
Pearson eText Organic Chemistry -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780135213711
Author: Paula Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON+
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 12, Problem 45P
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The change in the degree of regioselectivity compared to the ratio of relative rates found in problem 44 has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Chlorine radical forms a tertiary radical five times faster than a primary radical and it forms a secondary radical 3.8 times faster than a primary radical.
Relative rates of alkyl radical formation by a chlorine radical at 125 °C.
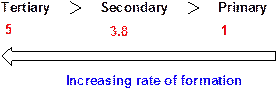
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
In unpolluted air at 300 K, the hydroxyl radical OH reacts
with CO with a bimolecular rate constant of 1.6 × 101' L
mol-1 s-1 and with CH4 with a rate constant of 3.8 ×
10° L mol¬1 s-1. Take the partial pressure of CO in air to
be constant at 1.0 × 10-7 atm and that of CH4 to be 1.7 x
10-6 atm, and assume that these are the primary mecha-
nisms by which OH is consumed in the atmosphere. Cal-
culate the half-life of OH under these conditions.
The chemical rxn : N2 + O2 ⟶⟶ NO can be described by the following mechanism.
step-1) N2 + 2O2 ⟶⟶ 2NO2 ΔΔH1
step-2) NO + 1212 O2 ⟶⟶ NO2 ΔΔH2
Identify which expression is most consistent with the enthalpy of formation of NO.
The mechanism for the reaction described by
nust. A common
d(a stronger
whch ont of
ice
prhct
NO,(g) + CO(g) → CO,(g) + NO(g)
coor
on be c
is suggested to be
(1) 2NO,(g) –→ NO,(g) + NO(g)
k1
->
k2
(2) NO,(g) + CO(g) → NO,(g) + CO,(g)
d[CO2]
k[NO2]?
%3D
The experimental rate law for the production of [CO2] = k1 [NO2J² or
dt
d[NO3]
0 ), is this a valid mechanism? i.e show
Assuming that [NO3] is governed by a steady state (
dt
that using elementary reactions 1 and 2, the experimental rate law can found. (Hint write out all the ways
d[NO3]
= ?
d[C02] = ? )
%3|
and
%3D
dt
that [NO3] and [CO2] are created and destroyed,
dt
owing clecre
cel
at 25 C
NiC
C)Cu
a062
0.62 V
0.00 V
4. 460 V
Chapter 12 Solutions
Pearson eText Organic Chemistry -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 1PCh. 12.2 - Write the steps for formation of...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 3PCh. 12.4 - How many alkyl chlorides are obtained from...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 6PCh. 12.5 - Prob. 8PCh. 12.5 - a. Would chlorination or bromination produce a...Ch. 12.5 - Show how the following compounds could be prepared...Ch. 12.6 - Prob. 12PCh. 12.7 - Prob. 13P
Ch. 12.7 - Prob. 14PCh. 12.8 - Prob. 15PCh. 12.8 - Draw the stereoisomers of the major...Ch. 12.9 - Prob. 18PCh. 12.9 - How many allylic substituted bromoalkenes are...Ch. 12.9 - a. How many stereoisomers are formed from the...Ch. 12.9 - Prob. 21PCh. 12.9 - Prob. 22PCh. 12.10 - Prob. 23PCh. 12.11 - How many atoms share the unpaired electrons in...Ch. 12.11 - Prob. 25PCh. 12 - Prob. 26PCh. 12 - Prob. 27PCh. 12 - Prob. 28PCh. 12 - Prob. 29PCh. 12 - Prob. 30PCh. 12 - Prob. 31PCh. 12 - Prob. 32PCh. 12 - Prob. 33PCh. 12 - Prob. 34PCh. 12 - Prob. 35PCh. 12 - Prob. 36PCh. 12 - Prob. 37PCh. 12 - a. What five-carbon alkene forms the same product...Ch. 12 - Prob. 39PCh. 12 - Starting with cyclohexane, how could the following...Ch. 12 - a. Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:...Ch. 12 - What stereoisomers are obtained from the following...Ch. 12 - Prob. 43PCh. 12 - Prob. 44PCh. 12 - Prob. 45PCh. 12 - Draw the products of the following reactions,...Ch. 12 - Prob. 47PCh. 12 - Prob. 48PCh. 12 - Prob. 49PCh. 12 - Explain why the rate of bromination of methane...Ch. 12 - Prob. 51PCh. 12 - Prob. 1PCh. 12 - Prob. 2PCh. 12 - Prob. 3PCh. 12 - Prob. 4P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5. For the chlorination of ethane, represented by the equation: CH3CH3 + Cl2 + hv→ CH3CH2CI + HCI, the following radical-mediated mechanism has been proposed: Cl2 2 Cl· + CI - CH4 + Cl. → CH3· + HCI CH3: + Cl2 → CH3CI + Cl· k1, k.1 k2 k3 CH3* + Cl· 2CH3CI ka, k.4 Additionally, it has been possible to establish, under certain experimental conditions, that the reaction is first order with respect to the methane, and three halves with respect to chlorine. a) Classify the different steps of this mechanism (i.e. initiation, propagation, etc.). b) Derive the rate law for the chlorination of ethane, based on the mechanism proposed. c) Identify which is the rate-determining step. Justify your selection. d) Indicate which are the assumptions and approximations you used so that this model could work (i.e. pre- equilibrium condition, steady state approximation, neglecting the contribution of a step, etc.).arrow_forwardCalculate the orders of the reaction with respect to I–, BrO3 , and H+ –using the aforementioned systematic approach. In order to simplify this task, the proper experiments are provided. The orders should be rounded to the nearest integer.arrow_forwardIn a research paper, (Orkin et al., J. Phys. Chem., 1997, 101: 174) rate constants were determined for the reaction between the hydroxyl radical and chlorobromomethane: OH• + CH2BrCI → products Data that were obtained included the following values of the rate constant k for the following temperatures: Т, К k, cm³/molecule•sec 298 1.11 x 10 13 313 1.34 x 10 13 330 1.58 x 10 13 Determine the E, and the pre-exponential factor. E = J/mol A = cm3/molecule•secarrow_forward
- TRUE or FALSE: For a transition state to be considered as the rate- determining step (rds) in a multi-step reaction, it must have the highest change in enthalpy.arrow_forwardThe data below show the concentration of N2O5 versus time for the following reaction: N2O5 (g) → NO3 (g) + NO2(g) Time (s) [N2O5] (M) 1.000 25 0.822 50 0.677 75 0.557 100 0.458 125 0.377 150 0.310 175 0.255 200 0.210arrow_forwardThe second-order rate constants for the reaction of oxygen atoms with aromatic hydrocarbons have been measured (R. Atkinson and J.N. Pitts, J. Phys. Chem. 79, 295 (1975)). In the reaction with benzene the rate constants are 1.44 × 107 dm3 mol−1 s−1 at 300.3 K, 3.03 × 107 dm3 mol−1 s−1 at 341.2 K, and 6.9 × 107 dm3 mol−1 s−1 at 392.2 K. Find the frequency factor and activation energy of the reaction.arrow_forward
- (d) The first-order rate constants for the fluorescence and phosphorescence of molecule X are 4.5 × 10" s' and 0.50 s', respectively. Briefly explain the large order of magnitude difference in the rate constant values. (e) Explain how long (in s) it takes for 1.0% of fluorescence and phosphorescence to occur following termination of excitation.arrow_forward2. The following sequence of steps has been proposed for the overall reaction between H₂ and Br₂ to form HBr: (1) Br2(g) 2Br(g) (2) Br(g) + H₂(g) HBr(g) + H(g) (3) H(g) + Br(g) HBr(g) Write the overall balanced equation and show that the overall Qc is the product of the Qc's for the individual steps.arrow_forward4. Write the free radical chain mechanism for the following bromination reaction: BrCC13 hv + Br HCC13arrow_forward
- Write the steps of ‘Modern Adsorption Theory of Heterogenous Catalysis.’arrow_forwardNitric oxide, NO·, is another radical also thought to cause ozone destruction by a similar mechanism. One source of NO· in the stratosphere is supersonic aircraft whose jet engines convert small amounts of N2 and O2 to NO·. Write the propagation steps for the reaction of O3 with NO·.arrow_forwardA minor route for ozone destruction in the ozone hole involves Mechanism II with bromine as X' and chlorine as X (or vice-versa). The CIO and BrO free radical molecules produced in these processes then collide with each other and rearrange their atoms to eventually yield O, and atomic chlorine and bromine. Write out the mechanism for this process, and add up the steps to determine the overall reaction.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

Kinetics: Initial Rates and Integrated Rate Laws; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wYqQCojggyM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY