
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The orbital energy level diagram and the number of unpaired electrons in
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The oxidation number of cobalt in
The orbital energy level diagram for
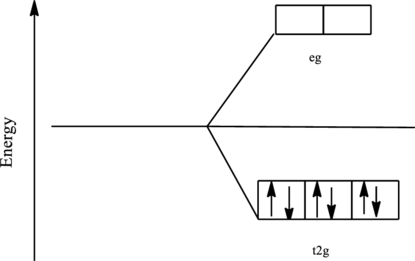
Since, ammonia acts as a strong ligand in
(b)
Interpretation:
The orbital energy level diagram and the number of unpaired electrons in
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The oxidation number of nickel in
The orbital energy level diagram for
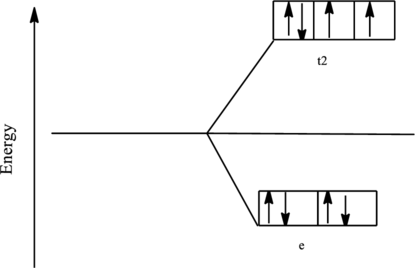
Since, chloride ion is a weak ligand the electrons are filled according to the Hund’s rule in the d-orbitals and the number of unpaired electron in nickel complex is two.
(c)
Interpretation:
The orbital energy level diagram and the number of unpaired electrons in
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The oxidation number of iron in
The orbital energy level diagram for
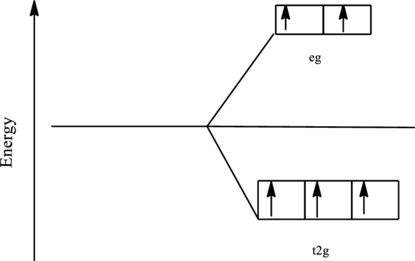
Since, water is a weak ligand the electrons are filled according to the Hund’s rule in the d-orbitals and the number of unpaired electron in iron complex is five.
(d)
Interpretation:
The orbital energy level diagram and the number of unpaired electrons in
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The oxidation number of iron in
The orbital energy level diagram for
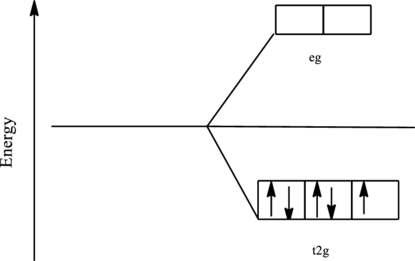
Since, cyanide acts as a strong ligand in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES W/SAPLING
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





