In the figures below, observe the biosynthesis of scopolamine and its intermediates. THE scopolamine is formed by the fusion of two biosynthetic pathways. One derived from L-ornithine and the other from L-phenylalanine. In the bold rectangles are the respective key enzymes that catalyze each of the biosynthesis steps. Scopolamine is a competitive, non-selective muscarinic receptor antagonist drug acetylcholine receptor antagonist (mACHR) giving rise to important pharmacological effects, such as by example antispasmodic action in the gastrointestinal tract. Answer: 1) Does scopolamine belong to which chemical class/subclass of natural products? 2) This substance can
In the figures below, observe the biosynthesis of scopolamine and its intermediates. THE scopolamine is formed by the fusion of two biosynthetic pathways. One derived from L-ornithine and the other from L-phenylalanine. In the bold rectangles are the respective key enzymes that catalyze each of the biosynthesis steps. Scopolamine is a competitive, non-selective muscarinic receptor antagonist drug acetylcholine receptor antagonist (mACHR) giving rise to important pharmacological effects, such as by example antispasmodic action in the gastrointestinal tract. Answer: 1) Does scopolamine belong to which chemical class/subclass of natural products? 2) This substance can
Chapter1: Numerals And Fractions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7RP
Related questions
Question
In the figures below, observe the biosynthesis of scopolamine and its intermediates. THE scopolamine is formed by the fusion of two biosynthetic pathways. One derived from L-ornithine and the other from L-phenylalanine. In the bold rectangles are the respective key enzymes that catalyze each of the biosynthesis steps. Scopolamine is a competitive, non-selective muscarinic receptor antagonist drug acetylcholine receptor antagonist (mACHR) giving rise to important pharmacological effects, such as by example antispasmodic action in the gastrointestinal tract.
Answer:
1) Does scopolamine belong to which chemical class/subclass of natural products?
2) This substance can be extracted from different plant species, such as: Atropa,
Duboisia, Hyoscyamus, Mandragora and Datura. What is the botanical family of these species?
3) What are the biogenetic origins (biosynthetic pathways) of ornithine and phenylalanine?
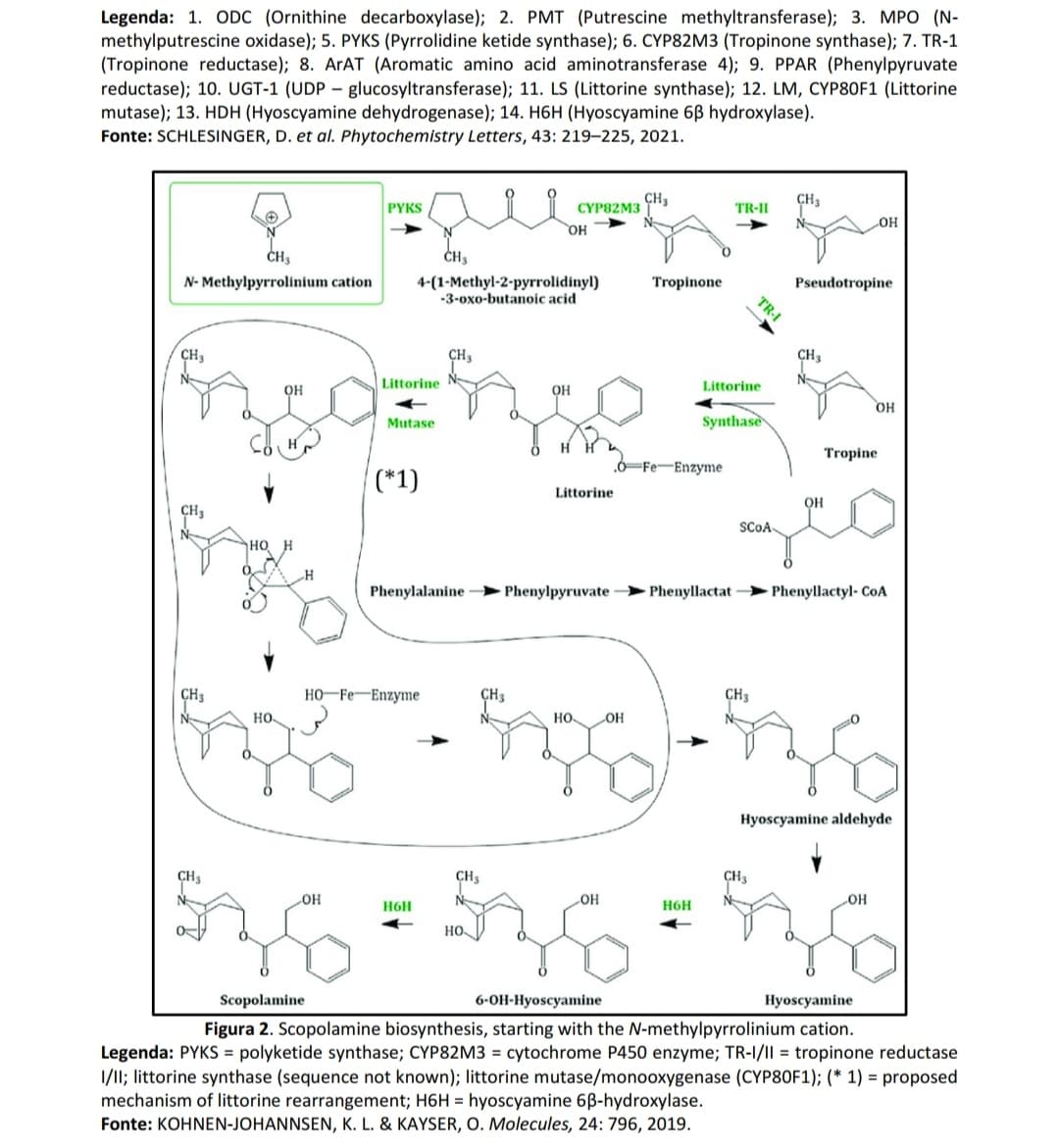
Transcribed Image Text:МРО (N-
Legenda: 1. ODC (Ornithine decarboxylase); 2. PMT (Putrescine methyltransferase);
methylputrescine oxidase); 5. PYKS (Pyrrolidine ketide synthase); 6. CYP82M3 (Tropinone synthase); 7. TR-1
(Tropinone reductase); 8. ArAT (Aromatic amino acid aminotransferase 4); 9. PPAR (Phenylpyruvate
reductase); 10. UGT-1 (UDP – glucosyltransferase); 11. LS (Littorine synthase); 12. LM, CYP80F1 (Littorine
mutase); 13. HDH (Hyoscyamine dehydrogenase); 14. H6H (Hyoscyamine 6B hydroxylase).
Fonte: SCHLESINGER, D. et al. Phytochemistry Letters, 43: 219–225, 2021.
CH3
CYP82M3
CH3
PYKS
TR-II
N
OH
HO
N- Methylpyrrolinium cation
4-(1-Methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)
-3-oxo-butanoic acid
Tropinone
Pseudotropine
TR-I
CH3
ÇH3
CH3
Littorine
Littorine
он
OH
OH
Mutase
Synthase
Tropine
.6-Fe-Enzyme
(*1)
Littorine
OH
CH3
SCOA
но
Phenylalanine
Phenylpyruvate > Phenyllactat
Phenyllactyl- CoA
CH3
но -Fe —Enzyme
CH3
HO
но
COH
Hyoscyamine aldehyde
CH3
CH3
CH3
он
OH
H6H
H6H
HO
Scopolamine
6-OH-Hyoscyamine
Hyoscyamine
Figura 2. Scopolamine biosynthesis, starting with the N-methylpyrrolinium cation.
Legenda: PYKS = polyketide synthase; CYP82M3 = cytochrome P450 enzyme; TR-I/II = tropinone reductase
1/1I; littorine synthase (sequence not known); littorine mutase/monooxygenase (CYP80F1); (* 1) = proposed
mechanism of littorine rearrangement; H6H = hyoscyamine 6B-hydroxylase.
Fonte: KOHNEN-JOHANNSEN, K. L. & KAYSER, O. Molecules, 24: 796, 2019.
