Explain these exceptions to the general trend. Match the items in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right. Reset Help To ionize beryllium and magnesium the electrons are coming from filled subshells higher which are in energy than the unfilled subshells from which the electrons come from when ionizing boron or aluminum. lower Since the subshells are higher in energy it is easier to remove electrons from them f and the ionization energies of boron and aluminum are d.
Explain these exceptions to the general trend. Match the items in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right. Reset Help To ionize beryllium and magnesium the electrons are coming from filled subshells higher which are in energy than the unfilled subshells from which the electrons come from when ionizing boron or aluminum. lower Since the subshells are higher in energy it is easier to remove electrons from them f and the ionization energies of boron and aluminum are d.
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Chapter7: Chemical Bonding And Molecular Geometry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 78E: The reaction of a metal, M, with a halogen, X2, proceeds by an exothermic reaction as indicated by...
Related questions
Question
100%
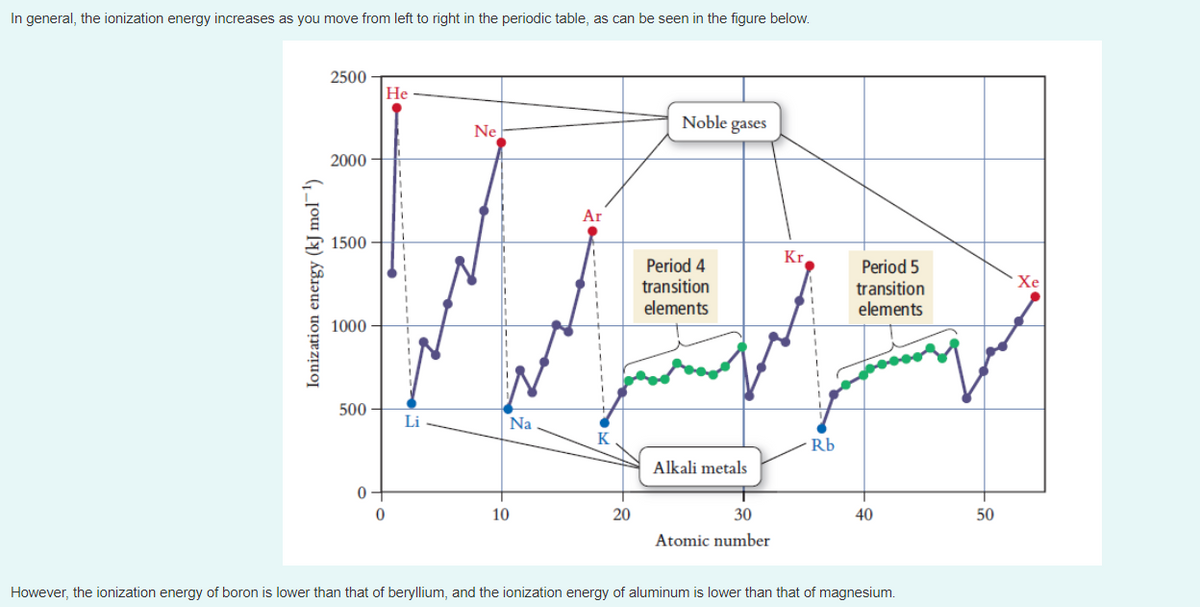
Transcribed Image Text:In general, the ionization energy increases as you move from left to right in the periodic table, as can be seen in the figure below.
2500
He
Noble gases
Ne
2000
Ar
1500
Kr
Period 4
transition
elements
Period 5
Хе
transition
elements
1000 –
500
Li
Na
K
Rb
Alkali metals
10
20
30
40
50
Atomic number
However, the ionization energy of boron is lower than that of beryllium, and the ionization energy of aluminum is lower than that of magnesium.
Ionization energy (kJ mol¬1)

Transcribed Image Text:Explain these exceptions to the general trend.
Match the items in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right.
Reset
Help
To ionize beryllium and magnesium the electrons are coming from filled
subshells
higher
which are
in energy than the unfilled
subshells from which the
electrons come from when ionizing boron or aluminum.
lower
Since the
subshells are higher in energy it is easier to remove electrons from them
and the ionization energies of boron and aluminum are
d
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning