
Concept explainers
a.
Explain how one would assess the fit based on the
a.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Answer will vary.
Here the data set B is taken, in which the midterm exam (X) and final exam score (Y) is given.
Hypotheses:
Null hypothesis:
That is, the slope is zero.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, the slope not equal to zero.
Regression:
Suppose
Where,
The total sum of squares is denoted as,
The regression sum of squares is denoted as,
The error sum of squares is denoted as,
From the regression the fitted line is denoted as,
The 95% confidence interval for the slope,
Where,
Software Procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to find R-squared using EXCEL is as follows:
- • Open an EXCEL file.
- • In column A and B, enter the Midterm Exam Score and Final Exam Score data.
- • Click on data > click on Data analysis.
- • Choose Regression > click OK.
- • Select Input Y range as the column of Final Exam Score.
- • Select Input X range as the column of Midterm Exam Score.
- • Select the output range.
- • Click OK.
- Output using EXCEL is given below:
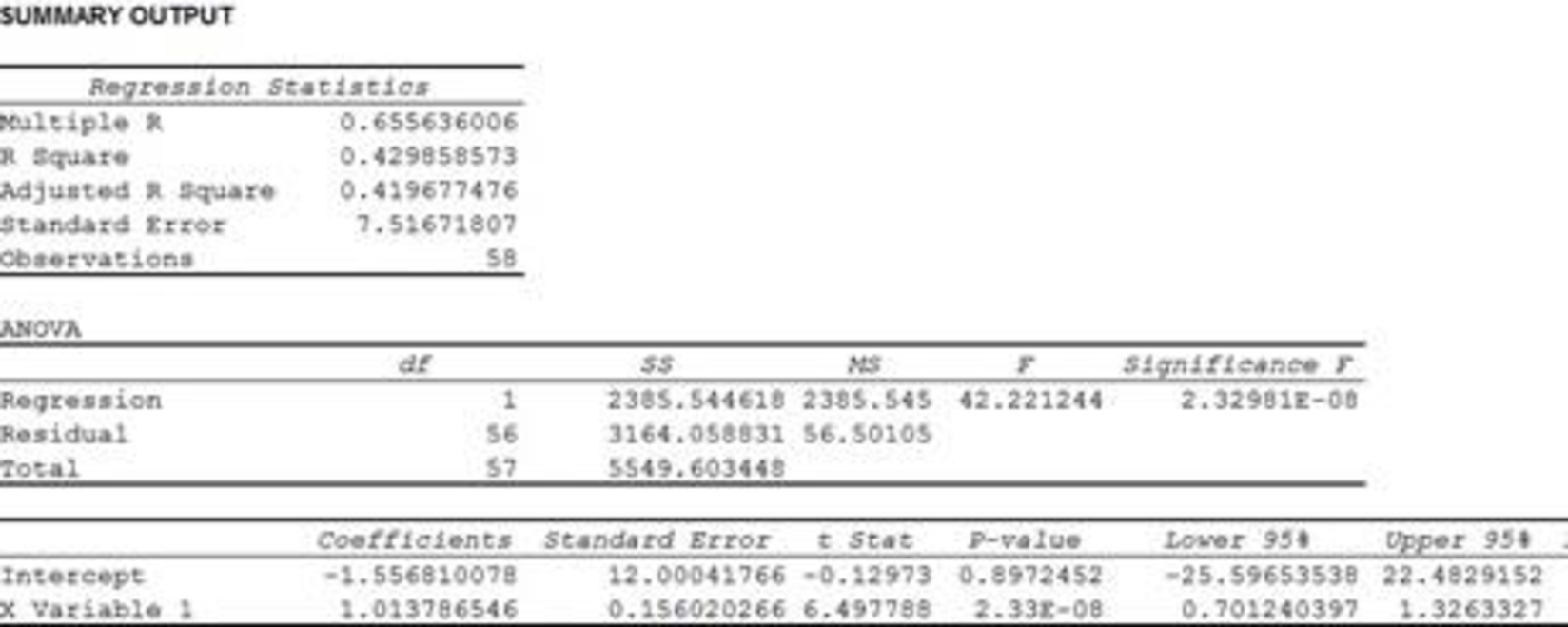
Thus, the R-squared value is 0.429.
The coefficient of determination (
The
b.
Interpret the p-value for the F statistic.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
For the F-test of the slope the p-value is 0.000.
Decision rule:
If
If
It is assumed that the level of significance is 0.05.
Conclusion:
Here the p-value is less than the level of significance.
That is,
Hence, by the decision rule, reject the null hypothesis.
Therefore, it can be concluded that there is not sufficient evidence to support that the slope is zero.
Hence, the linear model provides significant fit.
c.
Check whether the model’s fit is good enough to be of practical value.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Now, a hypothesis test is needed to check the whether the model provides good fit or not.
Decision rule:
If
If
Critical value:
From the output it is observed that, the sample size is,
The degrees of freedom is,
Thus, the degrees of freedom is56.
For two tailed test, the critical value for t-test will be,
It is assumed that the level of significance,
Procedure for critical-value using EXCEL:
Software Procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain critical-value using EXCEL software is as follows:
- • Open an EXCEL file.
- • In cell A1, enter the formula “=F.INV.RT(0.05,1,56)”
- Output using EXCEL software is given below:
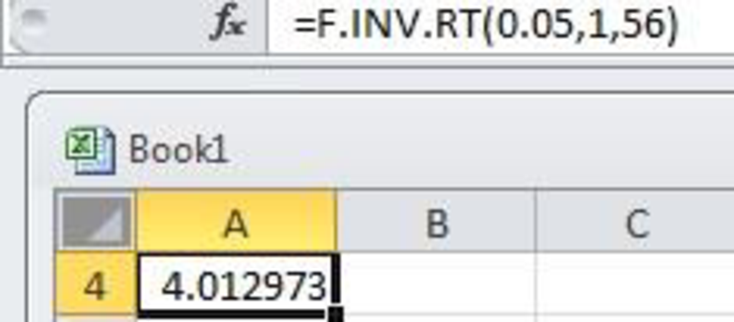
Hence, the critical value will be 4.013.
From the output in part (a), the F-statistic value is 42.22.
The level of significance is 0.05.
Conclusion:
Here the F-statistics is greater than the critical value.
That is,
Hence, by the decision rule, reject the null hypothesis.
Therefore, it can be concluded that there is not sufficient evidence to support that the slope is zero.
Hence, linear model provides significant fit.
The coefficient of determination (
Thus, using
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
APPLIED STAT.IN BUS.+ECON.-W/ACCESS
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





