
Concept explainers
a.
Find the expected frequencies.
a.
Answer to Problem 14E
The expected frequencies under the null hypothesis is obtained as,
| Number of Children | ||||||
| Siblings | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 | More Than 4 |
| 0 | 39.626 | 24.501 | 37.761 | 23.776 | 11.396 | 6.941 |
| 1 | 152.174 | 94.090 | 145.013 | 91.305 | 43.763 | 26.655 |
| 2 | 153 | 94.6 | 145.8 | 95.8 | 44 | 26.8 |
| 3 | 129.610 | 80.138 | 123.510 | 77.766 | 37.273 | 22.703 |
| 4 | 93.836 | 58.020 | 89.421 | 56.302 | 26.986 | 16.437 |
| More Than 4 | 196.754 | 121.653 | 187.495 | 118.052 | 56.583 | 34.464 |
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The contingency table with 6 rows consisting of six classification of number of siblings and6 columns consisting of six classification of number of children in families is given.
The sample of 2,780 is randomly selected.
Contingency table:
A contingency table is obtained as using two qualitative variables. One of the qualitative variable is row variable that has one category for each row of the table another is column variable has one category for each column of the table.
The hypotheses are:
Null Hypothesis:
Alternate Hypothesis:
Now, it is obtained that,
| Number of Children | |||||||
| Siblings | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 | More Than 4 | Row Total |
| 0 | 60 | 19 | 34 | 15 | 10 | 6 | 144 |
| 1 | 189 | 97 | 163 | 63 | 29 | 12 | 553 |
| 2 | 179 | 98 | 137 | 81 | 41 | 20 | 556 |
| 3 | 124 | 85 | 132 | 83 | 31 | 16 | 471 |
| 4 | 85 | 53 | 88 | 61 | 32 | 22 | 341 |
| More Than 4 | 128 | 121 | 175 | 156 | 77 | 58 | 715 |
| Column Total | 765 | 473 | 729 | 459 | 220 | 134 | 2,780 |
Expected frequencies:
The expected frequencies in case of contingency table is obtained as,
Now, using the formula of expected frequency it is found that the expected frequency for the number of children of 1 and the number of siblings of 1 is obtained as,
Hence, in similar way the expected frequencies are obtained as,
| Number of Children | ||||||
| Siblings | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 | More Than 4 |
| 0 | ||||||
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | ||||||
| 3 | ||||||
| 4 | ||||||
| More Than 4 | ||||||
b.
Find the value of chi-square statistic.
b.
Answer to Problem 14E
The value of chi-square statistic is 126.444.
Explanation of Solution
Chi-Square statistic:
The chi-square statistic is obtained as
The classifications of number of children can be written as,
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 4 |
| 4 | 5 |
| More Than 4 | 6 |
Test Statistic:
Software procedure:
Step -by-step software procedure to obtain test statistic using MINITAB software is as follows:
- • Select Stat>Table>Cross Tabulation and Chi-Square.
- • Check the box of Raw data (categorical variables).
- • Under For rows enter Siblings.
- • Under For columns enter Number of Children.
- • Check the box of Count under Display.
- • Under Chi-Square, click the box of Chi-Square test.
- • Select OK.
