
Interpretation:
The reason why bond energy of
Concept Introduction:
Molecular orbital theory:
Molecular orbital theory suggests the combination of all atomic orbitals having comparable energy and proper symmetry.
Postulates of MOT is,
- Atomic orbitals of same energy and proper symmetry combine together to form molecular orbitals.
- The movement of electrons in a molecular orbital is influenced by all the nuclei of combining atoms.
- The number of molecular orbitals formed is equal to the number of combining atomic orbital when two atomic orbitals combined two molecular orbitals are formed. One molecular orbital has high energy than the corresponding atomic orbitals and is called antibonding orbital and the other one with lower energy is called bonding orbital.
- In molecular orbitals, the electrons are filled according to the Pauli’s exculsion principle, Aufbau principle and the Hund’s rule.
Bond order
Where,
Explanation of Solution
The bond energy of
The
The electronic configuration of
The molecular configuration of
MO diagram of
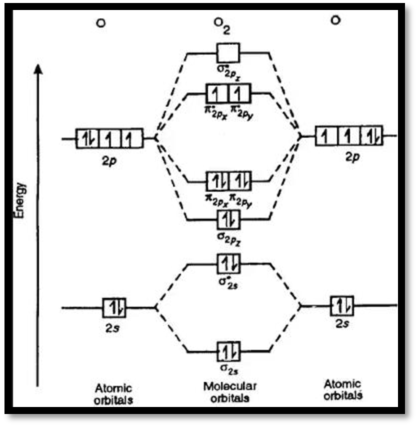
Figure 1: MO diagram of oxygen
Bond order can be calculated as,
Bond order
There are ten electrons in bonding orbital and six electrons antibonding orbitals.
Bond order of
The molecular configuration of
Bond order of
Bond order of
The bond order of the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
GENERAL CHEMISTRY ACHIEVE ACCESS W/BOOK
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





