one of the building blocks of proteins found in our bodies: Draw a complete Lewis structure for histidine in which all atoms have a formal charge of zero.arrow_forwardWrite Lewis structures and predict the molecular structures of the following. (See Exercises 115 and 116.) a. OCl2, KrF2, BeH2, SO2 b. SO3, NF3, IF3 c. CF4, SeF4, KrF4 d. IF5, AsF5 Which of these compounds are polar?arrow_forwardThe skeleton structure for disulfur dinitride, S2N2, isDraw possible resonance forms of this moleculearrow_forward
- How many covalent bonds are there in ClO2? Assume Cl will expand its octet to minimize formal charges.arrow_forward1) Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using the molecular models (ball and stick) as learning aids. Recommend an alternative to using this method for modeling molecules. 2) Build C6H6 as a ring. What do you notice about the placement of the bonds? This is an example of resonance. What is a resonant Lewis structure? 3) Explain how a diminished and expanded octet can be formed.arrow_forwardWhat are possible Lewis structures for pci3, h2s, chbr3, c2h2br2?arrow_forward
- Lewis structures of molecules are important for finding small molecule drug candidates for diseased states such as cancer, HIV, hepatitis C, COVID 19, etc. Why are Lewis structures important for this? please explainarrow_forwardIn the molecule NH3, in the BEST Lewis structure, there are a total of _________ valence electrons involved in bonding and a total of __________ valence electrons that are nonbonding.arrow_forwardWhich of these molecules have octet and which are exceptions, include the type of exception, if having any: NO2, SCl2, NH3? Justify your answer.arrow_forward
- Chemical species are said to be isoelectronic if they have the same Lewis structure (regardless of charge). Consider these ions and write a Lewis structure for a neutral molecule that is isoelectronic with them. (a) CN–, (b) NH4+ (c) CO3 2–arrow_forwardWrite Lewis structures for the following molecules or ions:(a) SbH3(b) XeF2(c) Se8 (a cyclic molecule with a ring of eight Se atoms)arrow_forwardEach Lewis structure of benzene has three C“C double bonds. Anotherhydrocarbon containing three C“C double bonds is hexatriene, C6H8. A Lewisstructure of hexatriene is Experiments show that three of the C¬C bonds in hexatriene are shorter than theother two. Does this data suggest that hexatriene exhibits resonance structures?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning




