
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The mechanism for each of the given reactions are to be written.
Concept introduction:
舧 Electrophiles are electron-deficient species, which has positive or partially positive charge. Lewis acids are electrophiles, which accept electron pair.
舧 Nucleophiles are electron-rich species, which has negative or partially negative charge. Lewis bases are nucleophiles, which donate electron pair.
舧 The reaction in which there is addition of halogen (F, Cl, Br, and I) to the compound is called halogenation reaction.
舧 A type of halogenation in which
舧 Hydride shift is defined as the rearrangement of hydrogen atoms.
Answer to Problem 1P
Solution:
(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

Explanation of Solution
a)
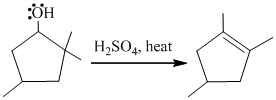
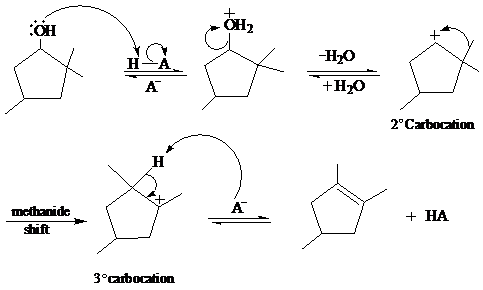
In the given reaction, cyclopentanol reacts with sulfuric acid in presence of heat to form the required product. The mechanism of this reaction takes place when the hydroxy group, which is having lone pair of electron, attacks on hydrogen atom (H) and withdraw it. After that equilibrium forms and removal of water takes place, which leads to the formation of secondary carbocation. The secondary carbocations are very unstable so methanide shift takes place and stable tertiary carbocation forms.
The mechanism of the reaction is as follows:
b)
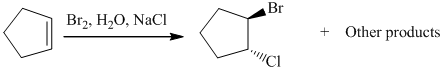
The given reaction take place when cyclopentene ring reacts with bromine in presence of light by the help of free radical halogenation. In the mechanism, the cyclopentene attacks on Br and addition of Br cation takes place at cyclopentene ring. The cyclopentene ring becomes electron deficient after the addition of Br so addition of chlorine atom takes place at cyclopentene ring and this leads to the formation of required product.
The mechanism is as follows:

c) The other products from the reaction given in part (b).
From the above reaction, one more product is formed. When addition of chlorine atom takes place at electron deficient cyclopentene ring then addition of chlorine takes place but the product formed here is an enantiomer of the product formed above. So two products are formed, both are in equimolar amount and are enantiomer of each other.
The second product of the reaction is as follows:

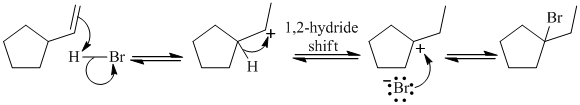
d)
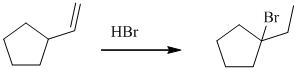
The given reaction takes place, when
The mechanism is represented below:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter FRP Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- The following equation shows the bromination of compound 1. Propose a structure for product D and a curved arrow mechanism that accounts for its formation featuring the initiation, propagation and termination steps. can you also discuss the stereochemical outcome.arrow_forwardThe sex attractant of the female arctiid moth contains, among other components, a compound of molecular formula C21H40 that yields on ozonolysis. What is the constitution of this material?arrow_forwardIdentify the reagents you would use to achieve of the following transformation. Identify these reactions as SN1 or Sn2. (a) (b) (c) (d)arrow_forward
- Suggest reactivity of compound A, B and C in increasing order of E2 reactionarrow_forwardWhen compound (7) is subjected to reaction (5) a different compound (9) with a formula of C9H18O2 is obtained. Draw the chemical structure of the product (9) and provide a detailed mechanism for its formationarrow_forwardThe sex attractant of the housefly has the formula C23 H46. When treated with warm potassium permanganate, this phero- mone gives two products: CH3(CH2)12COOH and CH3(CH2)7COOH. Suggest a structure for this sex attractant. Explain which part of the structure is uncertain.arrow_forward
- Draw/outline a reasonable and detailed mechanism for the dehydration of 2-methylcyclohexanol catalyzed by phosphoric acid. Use curved arrows to show the flow of electrons and draw the structures of all intermediates and byproducts formed in the reaction. Predict and rationalize the expected product distribution based on thermodynamic aspectsarrow_forwardExplain with a mechanism the formation of the following compound, and suggest an alternative product that could be formed.arrow_forwardCompound A produce compound D while undergo Friedel Crafts Alkylation. Compound D is then oxidized and produce compound E (C11H12O3) as a major product.What are the possible structural formula of compound D and E?arrow_forward
- Provide a mechanism which explains the following conversions. Include all intermediates (where appropriate) and watch your arrows and chargesarrow_forwardBenzenediazonium carboxylate decomposes when heated to yield N2, CO2, and a reactive substance that can't be isolated. When benzenediazonium carboxylate is heated in the presence of furan, the following reaction is observe. Propose a structure for the intermediate in this reaction.arrow_forwardBelow is a schematic representation of possible reactions that Compound X can undergo. Use the scheme to answer the following questions. Illustrating with reaction mechanisms, show how compounds [1], [2], [3] and [4] are formed. Which of the compounds in the following pairs will occur in relatively higher yields and why? [1] and [2] [3] and [4]arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

