
(a)
Interpretation:
The least-squares estimates of the slope and intercept for the given data set should be calculated.
Concept introduction:
The least-squares estimates of a set of data behaving linearly are defined as follows:
Answer to Problem 1.10QAP
Explanation of Solution
Given:
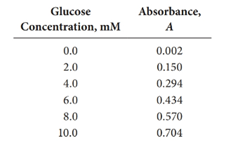
First, the data should be utilized to obtain
How to calculate
The above calculated values in the table are used to calculate
How to calculate
First, use the data in the above table to obtain
(b)
Interpretation:
Standard deviations of the slope and intercept and the standard error of the estimates for the given data set should be calculated using the LINEST function in EXCEL.
Concept introduction:
In order to use the LINEST function in EXCEL to obtain statistical values for a given data set, the following command should be typed on an EXCEL spread sheet, in which the given data is already been typed in two columns.
Answer to Problem 1.10QAP
Explanation of Solution
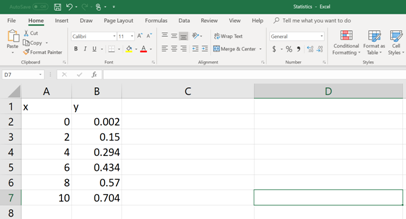
First, the data set should be entered in to an EXCEL spread sheet (See the figure below).
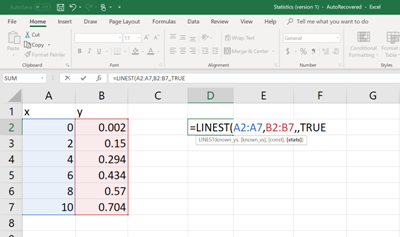
Then on a different cell, type the following command (See figure below). In order to enter the cell numbers of the unknown
Once the formula command is written and the parenthesis is closed, then hit the ENTER button. Now, the value of
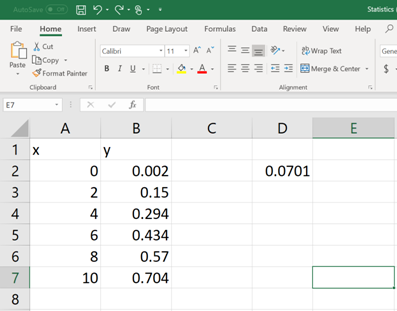
Now, select few more cells including the cell in which the command is typed and then click on the cursor bar (See below).
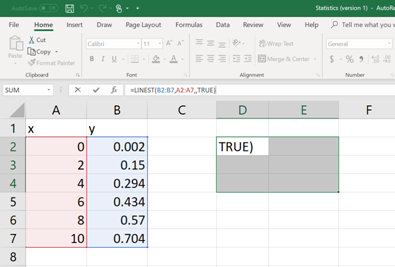
Then hit
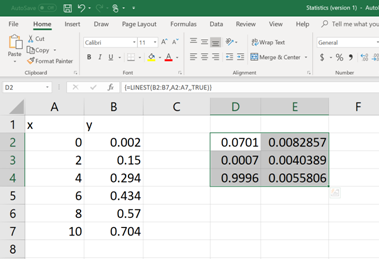
Each of these numerical values is relevant to a statistical data (mentioned in BOLD, See below). Now pick the apocopate answers required.
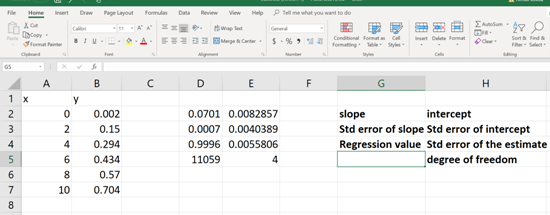
(c)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
The general formula to calculate the
Answer to Problem 1.10QAP
Explanation of Solution
The t value of the above equation depends on the confidence level (95 % in this question) and the degrees of freedom of the data set.
The degrees of freedom for a regression analysis =
Once the degree of freedom is calculated the t value can be extracted from a standard table similar to the table shown below:
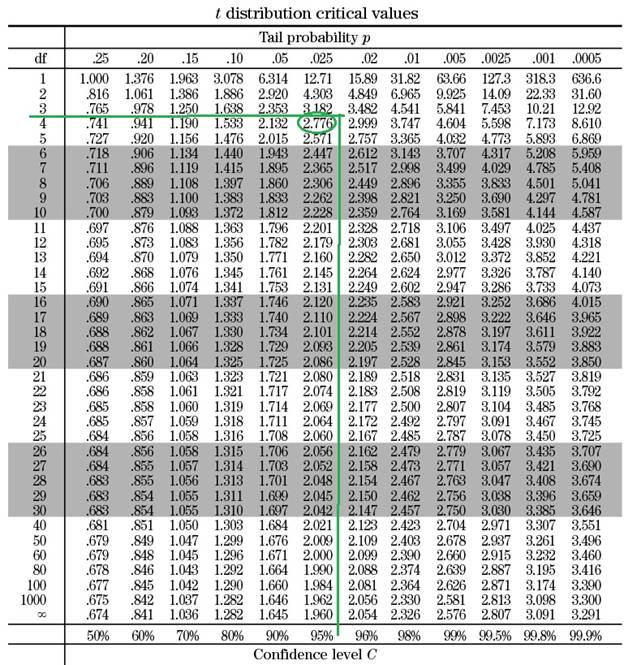
Based on the table, when the degree of freedom is 4 and the cofidence interval is 95 %, the t value is
(d)
Interpretation:
The glucose concentration and its standard deviation of a serum sample, which gave an absorbance of 0.350 should be calculated.
Concept introduction:
To determine an unknown glucose concentration
The standard deviation of
Answer to Problem 1.10QAP
Explanation of Solution
Plug in the appropriate numerical values in the below equation to determine the
How to calculate
Want to see more full solutions like this?
 Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning



