
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780133594140
Author: James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
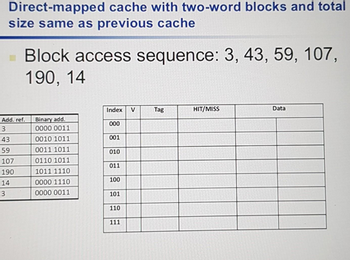
Transcribed Image Text:Direct-mapped cache with two-word blocks and total
size same as previous cache
Block access sequence: 3, 43, 59, 107,
190, 14
Add. ref.
3
43
59
107
190
14
3
Binary add.
0000 0011
0010 1011
0011 1011
0110 1011
1011 1110
0000 1110
0000 0011
Index V Tag
000
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
HIT/MISS
Data
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Please explain 1,2,and 3 Consider following cache elements Cache can hold 32 kB Data are transferred between main memory and the cache in blocks of 8 bytes each Main memory consists of 256 MB For the hexadecimal main memory address 1234567, show the following information (in hexadecimal format) Tag, Line, and Offset(word) values for Direct-mapped Cache Tag and Offset(Word) values for Associative Cache Tag, Set, and Offset(word) values for aa 4-way Set-associative Cachearrow_forwardExplain why it is difficult to devise a suitable cache replacement technique for all address sequences.arrow_forwardConsider 16-bit memory addresses • 4KB byte-aligned fully associative cache 16-byte blocks Provide how many bits are required for tag, index, and offset. Tag: Offset: * Previousarrow_forward
- Given the following setup, how many words can be stored in the cache at the same time when the cache is full? A. Direct mapped cache Tag (T) Index (I) Word (W) Byte (B) 17 11 2 2 B. 2-way associative cache Tag (T) Index (I) Word (W) Byte (B) 18 10 2 2 C. 4-way associative cache Tag (T) Index (I) Word (W) Byte (B) 19 9 2 2 D. Fully associative cache Tag (T) Index (I) Word (W) Byte (B) 28 0 2 2arrow_forwardCalculate the number of bits used for data and overhead for the following caches A. 64-block/line, direct-mapped, write-through, 8 byte block/linearrow_forwardExplain why it's difficult to design a universal cache replacement technique that works for all possible address sequences.arrow_forward
- A cache designer wishes to enhance the size of a 4 KiB physically labeled, virtually indexed cache. Is it feasible to create a 16 KiB direct-mapped cache with the page size mentioned above, assuming two words per block? How would the designer expand the cache's data size?arrow_forwardQuestion : 1 The contents of the memory as follow: Address Data Address Data 000 1000 100 0001 001 1101 101 0011 010 1010 110 0111 011 1111 111 1001 By using direct-mapped cache, Please map the following addresses from main memory to the cache as ordered 001,010, 100, 101, 111. Imirarrow_forwardExplain the differences between a directly mapped cache and a fully associative cache.arrow_forward
- Explain why it is difficult to devise a suitable cache replacement technique for all address sequences.arrow_forwardConsider a cache with 32KİB data, 16-word blocks, and 24-bit addresses, answer the following questions: a) For the direct-mapped configuration, determine the number of index bits and tag bits in the 24-bit address. b) For 4-way set associative configuration, determine the number of index bits and tag bits in the 24-bit address. c) For fully associative contiguration, determine the number of index bits and tag bits in the 24-bit address. d) For an 8-way set associative configuration, identify the set number in the cache to which the following 24-bit memory address maps: Ox001Z00 (Hexadecimal notation) where Z is the least significant digit in your student ID (written as a decimal number)arrow_forwardGiven an 8-word, 4-way set associative cache, and the sequence of address accesses below, enter the number of misses. 22 24 22 13 13 22arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science
Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning
Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education
Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY
Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780124077263
Author:David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337569330
Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337093422
Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133750423
Author:VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781119368830
Author:FITZGERALD
Publisher:WILEY