
Concept explainers
Mass of the object suspended from left end
Answer to Problem 59P
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Length of the rigid beam,
Spring constant,
At equilibrium, beam makes an angle
Height of post
Formula Used:
For translational and
Calculation:
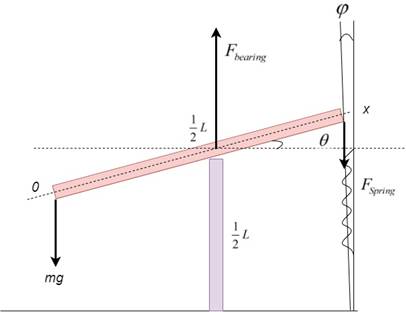
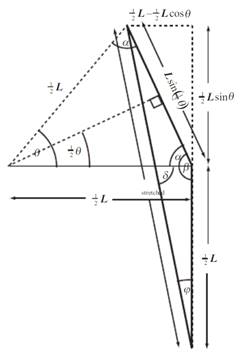
From Hooke’s law
Equation
From figure
Substitute the value of
From figure:
Apply the law of cosines to the triangle
From equation
From
Substitute the values and solve:
Conclusion:
Mass of the object is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Vol. 3
- In Fig. 12-31 show that, if the ball is to swing completely around the fixed peg, then d > 3L/5. (Hint: The ball must be moving at the top of its swing; otherwise the string will collapse.)arrow_forwardA uniform stick AB can be balanced on a knife edge 10 cm from one end when a weight of 200N is hung from that end. When the knife edge is removed 5cm further from that end, the 200 N weight has to be moved to a point 8.75 cm from the knife edge to obtain a balance. Find the length of the stick and it's weight.arrow_forwardA uniform ladder of length L, rests against a smooth, vertical wall. If the mass of the ladder is m and the coefficient of static friction between the ladder and the groundis μs = 0.40, find the minimum angle θmin at the ladder does not slip?arrow_forward
- A uniform log of length L is incline 30 ͦ from the horizontal when supported by a frictionless rock located 0.6Lfrom its left end. The mass of the log is 200 kg. an engineer with a mass of 53.5 kg walks along the log from theleft to the right until the log is balanced horizontally. How far from the left end of the log is the engineer when thelog is horizontal?arrow_forwardDuring a dunk, a basketball player will elevate theircenter of mass 70 cm (or more) while jumping off of one leg. What is the strain energy contribution to the energy required to elevate the center of mass given the following parameters? How much energy has to be contributed by active muscle contraction? mass = 82 kg, K leg = 35000N/m, dispacement = 0.11 m.arrow_forwardThe figure shows three boards clamped together. The center board weighs 93.5 N, and the coefficient of static friction between the boards is 0.490. What is the minimum magnitude of the horizontal compression forces (in N) acting on either side of the center board so it does not slip?arrow_forward
- The left-hand end of a uniform rod of mass 2.00 kgkg and length 1.10 mm is attached to a vertical wall by a frictionless hinge. The rod is held in a horizontal position by an aluminum wire that runs between the right-hand end of the rod and a point on the wall that is above the hinge. The cross-sectional radius of the wire is 2.50 mmmm, and the wire makes an angle of 30.0∘∘ with the rod. What is the length of the wire? Express your answer with the appropriate units. An object of mass 90.0 kgkg is suspended from the right-hand end of the rod. What is the increase in the length of the wire when this object is added? Express your answer with the appropriate units. In your analysis do you need to be concerned that the lengthening of the wire means that the rod is no longer horizontal?arrow_forwarda solid uniform ball with mass m and diameter d is supported against a vertical frictionless wall by a thin massless wire of length l find the tension in the wire?arrow_forwardA uniform 8.00 m, 1500 kg beat is hinged to a wall and supported by a thin cable attached 2.00 m from the free end of the beam. The beam is fixed to the wall by a hinge at an angle of 30.0 degrees above the horizontal. The angle between the cable and the beam is 40 degrees. What is the angle between the tension in the cable and the horizontal. (Hint angles in a triangle add to 180 degrees) -10 degrees -30 degrees -15 degrees -20 degreesarrow_forward
- The column is built up by gluing the two identical boards together. If the wood has an allowable normal stress of σallowσallowx = 5.6 MPaMPa , determine the maximum allowable eccentric force PP that can be applied to the column.arrow_forwardA uniform board is suspended from a ceiling and supported horizontally by two wires, A and B. The board is 2.0 m long and has a mass of 25 kg. What is the tension in each of the two wires when a sign of 35 kg is hung on the board a distance of 0.50 m from one end?arrow_forwardA uniform slender rod of length L = 36 in. and weight W = 4 lb hangs freely from a hinge at A. If a force P of magnitude 1.5 lb is applied at B horizontally to the left (h = L), determine (a) the angular acceleration of the rod, (b) the components of the reaction at A.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