- Output using MINITAB software is given below:
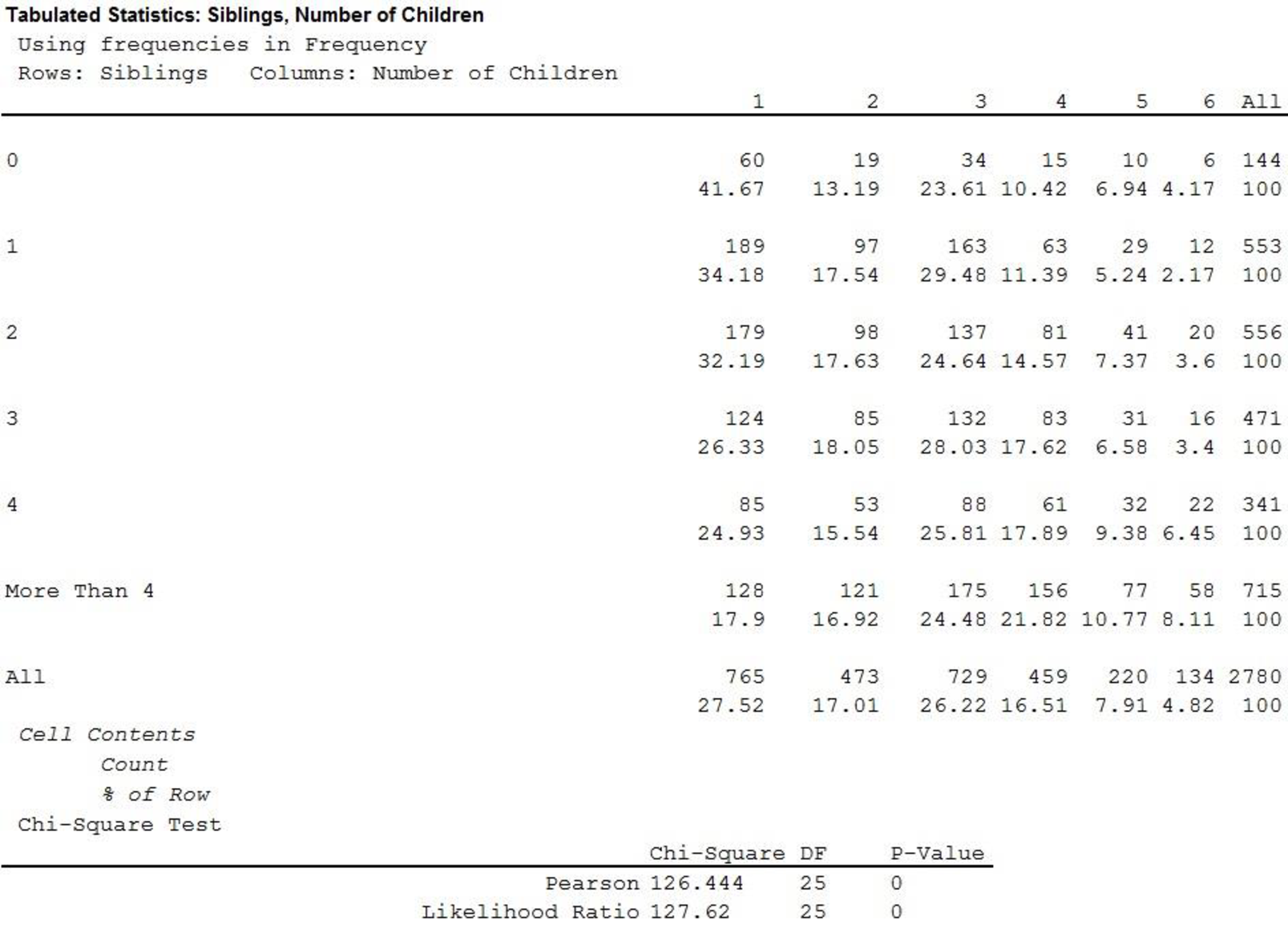
Thus, the value of chi-square statistic is126.444.
c.
Find the degrees of freedom.
c.
Answer to Problem 14E
The degrees of freedom is25.
Explanation of Solution
It is known that under the null hypothesis
In the given question there are 6rows and 6 columns.
Hence, the degrees of freedom is
Thus, the degrees of freedom is25.
d.
Perform a test of hypothesis of independence at the level of significance of
Draw conclusions.
d.
Answer to Problem 14E
There is no enough evidence to conclude that the number of sibling and the number of children are independent.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
It is known that when the null hypothesis
In part (a) it is found that all the expected frequencies corresponding to all rows and columns of the given contingency table are more than 5.
Hence, the test of independence is appropriate.
The hypotheses are:
Null Hypothesis:
Alternate Hypothesis:
From parts (b) and (c), the value of test statistic is 126.444with the degrees of freedom 25.
Level of significance:
The level of significance is given as 0.05.
