A new virus has taken root in a country. Government officials are reporting that 15% of the population is currently infected with the virus. However, epidemiologists across the country claim to be observing a much higher infection rate. It was found that 157 people out of a randomly selected sample of 1040 people from around the country were infected with the virus. Use the critical value method to determine if the sample data support the epidemiologists' supposition that the true rate of infection in the country is higher than 15%. Use a significance level of 5%. State the null and alternative hypothesis for this test. Ho: v H₁: ? Determine if this test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed. Oright-tailed Otwo-tailed Oleft-tailed Should the standard normal (2) distribution or Student's (t) distribution be used for this test? The standard normal (2) distribution should be used O The Student's t distribution should be used Determine the critical value(s) for this hypothesis test. Round the solution(s) to two decimal places. If more than one critical value exists, enter the solutions using a comma-separated list. Determine the test statistic. Round the solution to two decimal places. 225 10000 125 1000
A new virus has taken root in a country. Government officials are reporting that 15% of the population is currently infected with the virus. However, epidemiologists across the country claim to be observing a much higher infection rate. It was found that 157 people out of a randomly selected sample of 1040 people from around the country were infected with the virus. Use the critical value method to determine if the sample data support the epidemiologists' supposition that the true rate of infection in the country is higher than 15%. Use a significance level of 5%. State the null and alternative hypothesis for this test. Ho: v H₁: ? Determine if this test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed. Oright-tailed Otwo-tailed