
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780133594140
Author: James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
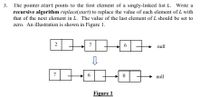
Transcribed Image Text:The pointer start points to the first element of a singly-linked list L. Write a
recursive algorithm replace(start) to replace the value of each element of L with
that of the next element in L. The value of the last element of L should be set to
3.
zero. An illustration is shown in Figure 1.
2
7
6.
null
7
null
Figure 1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Towers of Hanoi. There is a story about Buddhist monks who are playing this puzzle with 64 stone disks. The story claims that when the monks finish moving the disks from one post to a second via the third post, time will end. Eschatology (concerns about the end of time) and theology will be left to those better qualified; our interest is limited to the recur- sive solution to the problem. A stack of n disks of decreasing size is placed on one of three posts. The task is to move the disks one at a time from the first post to the second. To do this, any disk can be moved from any post to any other post, subject to the rule that you can never place a larger disk over a smaller disk. The (spare) third post is provided to make the solution possible. Your task is using c++ write a recursive function that describes instructions for a solution to this problem. We don’t have graphics available, so you should output a sequence of instructions that will solve the problem. Hint: If you could…arrow_forwardConsider the following multiplication problem: Given an integer list (an array) of size n, we want to calculate the product of all numbers in the list and display the result. (a) Define an instance of a problem in general. (b) Specify two different instances of the multiplication problem defined above. (c) What is the solution for each instance in part (b). How did you come up with that solution?arrow_forwarddef reverse_list (1st: List [Any], start: int, end: int) -> None: """Reverse the order of the items in list , between the indexes and (including the item at the index). If start or end are out of the list bounds, then raise an IndexError. The function must be implemented **recursively**. >>> lst ['2', '2', 'v', 'e'] >>>reverse_list (lst, 0, 3) >>> lst ['e', 'v', 'i', '2'] >>> lst [] >>>reverse_list (lst, 0, 0) >>> lst [0] >>> Ist = [] >>> reverse_list (lst, 0, 1) Traceback (most recent call last): IndexError #1 #1arrow_forward
- Let xHead, yHead and zHead be the head pointers of 3 linked lists of integers (called X-list, Y-list and Z-list, respectively, from here). X-list and Y-list are each sorted (in non-decreasing order) in itself and each may be empty. Z-list is initially empty (i.e., zHead initially contains the null pointer). Develop and test a recursive C++ function called SortedMergeRecur that combines the nodes in X-list and Y-list into Z-list such that, after calling the function, Z-list is a sorted list (in non-decreasing order) containing all the nodes initially contained in X-list and Y-list – X-list and Y-list should both be empty after the call. Other specifications/requirements: ● Each node of the list has the following structure: struct Node{ int data; Node *link;}; ● The function should: ► Have only three parameters (each a pointer-to-Node) and no return value (be a void function). ► Not use any global variables or static local…arrow_forwardThe language is in Racket. Please answer the question in the screenshot.arrow_forwardCode you provide code in python?arrow_forward
- EXERCISE 1 Consider a function doubles :: Cint]Eint] that doubles every item in list doubles [3, 4,1,2] [6,8, 2,4] a) write a version doubles Rec using recursion for the aboe functionarrow_forwardQuick Sort We choose an element from the list, called the pivot. We'll use it to divide the list into two sub-lists. We reorder all the elements around the pivot The ones with smaller value are placed before it All the elements greater than the pivot after it. After this step, the pivot is in its final position. This is the important partition step. We apply the above steps recursively to both sub-lists on the left and right of the pivot. Quick Sort (Example) Consider the following array Arr[] = {5, 9, 4, 6, 5, 3} Let's suppose we pick 5 as the pivot for simplicity We'll first put all elements less than 5 in the first position of the array: {3, 4, 5, 6, 5, 9} We'll then repeat it for the left sub-array {3,4}, taking 3 as the pivot There are no elements less than 3 We apply quicksort on the sub-array in the right of the pivot, i.e. {4} This sub-array consists of only one sorted element We continue with the right part of the original array, {6, 5, 9} until we get the final ordered…arrow_forwardUsing C, Must be in C Create a menu driven program that performs the following tasks (each task is a menu item): a. Create a doubly linked list of length 5 using dynamic allocation. Your linked-list should support method Write a function on to print the content of the linked list following its order. Write a function on to reverse the doubly linked list. Write a function to Delete the first node in your doubly Linked listarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science
Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning
Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education
Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY
Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780124077263
Author:David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337569330
Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337093422
Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133750423
Author:VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781119368830
Author:FITZGERALD
Publisher:WILEY