
Concept explainers
Arrange the compounds of each of the following series in order of increasing acidity:
Interpretation:
The compounds of each of the given series are to be arranged in order of increasing acidity.
Concept introduction:
Acidity depends on the
Resonance structures are the structures in which two or more possible electron structures are drawn. In the resonance structure, the position of the atoms is the same but position of the electrons is different.
Resonance causes delocalization of electron pairs, which increases the stability of the base.
Answer to Problem 1P
Solution:
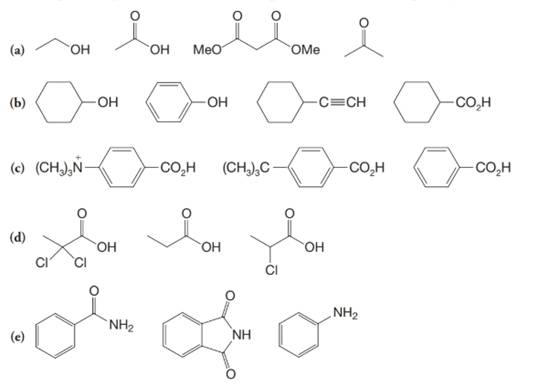
(a)
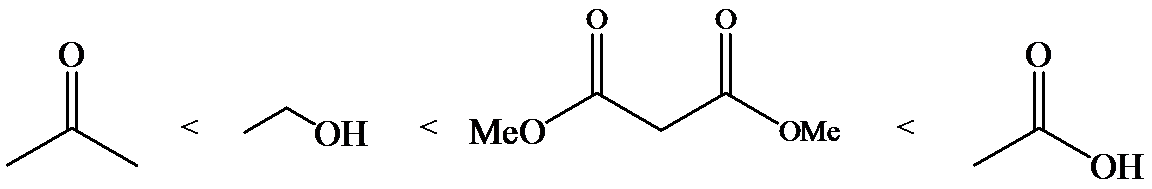
(b)
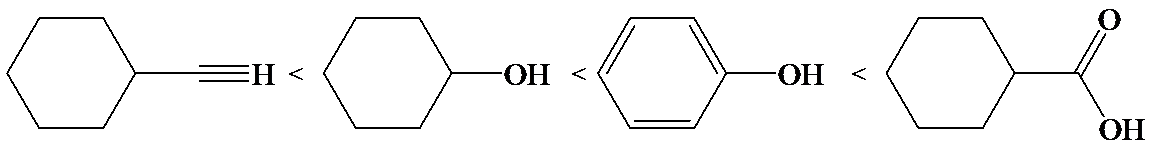
(c)

(d)
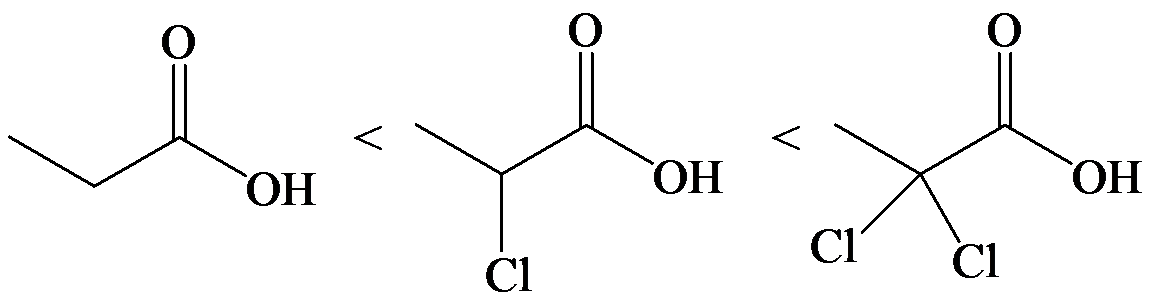
(e)
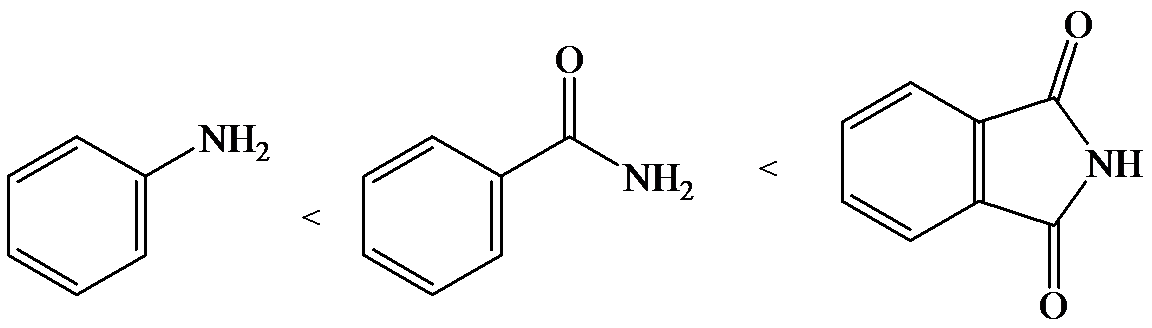
Explanation of Solution
a)
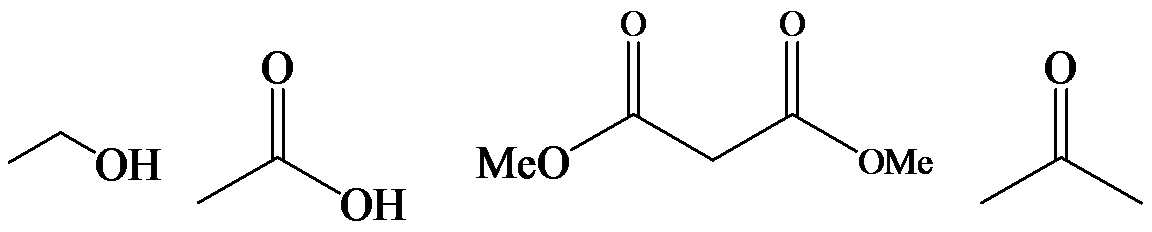
The α-hydrogen atoms of carbonyl groups are acidic. The acidity arises from the electron withdrawing effect of the carbonyl and resonance stabilization of its conjugate base. The electron donating effect of 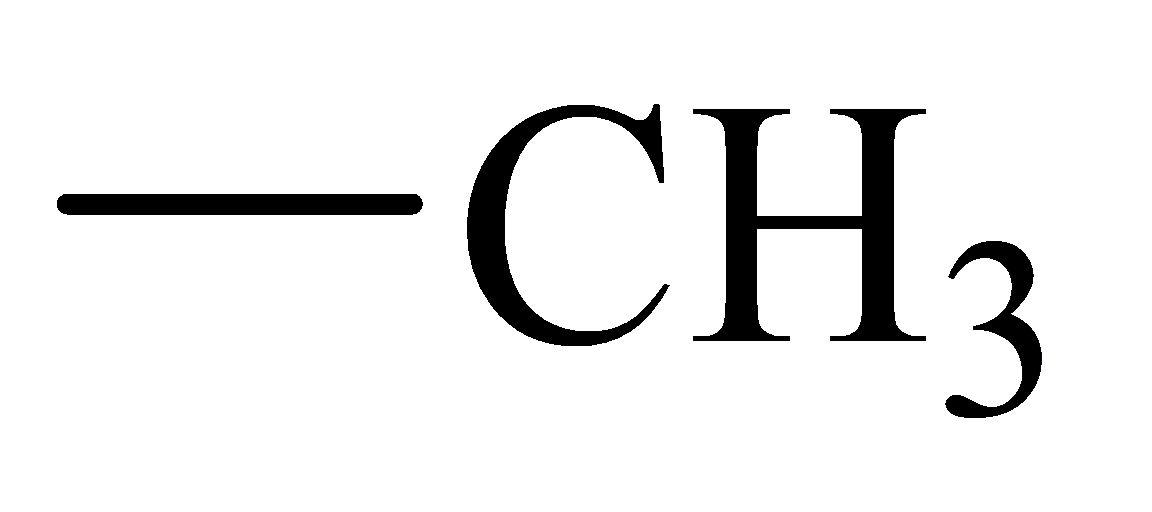 groups tends to destabilize anions. In diketone, there is an active methylene, adjacent to two carbonyl groups. This indicates more resonance stabilization. The charge of anion can be delocalized to both oxygen atoms. The hydroxyl proton in carboxylic acid is an α-proton. On comparing the acidity of carboxylic acids and alcohols, alcohol is less acidic than carboxylic acid.