Critical value:
In a test of hypotheses the critical value is the point by which one can reject or accept the null hypothesis.
Software procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain critical value using MINITAB software is as follows:
- • Select Graph>Probability distribution plot > view probability
- • Select Chi -Square under distribution.
- • In Degrees of freedom, enter 25.
- • Choose Probability Value and Right Tail for the region of the curve to shade.
- • Enter the Probability value as 0.05 under shaded area.
- • Select OK.
- Output using MINITAB software is given below:
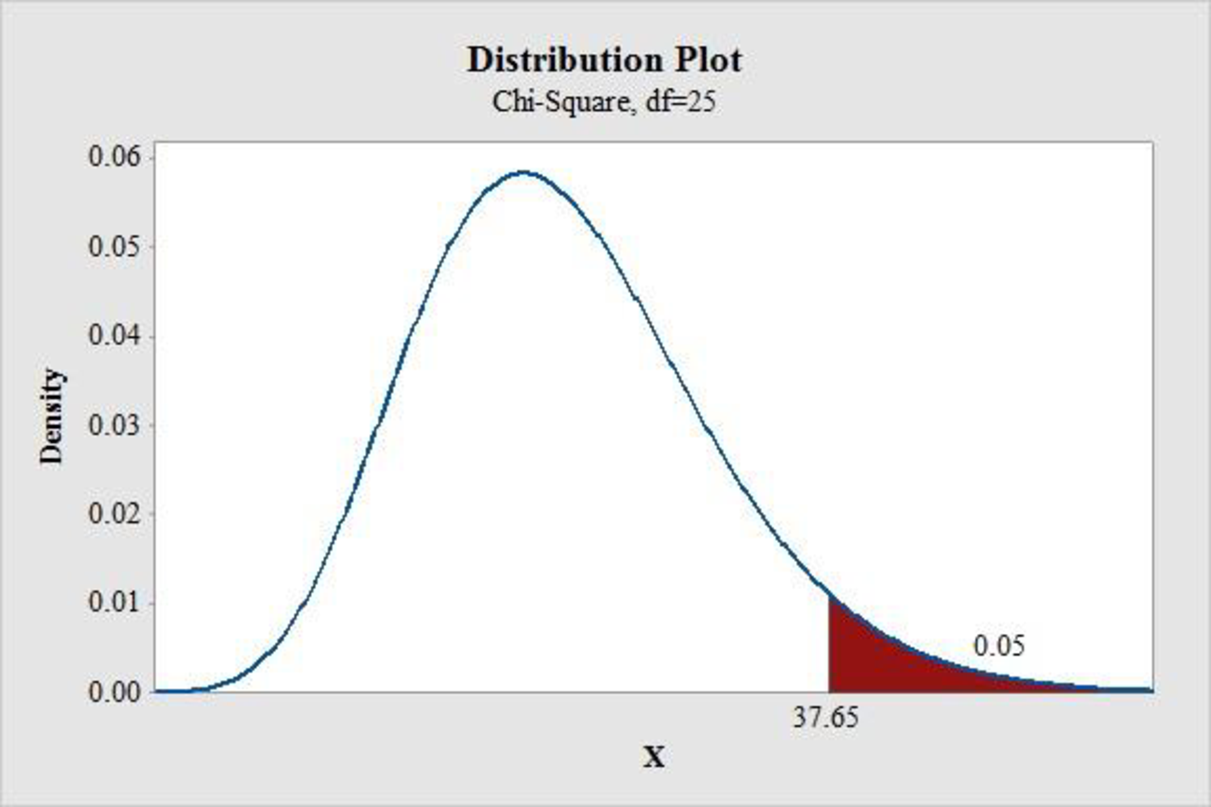
Hence, the critical value at
Rejection rule:
If the
Conclusion:
Here, the
That is,
Thus, the decision is “reject the null hypothesis”.
Thus, there is not enough evidence to conclude that the number of sibling and the number of children are independent.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
ESSENTIAL STATISTICS W/CONNECT
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