Oleft-tailed Should the standard normal (2) distribution or Student's (t) distribution be used for this test? The standard normal (2) distribution should be used O The Student's t distribution should be used Determine the critical value(s) for this hypothesis test. Round the solution(s) to two decimal places. If more than one critical value exists, enter the solutions using a comma-separated list. Determine the test statistic. Round the solution to two decimal places. 225 10000 125 1000
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section11.4: Collecting Data
Problem 2E
Related questions
Question
100%
#33). This is 1 question. Need help with critical value and test statistic.
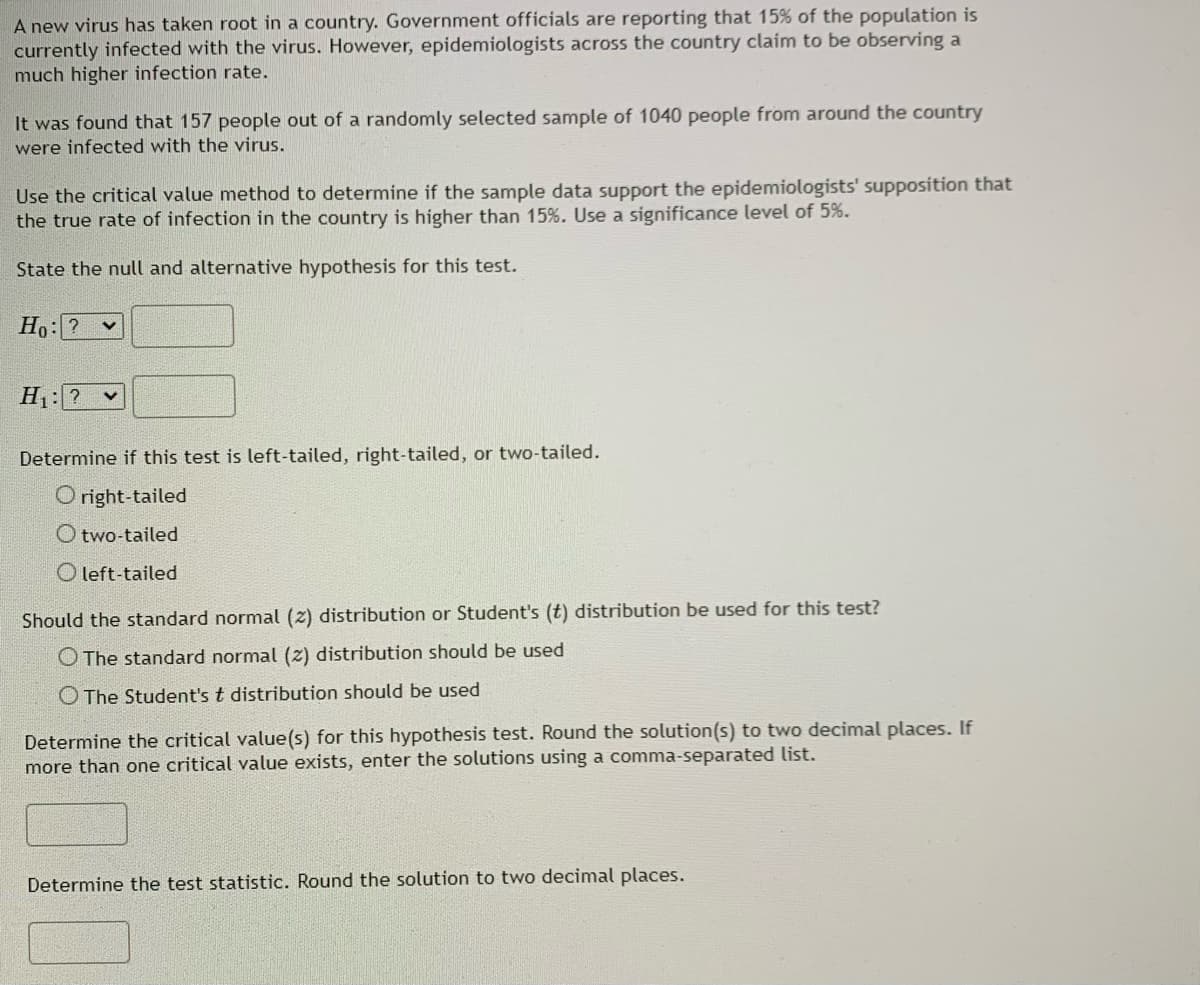
Transcribed Image Text:A new virus has taken root in a country. Government officials are reporting that 15% of the population is
currently infected with the virus. However, epidemiologists across the country claim to be observing a
much higher infection rate.
It was found that 157 people out of a randomly selected sample of 1040 people from around the country
were infected with the virus.
Use the critical value method to determine if the sample data support the epidemiologists' supposition that
the true rate of infection in the country is higher than 15%. Use a significance level of 5%.
State the null and alternative hypothesis for this test.
Ho: ? V
H₁: ? ✓
Determine if this test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed.
Oright-tailed
O two-tailed
Oleft-tailed
Should the standard normal (2) distribution or Student's (t) distribution be used for this test?
The standard normal (2) distribution should be used
O The Student's t distribution should be used
Determine the critical value(s) for this hypothesis test. Round the solution(s) to two decimal places. If
more than one critical value exists, enter the solutions using a comma-separated list.
Determine the test statistic. Round the solution to two decimal places.