groups tends to destabilize anions. In diketone, there is an active methylene, adjacent to two carbonyl groups. This indicates more resonance stabilization. The charge of anion can be delocalized to both oxygen atoms. The hydroxyl proton in carboxylic acid is an α-proton. On comparing the acidity of carboxylic acids and alcohols, alcohol is less acidic than carboxylic acid.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:
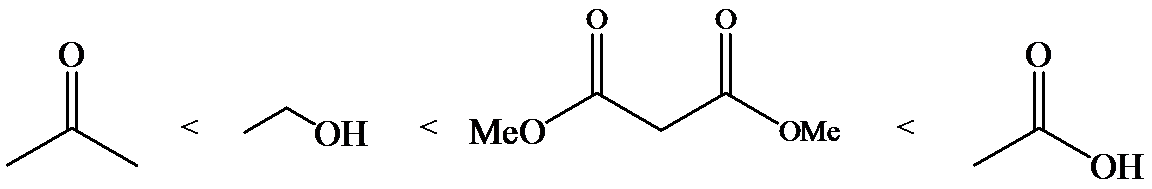
b)
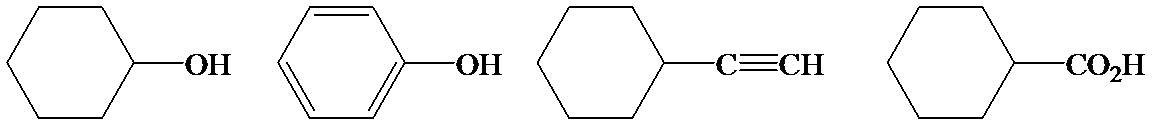
Phenol is more acidic than cyclohexanol because the resonance stabilization in both is different.
In the case of cyclohexane carboxylic acid, negative charge is shared between two different oxygen atoms making it more stabilized than phenoxide. Hence, the removal of proton from cyclohexane carboxylic acid is easier than phenol, making it more acidic than phenol.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:
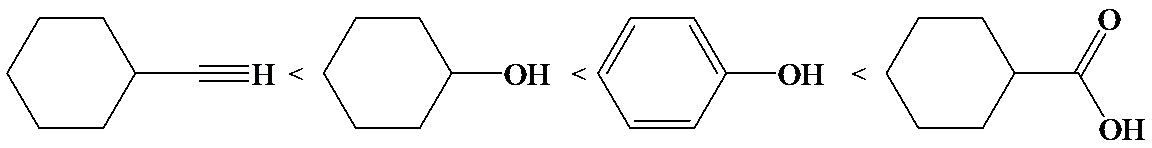
c)
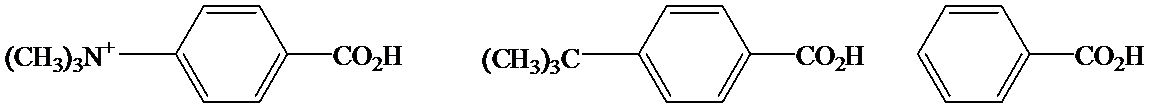
In the case of carboxylic acids, electron substituents increase acidity by inductive electron donation. The electron-donating tert-butyl group destabilizes the conjugate base of benzoic acid, making it less acidic.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:

d)
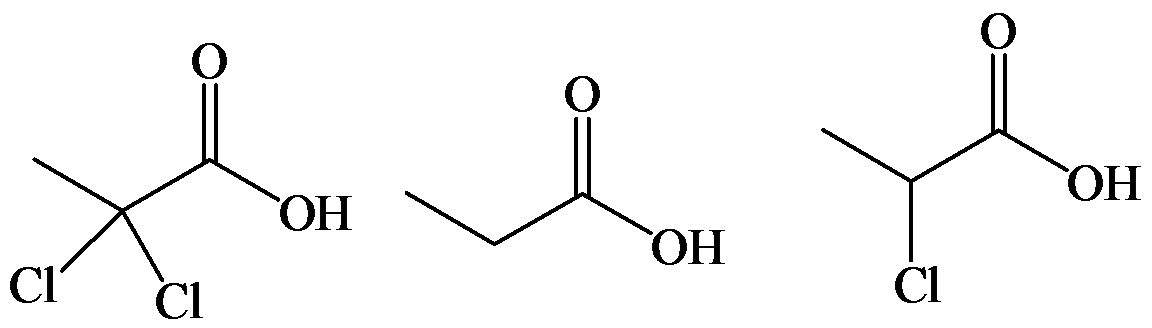
The electron-withdrawing chloro groups increase the acidity of carboxylic acid by increasing the stability of the carboxylate ion. Hence, the carboxylic acid with more chloro groups is more acidic.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:
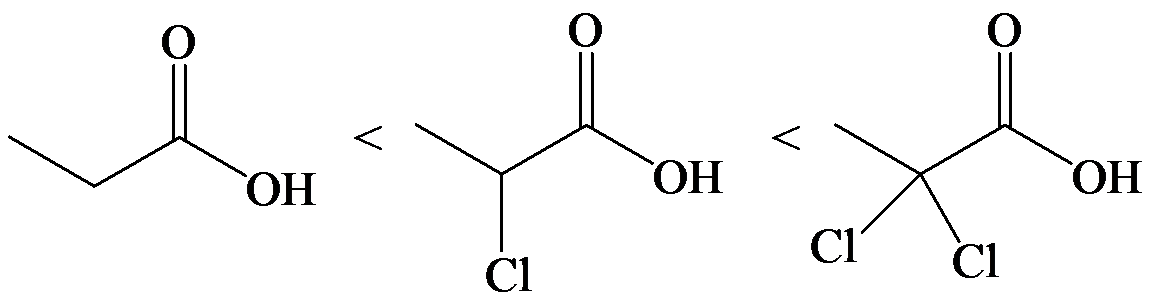
e)

The lone pair electron in aniline is localized on the nitrogen atom, whereas onbenzamide, it is delocalized between oxygen and nitrogen via resonance. Therefore, benzamide is more acidic than aniline.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:
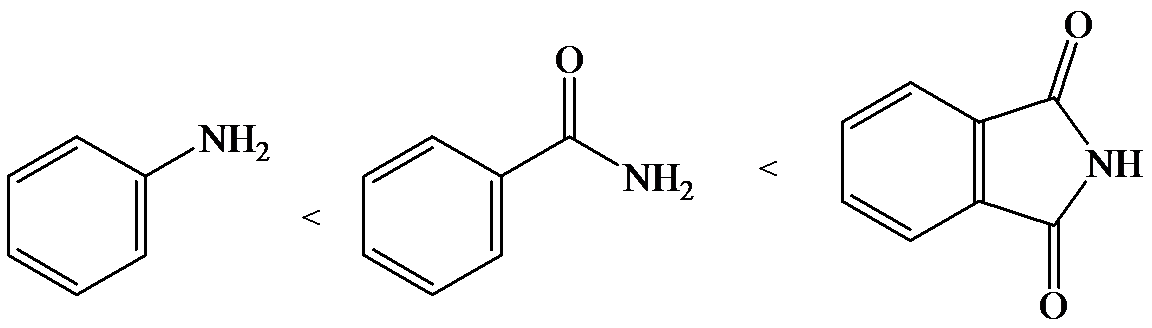
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter SRP Solutions
CHEM 313:ORG.CHEM V1 W/WLYLS BLKBRD >B
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry (7th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
Introductory Chemistry (5th Edition) (Standalone Book)
- Rank the attached compounds in order of increasing acidity, and explainin detail your choice of order.arrow_forwardPart 1. Choose the stronger acid in each pair of compounds. Part 2. Arrange the following compounds in order of increasing basicity. Part 3. Determine if the oxide is acidic or basearrow_forwardRank the following in order of acidity with 1 being the most acidicarrow_forward
- Arrange the following in order of increasing reactivity towards a hydrogen halide and explain.arrow_forwardRank each of the following sets of nitrogen bases in terms of basicity and explain your answerarrow_forward1- Arrange the following compounds in order of decreasing reactivity towards hydrolysis. 2- Arrange the following chemical species in order of decreasing basicity.arrow_forward
