
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The value of
Concept introduction:
The wavefunction contains all the information about the state of the system. The wavefunction is the function of the coordinates of particles and time. The wavefunction
Answer to Problem 12.56E
The values of
The simple potential energy diagram for this system is shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2.
Explanation of Solution
The value of
Where,
•
•
The value of
Where,
•
The value of
The wavefunction
The value of
Substitute the value of
Thus, the value of
Substitute the value of
Thus, the value of
Substitute the value of
Thus, the value of
Substitute the value of
Thus, the wavefunction
The value of
Substitute the value of
Thus, the value of
Substitute the value of
Thus, the value of
Substitute the value of
Thus, the value of
Substitute the value of
Thus, the wavefunction
The value of
Substitute the value of
Thus, the value of
Substitute the value of
Thus, the value of
Substitute the value of
Thus, the value of
Substitute the value of
Thus, the wavefunction
The value of
Substitute the value of
Thus, the value of
Substitute the value of
Thus, the value of
Substitute the value of
Thus, the value of
Substitute the value of
Thus, the wavefunction
The values of potential energy and
| Energy |
|
The plot between the potential energy with
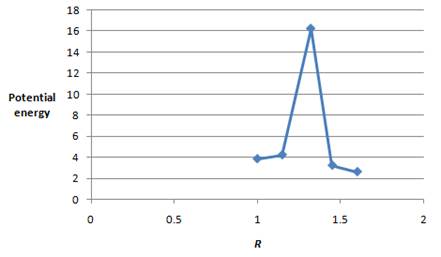
Figure 1
The values of potential energy and
| Energy |
|
The plot between the potential energy with
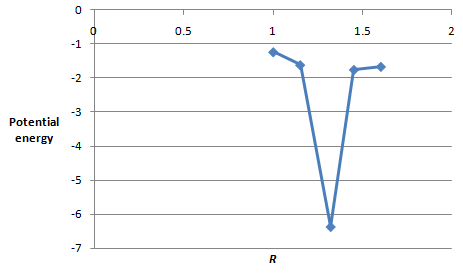
Figure 2
The values of
The simple potential energy diagram for this system is shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Physical Chemistry
- A diatomic Hydrogen (H2) molecule with a potential between its two Hydrogen atoms can be modelled using the Morse potential: V(x) = V0 e−αx (e−αx - 2), where α = 19.3 nm−1 and V0 = 4.52 eV. Assuming the H2 molecule has no rotational energy. Determine the minimum value of the Morse potential, V . (State in eV, to 3 s.f.)arrow_forwardUse the equipartition principle to estimate the values of γ = Cp/CV for gaseous ammonia and methane. Do this calculation with and without the vibrational contribution to the energy. Which is closer to the experimental value at 25 °C?arrow_forwardUse the equipartition principle to estimate the value of γ = Cp/CV for carbon dioxide. Do this calculation with and without the vibrational contribution to the energy. Which is closer to the experimental value at 25 °C?arrow_forward
- Calculate the relative intensities M+1 and M+2 for CH3COOHarrow_forward2. Explainthefollowing,relatedtophysicalinsighttointernalenergy(i)Translationenergy(ii)rotational kinetic energy (iii) vibrational kinetic energy (iv) Internal energy (v) spin energy (vi) sensible energy (vii) latent energy (viii) chemical energy (ix) nuclear energy (x) thermal energyarrow_forwardBriefly describe the contributions of Walter Nernst, T. W. Richards, Max Planck and G. N. Lewisin the development of the third law of thermodynamics.arrow_forward
- Use the equipartition theorem to estimate the molar internal energy of (i) I2, (ii) CH4, (iii) C6H6 in the gas phase at 25 °C.arrow_forwardWhat is the temperature of a two-level system of energy separation equivalent to 300 cm−1 when the population of the upper state is one-half that of the lower state?arrow_forwardGive the effect on point (x,y,x) on each operation: (a) C2(x) (b) C2(z)arrow_forward
- What are the salient features of Aufbau principle?arrow_forwardEstimate the values of γ = Cp,m/CV,m for gaseous ammonia and methane. Do this calculation with and without the vibrational contribution to the energy. Which is closer to the experimental value at 25 °C? Hint: Note that Cp,m − CV,m = R for a perfect gas.arrow_forwardThe four lowest electronic levels of a Ti atom are 3F2, 3F3, 3F4, and 5F1, at 0, 170, 387, and 6557 cm−1, respectively. There are many other electronic states at higher energies. The boiling point of titanium is 3287 °C. What are the relative populations of these levels at the boiling point? Hint: The degeneracies of the levels are 2J + 1.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