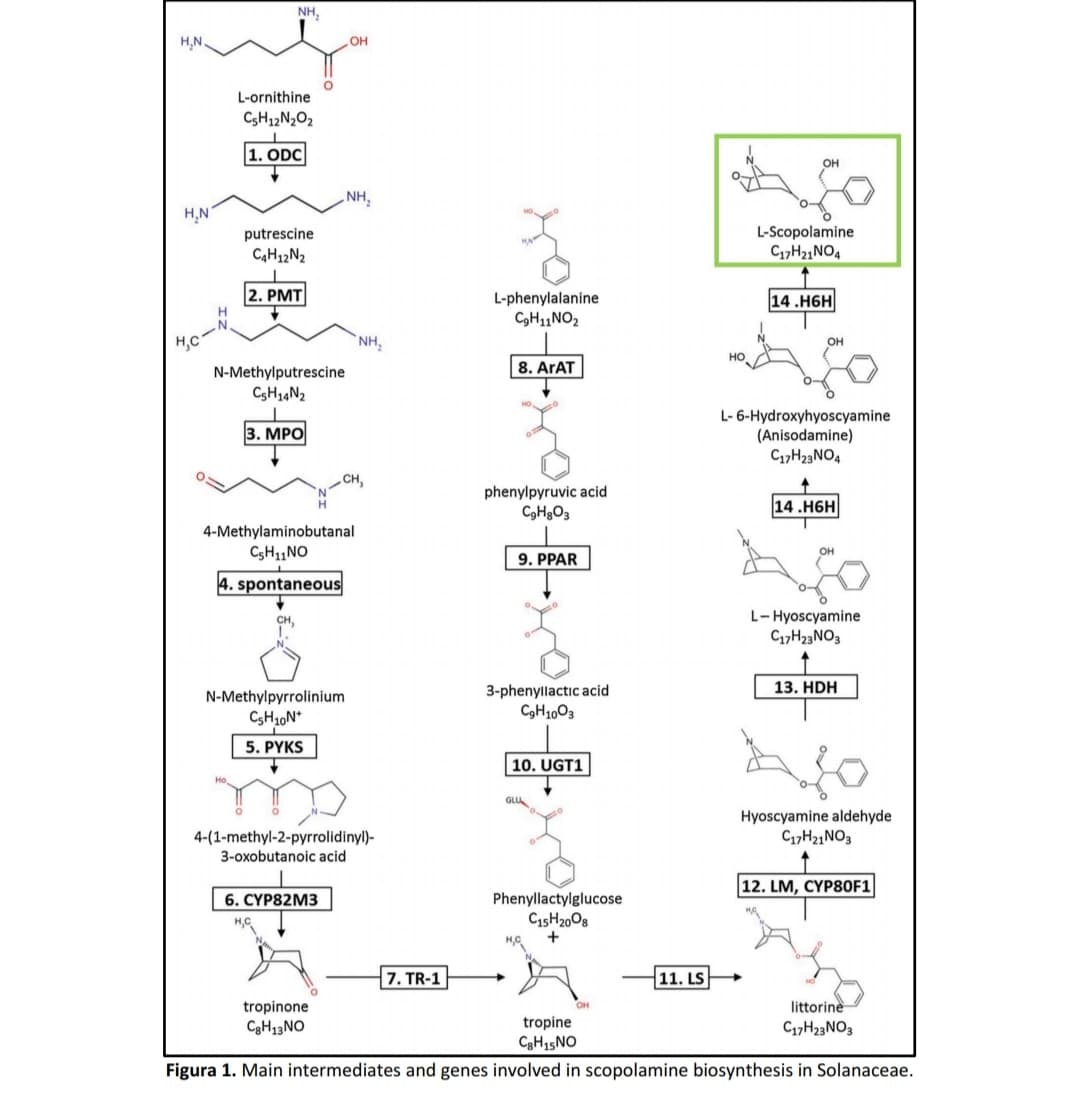
Transcribed Image Text:NH,
H,N.
OH
L-ornithine
C5H12N2O2
1. ODC
NH,
H,N°
L-Scopolamine
C1,H21NO4
putrescine
C4H12N2
2. PMT
L-phenylalanine
CH1NO2
14 .H6H
`NH,
OH
но
8. ArAT
N-Methylputrescine
CSH14N2
L- 6-Hydroxyhyoscyamine
(Anisodamine)
C17H23NO4
3. MPО
phenylpyruvic acid
14 .H6H
4-Methylaminobutanal
CSH11NO
9. PPAR
4. spontaneous
L- Hyoscyamine
C,,H23NO3
CH,
13. HDH
3-phenyllactic acid
C9H10O3
N-Methylpyrrolinium
5. PYKS
|10. UGT1
GLU
Hyoscyamine aldehyde
C1,H21NO3
4-(1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)-
3-oxobutanoic acid
12. LM, CYP80F1
Phenyllactylglucose
C15H2008
+
6. CYР82M3
7. TR-1
11. LS
littorine
tropinone
C3H13NO
OH
tropine
C17H23NO3
C3H15NO
Figura 1. Main intermediates and genes involved in scopolamine biosynthesis in Solanaceae.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

