
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The function of the given reagent has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
When a reagent functions as a nucleophile, substitution reaction takes place and when a reagent functions as a base, elimination reaction takes place. The first step is to determine the reagent to be strong or weak nucleophile and whether it is a strong or weak base. Basicity and nucleophilicity do not always parallel each other.
When comparing the atoms in the same row in periodic table, the basicity and nucleophilicity parallel each other. An example is,
When comparing the atoms in the same column in periodic table, the basicity and nucleophilicity do not parallel each other. An example is,
Basicity measures the charge stability on atom, while nucleophlicity measures how fast a nucleophile attacks. Basicity is a
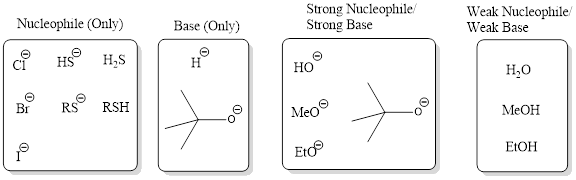
Nucleophile (Only): This category consists of reagents that act only as strong nucleophiles and not as bases. The reagent from this category involves in substitution reaction and not elimination.
Base (Only): This category consists of reagents that act only as bases and not as nucleophiles. The reagent from this category involves in elimination reaction and not substitution.
Strong Nucleophile/Strong Base: This category consists of reagents that are strong bases and also strong nucleophiles. This includes hydroxide, alkoxide ions. Generally these reagents are used for bimolecular process.
Weak Nucleophile/Weak Base: This category consists of reagents that are weak bases and weak nucleophile. This includes reagents such as water, alcohols. Generally these reagents are used for unimolecular process.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Organic Chemistry As a Second Language: First Semester Topics
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