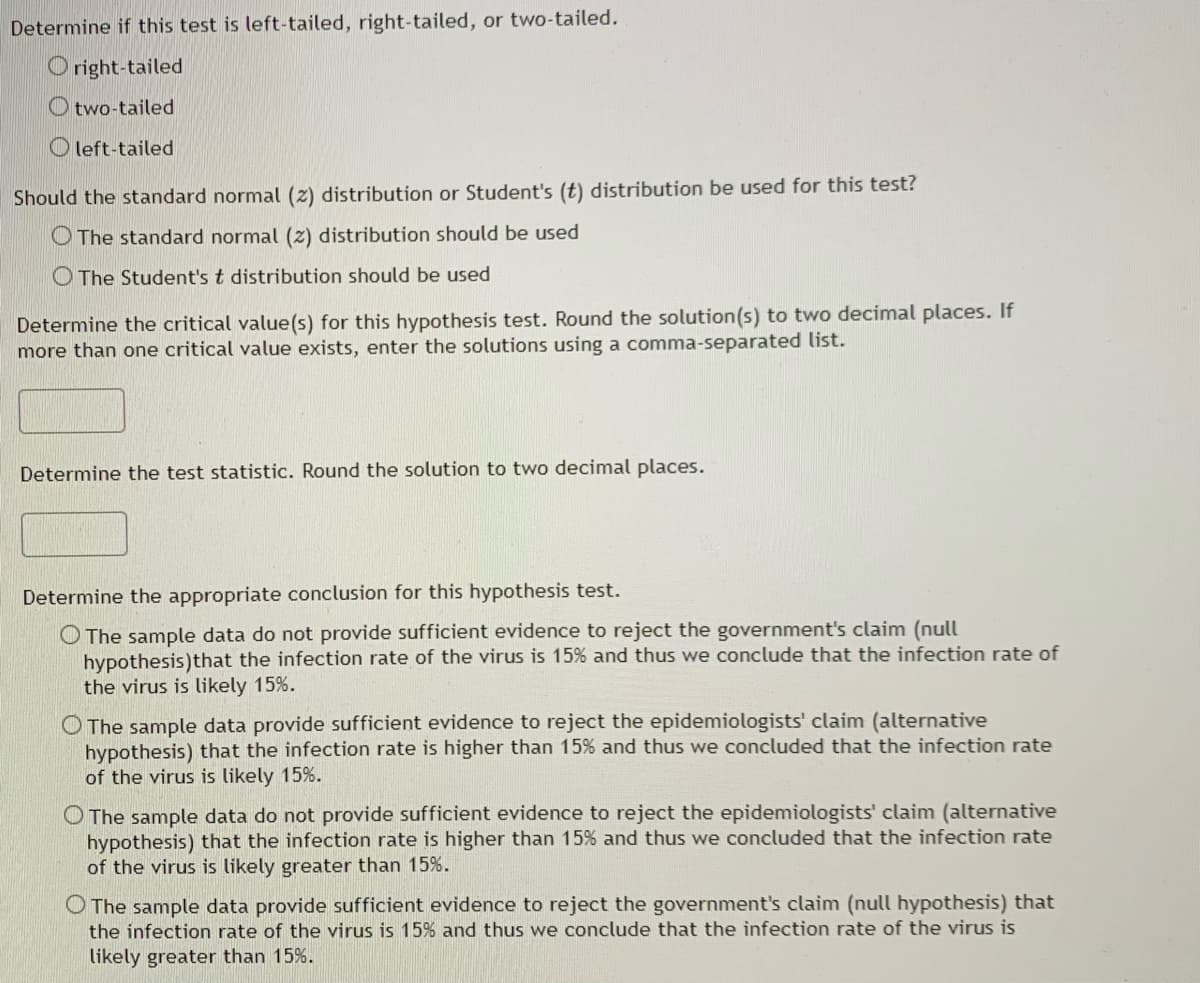
Transcribed Image Text:Determine if this test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed.
right-tailed
Otwo-tailed
left-tailed
Should the standard normal (2) distribution or Student's (t) distribution be used for this test?
The standard normal (2) distribution should be used
The Student's t distribution should be used
Determine the critical value(s) for this hypothesis test. Round the solution(s) to two decimal places. If
more than one critical value exists, enter the solutions using a comma-separated list.
Determine the test statistic. Round the solution to two decimal places.
Determine the appropriate conclusion for this hypothesis test.
O The sample data do not provide sufficient evidence to reject the government's claim (null
hypothesis) that the infection rate of the virus is 15% and thus we conclude that the infection rate of
the virus is likely 15%.
O The sample data provide sufficient evidence to reject the epidemiologists' claim (alternative
hypothesis) that the infection rate is higher than 15% and thus we concluded that the infection rate
of the virus is likely 15%.
O The sample data do not provide sufficient evidence to reject the epidemiologists' claim (alternative
hypothesis) that the infection rate is higher than 15% and thus we concluded that the infection rate
of the virus is likely greater than 15%.
O The sample data provide sufficient evidence to reject the government's claim (null hypothesis) that
the infection rate of the virus is 15% and thus we conclude that the infection rate of the virus is
likely greater than 15%.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning