
EBK OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
14th Edition
ISBN: 9781260718447
Author: Stevenson
Publisher: MCG COURSE
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 1P
Compute the total cost for each aggregate plan using these unit costs:
Regular output = $40
Overtime = $50
Subcontract = $60
Average Balance Inventory = $10
a. 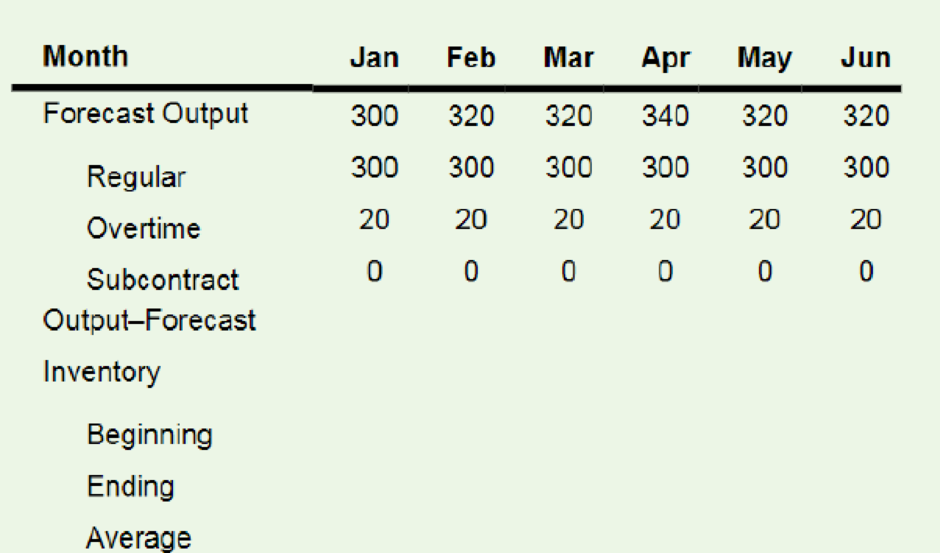
b. 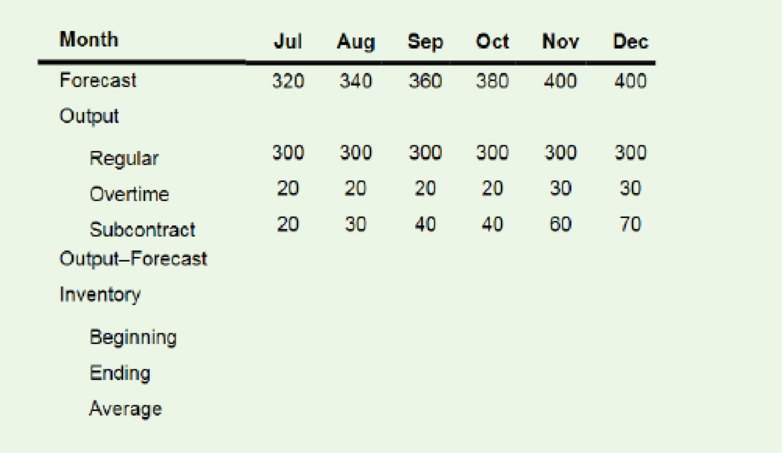
c. (Refer to part b) After complaints from some workers about working overtime every month during the first half of the year, the manager is now considering adding some temporary workers for the second half of the year, which would increase regular output to a steady 350 units a month, not using any overtime, and using subcontracting to make up needed output. Determine the total cost of that plan.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Planners for a company that makes several models of skateboards are about toprepare the aggregate plan that will cover six periods. They now want toevaluate a plan that calls for a steady rate of regular output, mainly usinginventory to absorb the uneven demand but allowing some backlog. Overtimeand subcontracting are not used because they want a steady output. They intendto start with zero inventory on hand in the first period. Prepare an aggregate planand determine its cost using the following information. Assume a level of outputrate of 300 units per period with regular time. Note that the planned endinginventory is zero. There are 15 workers, and each can produce 20 units per
Period
1
2
3
4
5
6
Total
Forecast
200
200
300
400
500
200
1800
Cost Information:Regular time = $2 per skateboardOvertime = $3 per skateboardSubcontract = $6 per skateboardInventory = $1 per skateboard per period on average inventoryBack orders = $5 per skateboard per period
Develop a level aggregate plan for the Draper Tax Companyif back orders are permitted.(a) Show what would happen if this plan were implemented.(b) Calculate the costs associated with this plan.(c) Evaluate the plan in terms of cost, customer service,operations, and human resources.
A. Planners for a company that makes several models of skateboards are about toprepare the aggregate plan that will cover six periods. They now want toevaluate a plan that calls for a steady rate of regular output, mainly usinginventory to absorb the uneven demand but allowing some backlog. Overtimeand subcontracting are not used because they want a steady output. They intendto start with zero inventory on hand in the first period. Prepare an aggregate planand determine its cost using the following information. Assume a level of outputrate of 300 units per period with regular time. Note that the planned endinginventory is zero. There are 15 workers, and each can produce 20 units perperiod.
Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 TotalForecast 200 200 300 400 500 200 1800
Cost Information:Regular time = $2 per skateboardOvertime = $3 per skateboardSubcontract = $6 per skateboardInventory = $1 per skateboard per period on…
Chapter 11 Solutions
EBK OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
Ch. 11 - What three levels of planning involve operations...Ch. 11 - What are the three phases of intermediate...Ch. 11 - Prob. 3DRQCh. 11 - Why is there a need for aggregate planning?Ch. 11 - What are the most common decision variables for...Ch. 11 - Prob. 6DRQCh. 11 - Briefly discuss the advantages and disadvantages...Ch. 11 - What are the primary advantages and limitations of...Ch. 11 - Briefly describe the planning techniques listed as...Ch. 11 - What are the inputs to master scheduling? What are...
Ch. 11 - Prob. 11DRQCh. 11 - What general trade-offs are involved in master...Ch. 11 - Who needs to interface with the master schedule...Ch. 11 - How has technology had an impact on master...Ch. 11 - Service operations often face more difficulty in...Ch. 11 - Name several behaviors related to aggregate...Ch. 11 - Compute the total cost for each aggregate plan...Ch. 11 - A manager would like to know the total cost of a...Ch. 11 - Determine the total cost for this plan given the...Ch. 11 - a. Given the following forecast and steady regular...Ch. 11 - Manager T. C. Downs of Plum Engines, a producer of...Ch. 11 - Manager Chris Channing of Fabric Mills, Inc., has...Ch. 11 - SummerFun. Inc., produces a variety of recreation...Ch. 11 - Nowjuice, Inc., produces Shakewell fruit juice. A...Ch. 11 - Wormwood, Ltd., produces a variety of furniture...Ch. 11 - Refer to Solved Problem 1. Prepare two additional...Ch. 11 - Refer to Solved Problem 1. Suppose another option...Ch. 11 - Prob. 12PCh. 11 - Prob. 13PCh. 11 - Prob. 14PCh. 11 - Prob. 15PCh. 11 - Refer to Example 3. Suppose that regular-time...Ch. 11 - Prob. 17PCh. 11 - Prob. 18PCh. 11 - Prepare a master production schedule for...Ch. 11 - Update the master schedule shown in Figure 11.11...Ch. 11 - Prepare a master schedule like that shown in...Ch. 11 - Determine the available-to-promise (ATP)...Ch. 11 - Prepare a schedule like that shown in Figure 11.12...Ch. 11 - The objective is to choose the plan that has the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 2CQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, operations-management and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Mavis and John have joined forces to start M&J Food Products, a processor of packaged shredded lettuce for institutional use. John has years of food processing experience, and Mavis has extensive commercial food preparation experience. The process will consist of opening crates of lettuce and then sorting, washing, slicing, preserving, and finally packaging the prepared lettuce. Together, with help from vendors, they think they can adequately estimate demand, fixed costs, revenues, and variable cost per 5-pound bag of lettuce. They think a largely manual process will have monthly fixed cost of $50,000and a variable cost of $2.50 per bag. They expect to sell 75,000 bags of lettuce per month. They expect to sell the shredded lettuce for $3.25 per 5-pound bag. John and Mavis has been contacted by a vendor to consider a more mechanized process. This new process will have monthly fixed cost of $125,000 per month with a variable cost of $1.75 per bag. Based on the above scenario: Should…arrow_forwardA. When aggregate planning seeks to influence demand and supply, both the marketing and operations functions are involved. In this case, the goal is generally to find: a. A lower total cost plan b. A higher profit plan c. A higher sales revenue plan d. A lower cost of goods manufactured plan B. In a market situation where demand is exceeding supply, which from the following list would you generally work on first? a. Distribution b. Work force level c. Promotion d. Pricearrow_forwardTable shows the aggregate demand requirements of a manufacturing company. The operations manager is going to use a new plan, which begins in January with 200 units on hand and ends with zero inventory in August. Assume, Inventory holding cost is $20 per unit per month and stockout cost of lost sales is $100 per unit. The plan is called plan A. Compute the cost of plan A. Plan A: Vary the workforce level to execute a “chase” strategy by producing the quantity demanded in the prior month. The December demand and rate of production are both 1,600 units per month. The cost of hiring additional workers is $5,000 per 100 units. The cost of laying off workers is $7,500 per 100 units. Evaluate this plan.arrow_forward
