
Concept explainers
(a)
The magnitude of slope of the graph.
To show: The relation
(a)
Answer to Problem 59A
The slope of the graph
The force
Explanation of Solution
Given:
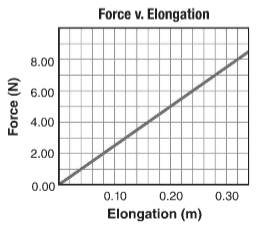
The given force-elongation graph is shown below.
Formula used:
For the graph, the expression for the slope is,
Here,
Calculation:
Consider the given graph. The slope of the graph is,
From the graph, the distance
Substitute the value of k and d in
Hence, the force
Conclusion:
Thus, the slope of the graph is
(b)
The work done in stretching the spring using the graph.
(b)
Answer to Problem 59A
The work done in stretching the spring is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
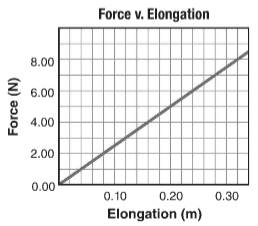
The given force-elongation graph is shown below.
Formula used:
The expression for the graph is,
Calculation:
Consider the given graph, the work done in stretching the spring is
Conclusion:
Thus, the work done in stretching the spring is
(c)
To show:The work done obtained in part (b) is valid for the given values.
(c)
Answer to Problem 59A
The work done in stretching the spring is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given force-elongation graph is shown below.
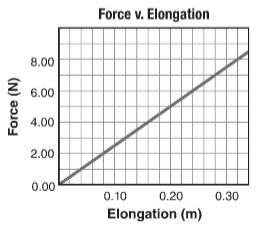
The distance is 0.20 m.
Spring constant is
Formula used:
The expression for the graph using the graph as follows:
Here,
Calculation:
Work done obtained in part (b) is 0.50 J.
For the given values, work done in stretching the spring is,
So, the work done in stretching the spring is
Conclusion:
Thus, the work done in stretching the spring is same as the given value.
Chapter 10 Solutions
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
College Physics (10th Edition)
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
University Physics Volume 1
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





