
a.
Planer Patch:
The patch formed by joining points in the plane is called planer patch.
Planar patch for given question:
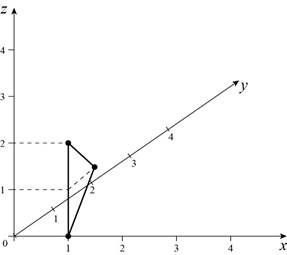
Explanation:
From the above diagram, the planer patch is parallel to “yz” plane. The points are viewed from outside of the object. So, the left most portion of the patch lies inside.
Explanation of Solution
b.
Determine a ray of light originating at the point (2, 0, 0):
The 3D plot of the patch with the point (2, 0, 0) is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
c.
Determine a ray of light originating at the point (2, 1, 1):
The 3D plot of the patch with the point (2, 1, 1) is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
d.
Determine a ray of light originating at the point (3, 2, 1):
The 3D plot of the patch with the point (3, 2, 1) is shown below:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- 3D computer graphics Briefly explain in your own words why the mip-mapping process is also called the level-of-detail process in the context of texturing.arrow_forwardSuppose that an imaging system samples a checkerboard image at 8 samples (pixels) / mm of the checkerboard. What should be the minimum size (side-length (mm) x side-length (mm)) of a square of the checkerboard, which will not cause aliasing in the image?arrow_forwardConsider two images. One should be relatively large, like 512 x 512 pixels that contains several sparsely populated points with magnitude 255, and the other is small such as 15 x 15 that contains a non-symmetric object like, with the object white and the background black for both images. Perform both the correlation, and convolution of the two images separately and correctly label each result. Make the resulting image the same size as the larger input image.arrow_forward
- For an object detection problem, assume you are designing a YOLO like model to do the job. Your input image size is 127x127 (RGB). We are looking for a 3x3 output grid size. The number of classes is 20 and for each cell in the grid, we are considering 2 anchors. Design the CNN network and as a designer feel free to set your network's hyper-parameters as you wish. The output of your network needs to show the final height, width, and the channel. You do not need to include post-processing (nan-max suppression) step for YOLO. In Python-arrow_forwardComment on the contrast of the image on histogram information of the image.arrow_forwarduse java to solve problem 3 in the attached imagearrow_forward
- Explain and illustrate the differences between local illumination and global illumination as they apply to computer graphics.arrow_forwardComputer Science Given a 512 x 512 image that consists of a series of 8-pixel wide white, and 8-pixel wide dark lines, where each pixel is 0.1mm wide. What is the spatial frequency of the lines in lp/mm?arrow_forwardSuppose we want to put the camera in position e(1, 0, 1) and aim it at position a(0, 0, 0) with view up position u(0, 1, 0) in the world coordinate system. Write the related code using the look-at function to setup the model-view matrix.arrow_forward
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