- The Walden Manufacturing Corp. has office support salaries of $4,000, factory supplies of $1,000,indirect labor of $6,000, direct materials of $16,000, advertising expense of $2,500, office expense of$14,000, and direct labor of $20,000. What is the total period cost?arrow_forward3. What information is necessary for an operations manager to create the aggregate plan? List the capacity options and demand options of aggregate planning and explain the difference between them. Which strategy or model always gives the aggregate plan with the minimum total cost?arrow_forwardDevelop a production plan and calculate the annual cost for a firm whose demand forecast is fall, 11,000; winter, 8,000; spring, 6,000; summer, 13,000. Inventory at the beginning of fall is 500 units. At the beginning of fall you currently have 30 workers, but you plan to hire temporary workers at the beginning of summer and lay them off at the end of summer. In addition, you have negotiated with the union an option to use the regular workforce on overtime during winter or spring if overtime is necessary to prevent stockouts at the end of those quarters. Overtime is not available during the fall. Relevant costs are hiring, $100 for each temp; layoff $200 for each worker laid off; inventory holding, $5 per unit-quarter; backorder, $10 per unit; straight time, $5 per hour; overtime, $8 per hour. Assume that the productivity is 0.5 unit per worker hour, with eight hours per day and 60 days per season. a. What is the total cost for this plan?arrow_forward
- Develop a chase aggregate plan for Draper using apermanent workforce of 12 employees supplemented by overtime.All demand must be met each period.(a) Show what would happen if this plan were implemented.(b) Calculate the costs associated with this plan.(c) Evaluate the plan in terms of cost, customer service,operations, and human resources.arrow_forwardSoutheast Soda Pop, Inc., has a new fruit drink forwhich it has high hopes. John Mitten thai, the production planner,has assembled the fo llowing cost data and demand forecast: John's job is to develop an aggregate plan. The three initialoptions he wants to evaluate are:• Plan A: a strategy that hires and fires personnel as necessaryto meet the forecast.• Plan B: a level strategy.• Plan C: a level strategy that produces 1,200 cases per quarterand meets the fo recast demand with inventory and subcontracting.a) Which strategy is the lowest-cost plan?b) If you are John's boss, the VP for operations, which p lan doyou implement and why?arrow_forwardDevelop a production plan and calculate the annual cost for a firm whose demand forecast is: fall, 10,100; winter, 8,100; spring, 7,100; summer, 12,100. Inventory at the beginning of fall is 505 units. At the beginning of fall you currently have 30 workers, but you plan to hire temporary workers at the beginning of summer and lay them off at the end of summer. In addition, you have negotiated with the union an option to use the regular workforce on overtime during winter or spring if overtime is necessary to prevent stock-outs at the end of those quarters. Overtime is not available during the fall. Relevant costs are hiring, $100 for each temp; layoff, $200 for each worker laid off; inventory holding, $5 per unit-quarter; backorder, $10 per unit; regular time, $5 per hour; overtime, $8 per hour. Assume that the productivity is 0.5 unit per worker hour, with eight hours per day and 60 days per season. In each quarter, produce to the full output of your regular workforce, even if that…arrow_forward
- DAT, Inc., needs to develop an aggregate plan for its product line. Relevant data are Management prefers to keep a constant workforce and production level, absorbingvariations in demand through inventory excesses and shortages. Demand not met is carriedover to the following month.Develop an aggregate plan that will meet the demand and other conditions of theproblem. Do not try to i nd the optimum; just i nd a good solution and state the procedureyou might use to test for a better solution. Make any necessary assumptions.arrow_forwardAssume that Blue Button Manufacturing (BBM) has accepted the merits of aggregate planning. You have been requested to indicate the way forward and must recommend an aggregate planning strategy to the management team. Write a report in which you describe the concept “trade-offs in aggregate planning”, identify the potential strategies that could be followed, including the use case for each strategy, and then substantiate your choice of strategy for BBMarrow_forwardPlan production for a four-month period: February through May. For February and March, you should produce to exact demand forecast. For April and May, you should use overtime and inventory with a stable workforce; stable means that the number of workers needed for March will be held constant through May. However, government constraints put a maximum of 5,000 hours of overtime labor per month in April and May (zero overtime in February and March). If demand exceeds supply, then backorders occur. There are 100 workers on January 31. You are given the following demand forecast: February, 90,000; March 65,000; April 110,000; May, 55,000. Productivity is four units per worker hour, eight hours per day, 20 days per month. Assume zero inventory on February 1. Costs are hiring, $50 per new worker; layoff, $70 per worker laid off; inventory holding, $10 per unit-month; straight-time labor, $10 per hour; overtime, $15 per hour; backorder, $20 per unit a. Find the total cost of this plan?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Inventory Management | Concepts, Examples and Solved Problems; Author: Dr. Bharatendra Rai;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2n9NLZTIlz8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
