
Concept explainers
Polar amino acids can be classified as acidic, basic, or neutral.
- a. Draw an example of a possible amino acid for each of the three types of polar amino acid.
- b. For each example, determine if the side chain can make hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, or both.
- c. Describe each category in more detail. What
functional groups would you expect in the side chains?
(a)
Interpretation: The examples for each of the three types of polar amino acid have to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Amino acids:
Amino acids are the basic functional units of proteins. Amino acids form peptide bonds between them and the large numbers of peptides form the protein. So, amino acids are the basic monomeric units of the proteins which are biopolymers.
General structure of an amino acid can be drawn as shown here:
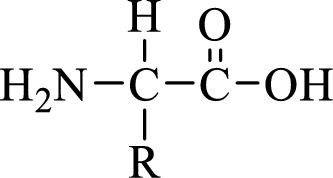
In amino acids, there are two major functional groups such as amine and carboxylic acid functional groups along with a side chain
Explanation of Solution
Polar amino acids are those which have polarity in there
There are three types of polar amino acids such as acidic, basic and neutral amino acids.
An example for the acidic amino acid is glutamic acid and its structure is drawn here:
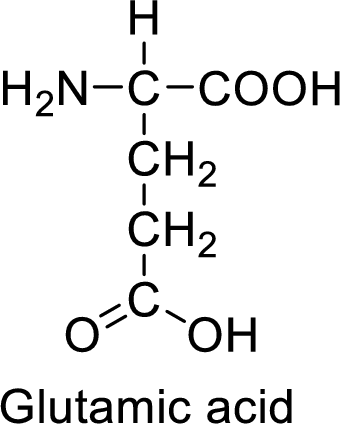
The side of glutamic acid has a carboxylic acid functional group which is a polar
An example for the basic amino acid is lysine and its structure is drawn here:
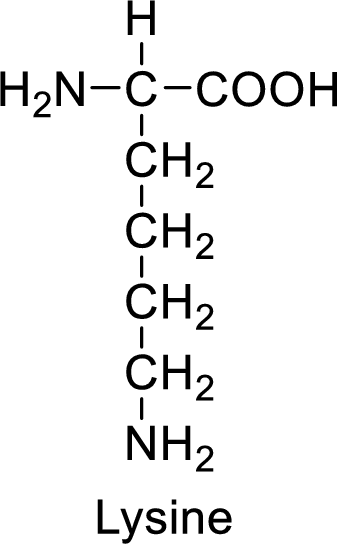
The side of lysine has an amine functional group which is a polar
An example for the neutral amino acid is serine and its structure is drawn here:
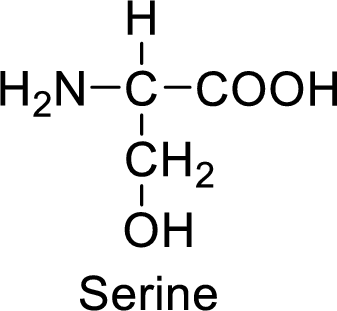
The side of serine has a hydroxyl functional group which is a polar
(b)
Interpretation: For each example in the subpart (a), determine whether the side chain can make hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds or both.
Concept Introduction:
Amino acids:
Amino acids are the basic functional units of proteins. Amino acids form peptide bonds between them and the large numbers of peptides form the protein. So, amino acids are the basic monomeric units of the proteins which are biopolymers.
General structure of an amino acid can be drawn as shown here:
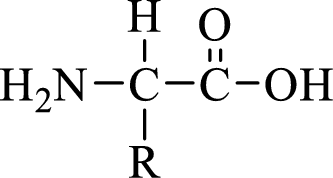
In amino acids, there are two major functional groups such as amine and carboxylic acid functional groups along with a side chain
Hydrogen bonding:
- • Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole interaction in a polar bond which has hydrogen atom and a highly electronegative atom such as Nitrogen, Oxygen and Fluorine.
- • Hydrogen bonding can also be defined as coulombic attraction between the hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom.
Ionic bonds are formed by complete transfer of one or more electrons to the other atom, thereby the bonded atoms acquire opposite charges to each other, so the ionic bond is formed due to the electrostatically attraction between these opposite charged atoms.
Explanation of Solution
An example for the acidic amino acid is glutamic acid and its structure is drawn here:
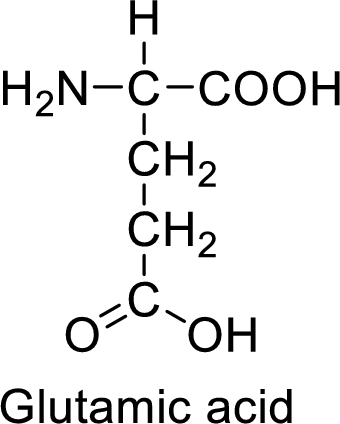
The side chain in the glutamic acid has carboxylic acid functional group which can make hydrogen bonding. The acidic amino acids like glutamic acid also form ionic bonds due to the polarity in the structure.
An example for the basic amino acid is lysine and its structure is drawn here:
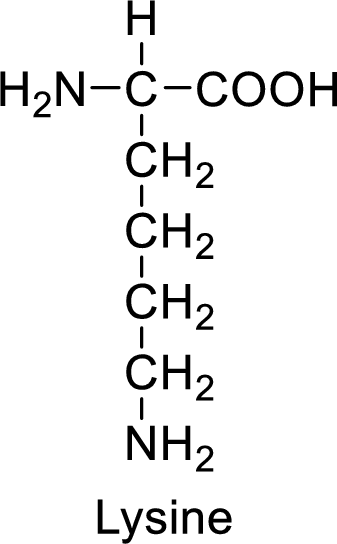
The side chain in the lysine has amine functional group which can make hydrogen bonding. The basic amino acids like lysine also form ionic bonds due to the polarity in the structure.
An example for the polar neutral amino acid is serine and its structure is drawn here:
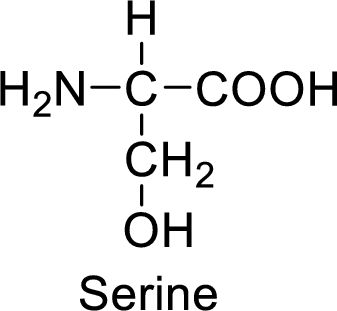
The side chain in the serine has hydroxyl functional group which can make hydrogen bonding. The neutral amino acids like serine do not form ionic bonds due to the lack of polarity in the structure.
(c)
Interpretation:
- • Each of the categories of amino acids has to be described in more detail.
- • The expected functional groups in the side chains have to be found.
Concept Introduction:
Amino acids:
Amino acids are the basic functional units of proteins. Amino acids form peptide bonds between them and the large numbers of peptides form the protein. So, amino acids are the basic monomeric units of the proteins which are biopolymers.
General structure of an amino acid can be drawn as shown here:
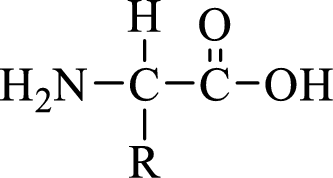
In amino acids, there are two major functional groups such as amine and carboxylic acid functional groups along with a side chain
Explanation of Solution
Polar amino acids are those which have polarity in their
All polar amino acids have the same general structure with the only difference in the
There are three types of polar amino acids such as acidic, basic and neutral amino acids.
Acidic amino acids:
Acidic amino acids have acidic functional groups such as carboxylic acids in the
An example for the acidic amino acid is glutamic acid and its structure is drawn here:
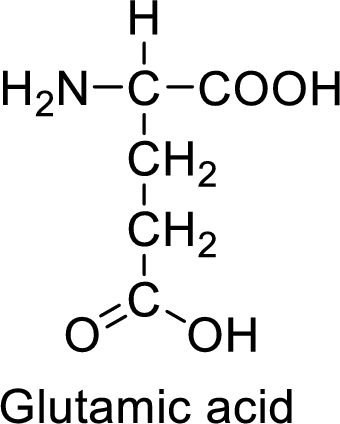
The side of glutamic acid has a carboxylic acid functional group which is a polar
Basic amino acids:
Basic amino acids have basic functional groups such as amine in the
An example for the basic amino acid is lysine and its structure is drawn here:
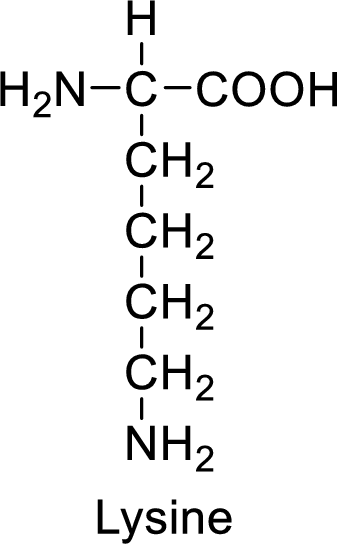
The side of lysine has an amine functional group which is a polar
Neutral amino acids:
Neutral amino acids have neutral functional groups such as amide and hydroxyl groups in the
An example for the neutral amino acid is serine and its structure is drawn here:
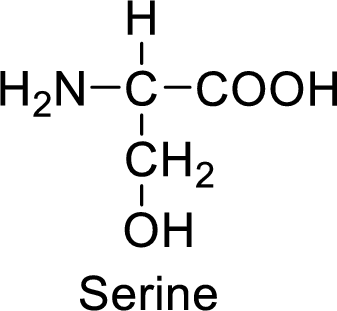
The side of serine has a hydroxyl functional group which is a polar
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Chemistry In Context
- Draw a segment of the backbone of a protein that is long enough for three peptide linkages to be present.arrow_forward(a) How many tripeptides can be made from glycine, alanine, and leucine, using each amino acid only once per tripeptide? (b) Write the structural formulas of these tripeptides and name them in the shorthand abbreviation used for showing amino acid sequences.arrow_forwardWhy is the phrase unstructured segment of a protein somewhat of a misnomer?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





