Part 1 See Periodic Table O See Hint For the regulation of the purine synthesis pathway shown, what would happen if there were an excess of AMP? Choose one or more: O A Excess AMP would directly lead to decreased GDP levels, accelerating production of all purines in this pathway. O B. Excess AMP would directly lead to decreased ATP, thereby decreasing GMP production. O CExcess AMP would directly decrease guanine nucleotide production. O D.Excess AMP would directly block the production of more adenine nucleotides. Part 2 O See Hint Howdoes this regulatory mechanism keep the balance of adenine versus guanine nucleotides? Choose one or more: O A High levels of any purine inhibit glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase, preferentlally inhibiting one purine synthesis pathway over the other. O B. The triphosphate form of one purine is necessary for synthesis of the other purine. Thus as the level of GTP is reduced, the capacity to produce AMP is reduced (and vice versa). O C High monophosphate forms of one purine inhibit further synthesis of its respective pathway, but not the other purine pathway. O D.The diphosphate forms positively feed back, accelerating purine synthesis.
Part 1 See Periodic Table O See Hint For the regulation of the purine synthesis pathway shown, what would happen if there were an excess of AMP? Choose one or more: O A Excess AMP would directly lead to decreased GDP levels, accelerating production of all purines in this pathway. O B. Excess AMP would directly lead to decreased ATP, thereby decreasing GMP production. O CExcess AMP would directly decrease guanine nucleotide production. O D.Excess AMP would directly block the production of more adenine nucleotides. Part 2 O See Hint Howdoes this regulatory mechanism keep the balance of adenine versus guanine nucleotides? Choose one or more: O A High levels of any purine inhibit glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase, preferentlally inhibiting one purine synthesis pathway over the other. O B. The triphosphate form of one purine is necessary for synthesis of the other purine. Thus as the level of GTP is reduced, the capacity to produce AMP is reduced (and vice versa). O C High monophosphate forms of one purine inhibit further synthesis of its respective pathway, but not the other purine pathway. O D.The diphosphate forms positively feed back, accelerating purine synthesis.
Biochemistry
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Chapter26: Synthesis And Degradation Of Nucleotides
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6P: Allosteric Regulation of Ribonucleotide Reductase by ATP and Deoxynucleotides Describe the...
Related questions
Question
7
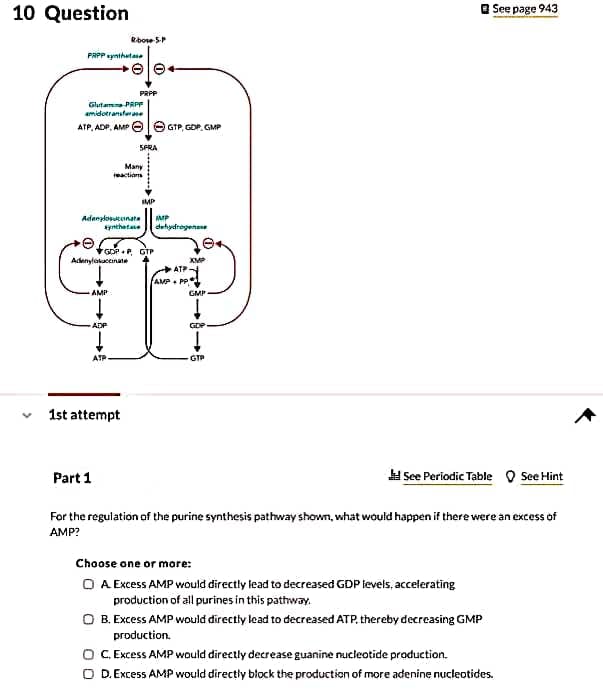
Transcribed Image Text:10 Question
e See page 943
RboseSP
PRPP synthatase
PRPP
Glutam PRPP
amidotranstese
ATP, ADP, AMP O O GTP, GDP. GMP
SPRA
Many
eactions
MP
Adanzlosuknata
*ynthetae
MP
dehydregenene
GDP P, GTP
Adenylatuccnate
XMP
ATP
AMP PP
AMP
GMP
ADP
GDP
ATP
GTP
1st attempt
Part 1
See Periodic Table O See Hint
For the regulation of the purine synthesis pathway shown, what would happen if there were an excess of
AMP?
Choose one or more:
O A Excess AMP would directly lead to decreased GDP levels, accelerating
production of all purines in this pathway.
O B. Excess AMP would directly lead to decreased ATP, thereby decreasing GMP
production.
O C. Excess AMP would directly decrease guanine nucieotide production.
O D. Excess AMP would directly block the production of more adenine nucleotides.

Transcribed Image Text:Part 1
l See Periodic Table O See Hint
For the regulation of the purine synthesis pathway shown, what would happen if there were an excess of
AMP?
Choose one or more:
O A Excess AMP would directly lead to decreased GDP levels, accelerating
production of all purines in this pathway.
O B. Excess AMP would directly lead to decreased ATP, thereby decreasing GMP
production.
O C.Excess AMP would directly decrease guanine nucleotide production.
O D. Excess AMP would directly block the production of more adenine nucleotides.
Part 2
O See Hint
How does this regulatory mechanism keep the balance of adenine versus guanine nucleotides?
Choose one or more:
O A High levels of any purine inhibit glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase, preferentlally
inhibiting one purine synthesis pathway over the other.
O B. The triphosphate form of one purine is necessary for synthesis of the other
purine. Thus as the level of GTP is reduced, the capacity to produce AMP is
reduced (and vice versa).
O C. High monophosphate forms of one purine inhibit further synthesis of its
respective pathway, but not the other purine pathway.
O D. The diphosphate forms positively feed back, accelerating purine synthesis.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax