
Alpha Communications, Inc., which produces telecommunications equipment in the United States, has a very strong local market for its circuit board. The variable production cost is $130, and the company can sell its entire supply domestically for $170. The U.S. lax rate is 40 percent.
Alternatively, Alpha can ship the circuit board to its division in Germany, to be used in a product that the German division will distribute throughout Europe. Information about the German product and the division’s operating environment follows.
Selling price of final product: $360
Shipping fees to import circuit board: $20
Labor, overhead, and additional material costs of final product: $115
Import duties levied on circuit board (to be paid by the German division): 10% of transfer price German tax rate: 60%
Assume that U.S. and German tax authorities allow a transfer price for the circuit board set at either U.S. variable
Required:
- 1. Compute overall company profitability per unit if all units are transferred and U.S. variable manufacturing cost is used as the transfer price. Show separate calculations for the U.S. operation and the German division.
- 2. Repeat requirement (1), assuming the use of the U.S. market price as the transfer price. Which of the two transfer prices is better for the firm?
- 3. Assume that the German division can obtain the circuit board in Germany for $155.
- a. If you were the head of the German division, would you rather do business with your U.S. division or buy the circuit board locally? Why?
- b. Rather than proceed with the transfer, is it in the best interest of Alpha to sell its goods domestically and allow the German division to acquire the circuit board in Germany? Why? Show computations to support your answer.
- 4. Generally speaking, when tax rates differ between countries, what strategy should a company use in setting its transfer prices?
- 5. Build a spreadsheet: Construct an Excel spreadsheet to solve requirements (1) and (2) above. Show how the solution will change if the following information changes: the U.S. tax rate is 35 percent, the German tax rate is 55 percent, and the import duties are 8 percent of the transfer price.
1.
Calculate the overall profitability per unit of company A and show separate calculation for U.S. operation and German operation.
Explanation of Solution
Return on investment (ROI): Return on investment evaluates how efficiently the assets are used in earning income from operations. So, ROI is a tool used to measure and compare the performance of a units or divisions or a companies.
Calculate the overall profitability per unit of company A and show separate calculation for U.S. operation and German operation as follows:
Profitability per unit of U. S. Operation:
| Particulars | $ per unit |
| Sales revenue | $130.00 |
| Less: Variable cost | $130.00 |
| Contribution margin | $0 |
Table (1)
Profitability per unit of German Operation:
| Particulars | $ per unit | $ per unit |
| Sales revenue | $360.00 | |
| Less: Transfer price | $130.00 | |
| Shipping fees | $20.00 | |
| Additional processing costs | $115.00 | |
| Import duties | $13.00 | $278.00 |
| Income before tax | $82.00 | |
| Less: Income tax expense | $49.20 | |
| Income after tax | $32.80 |
Table (2)
Overall profitability per unit of company A:
2.
Calculate the overall profitability per unit of company A and show separate calculation for U.S. operation and German operation if company uses the U.S market price as the transfer price. Indicate the transfer price which is best for the firm.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the overall profitability per unit of company A and show separate calculation for U.S. operation and German operation if company uses the U.S market price as the transfer price as follows:
Profitability per unit of U. S. Operation:
| Particulars | $ per unit |
| Sales revenue | $170.00 |
| Less: Variable cost | $130.00 |
| Income before tax | $40.00 |
| Less: Income tax expense | $16.00 |
| Income after tax | $24.00 |
Table (3)
Profitability per unit of German Operation:
| Particulars | $ per unit | $ per unit |
| Sales revenue | $360.00 | |
| Less: Transfer price | $170.00 | |
| Shipping fees | $20.00 | |
| Additional processing costs | $115.00 | |
| Import duties | $13.00 | $322.00 |
| Income before tax | $38.00 | |
| Less: Income tax expense | $22.80 | |
| Income after tax | $15.20 |
Table (4)
Overall profitability per unit of company A:
In this case, U.S. market price is better for the firm because it provides higher profitability ($39.20) than the U.S. variable manufacturing cost ($32.80).
3. a.
Explain whether the company can do business with U.S. division or buy the circuit board locally if the German division can obtain the circuit board for $155.
Explanation of Solution
When the circuit board can be obtained locally for $155, it is difficult to get excited to do business, because the cost of local circuit board ($155) is less than the cost of German division circuit board
3. b.
Explain whether company A can make circuit board or not if company does not have any transfer price and show necessary calculations.
Explanation of Solution
Explain whether company A can make circuit board or not if company does not have any transfer price and show necessary calculations as follows:
Profitability per unit of U. S. Operation:
| Particulars | $ per unit |
| Sales revenue | $170.00 |
| Less: Variable cost | $130.00 |
| Income before tax | $40.00 |
| Less: Income tax expense | $16.00 |
| Income after tax | $24.00 |
Table (5)
Profitability per unit of German Operation:
| Particulars | $ per unit | $ per unit |
| Sales revenue | $360.00 | |
| Less: Transfer price | $155.00 | |
| Additional processing costs | $115.00 | $270.00 |
| Income before tax | $90.00 | |
| Less: Income tax expense | $54.00 | |
| Income after tax | $36.00 |
Table (6)
Overall profitability per unit of company A:
Yes, Company A will make circuit board and sold in U.S. when the company does not have any transfer price, because the overall profitability without transfer price ($60 per unit) is more than the overall profitability with transfer price ($39.20 per unit).
4.
Explain the strategy that should a company use in setting the transfer prices when the tax rates differ between countries.
Explanation of Solution
In this case, the company should try to generate less income in high tax rate countries and high income in low tax rate countries when the tax rates differ. It is a best strategy to avoid more taxes in setting the transfer prices.
5.
Prepare a spreadsheet and solve the requirement (1) and (2) if the U.S. tax rate is 35% and German tax rate is 55%.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a spreadsheet and solve the requirement (1) and (2) if the U.S. tax rate is 35% and German tax rate is 55% as follows:
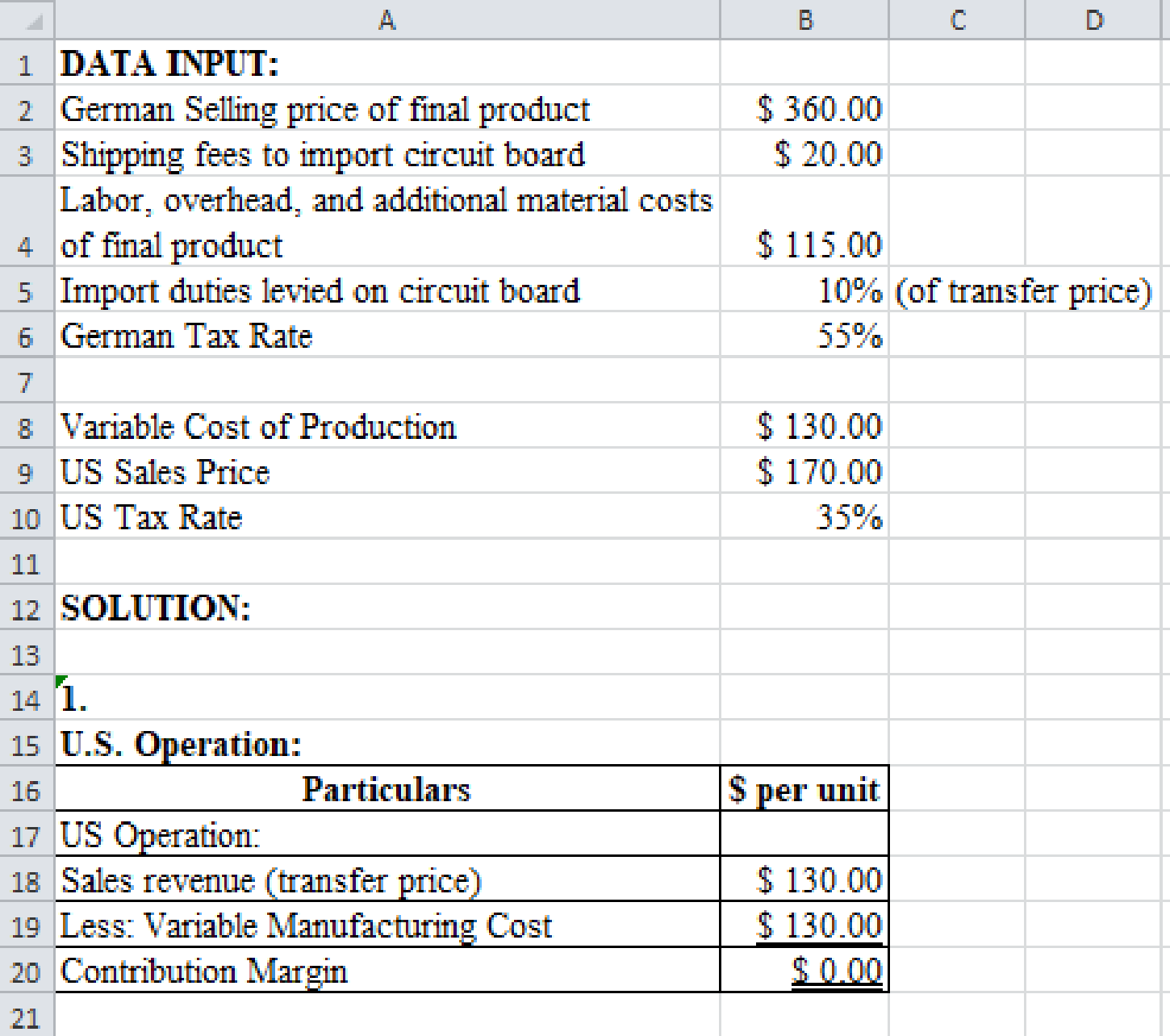
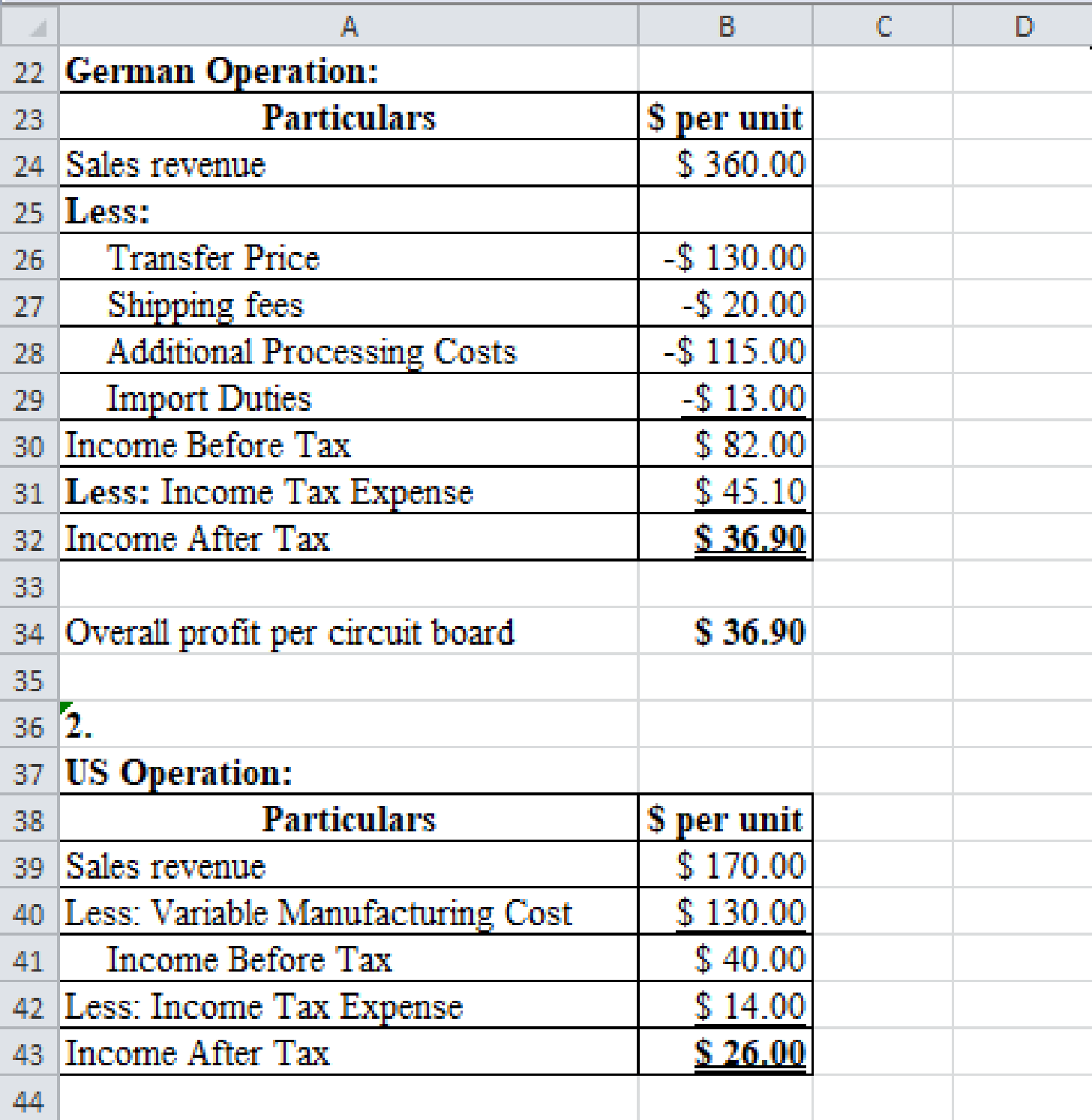
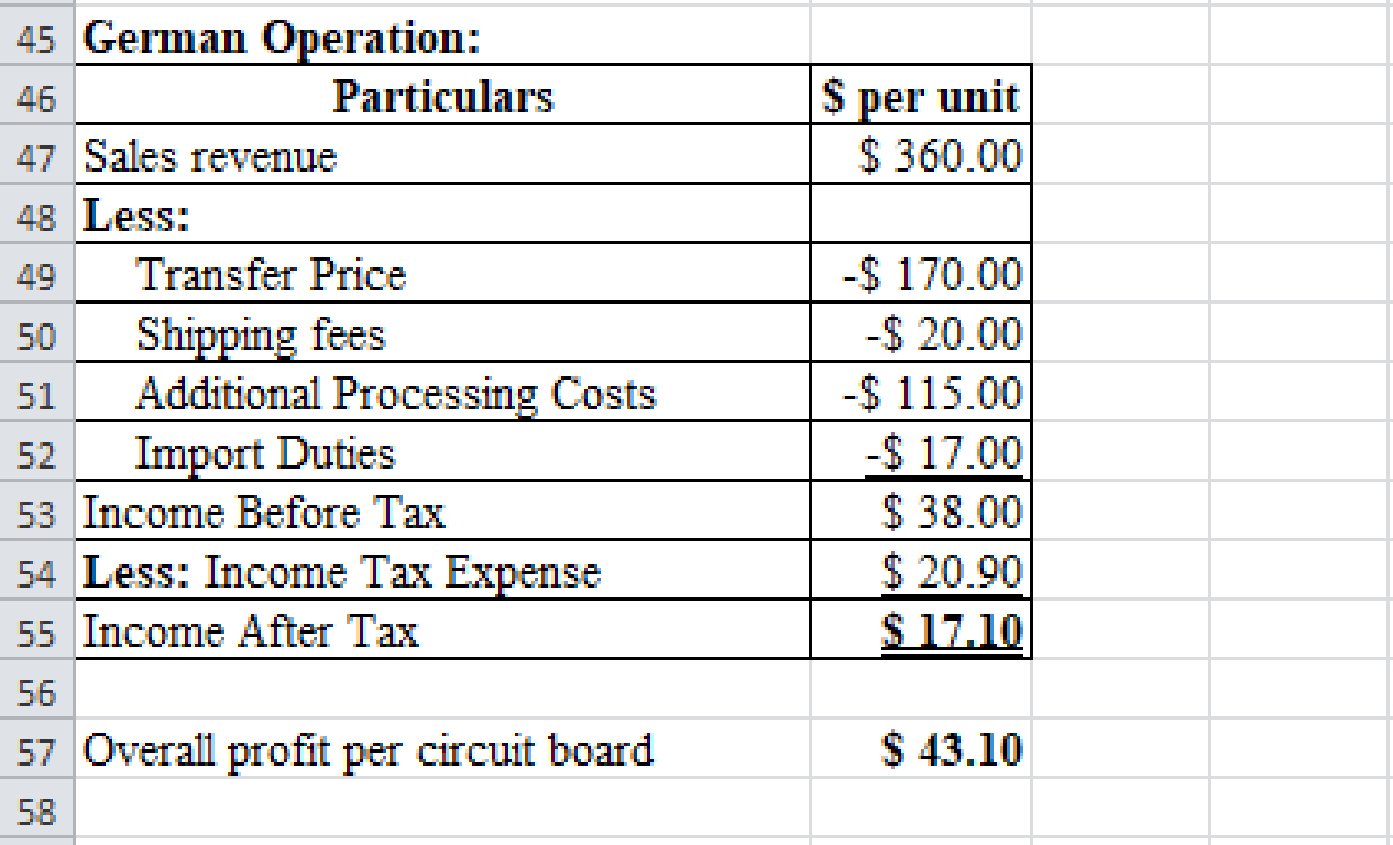
Figure (1)
Excel workings:
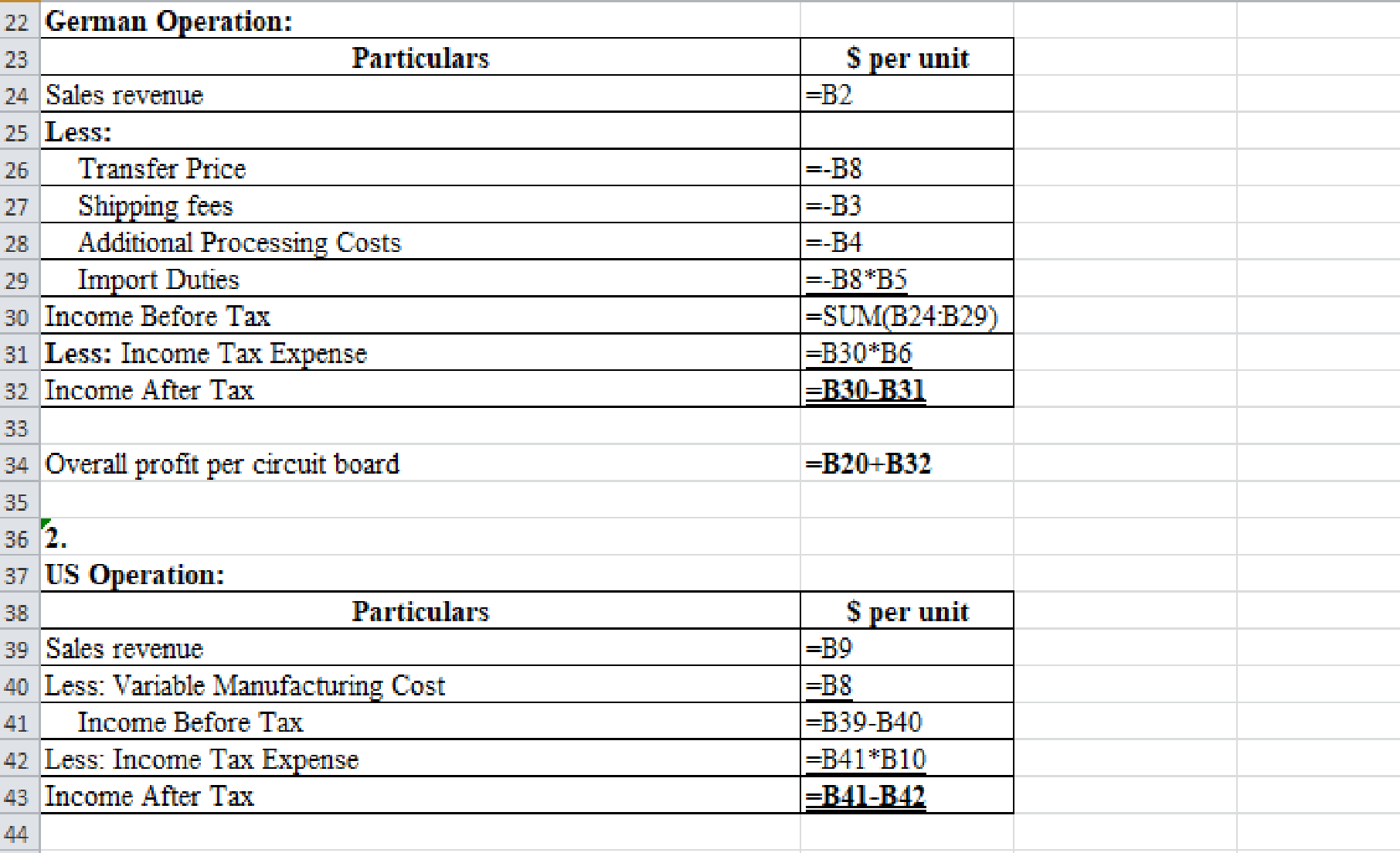
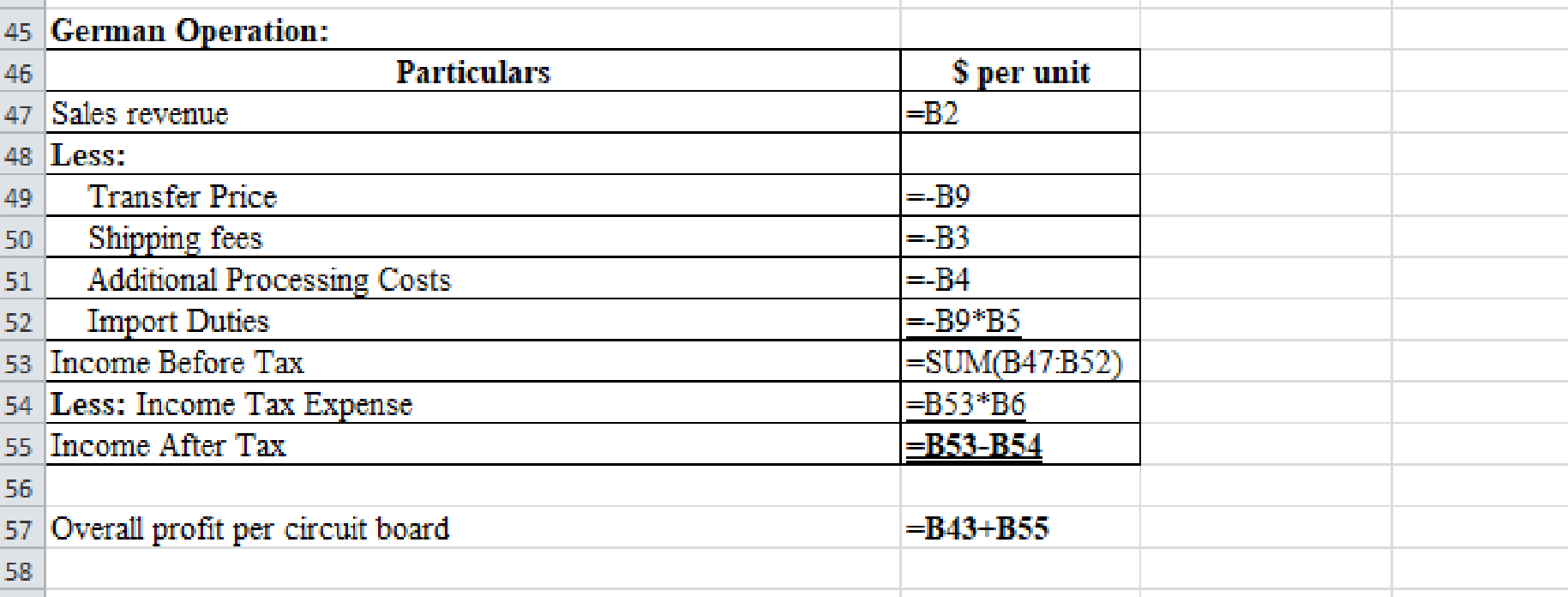
Figure (2)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Loose-Leaf for Managerial Accounting: Creating Value in a Dynamic Business Environment
- Mossfort, Inc., has a division in Canada that makes long-lasting exterior wood stain. Mossfort has another U.S. division, the Retail Division, that operates a chain of home improvement stores. The Retail Division would like to buy the unique, long-lasting wood stain from the Canadian division, since this type of stain is not currently available. The Exterior Stain Division incurs manufacturing costs of 13.45 for one gallon of stain. If the Retail Division purchases the stain from the Canadian division, the shipping costs will be 1.40 per gallon, but sales commissions of 0.75 per gallon will be avoided with an internal transfer. The Retail Division plans to sell the stain for 32.80 per gallon. Normally, the Retail Division earns a gross margin of 35 percent above cost of goods sold. Required: 1. Which Section 482 method should be used to calculate the allowable transfer price? 2. Calculate the appropriate transfer price per gallon. (Round to the nearest cent.)arrow_forwardGlobal Reach, Inc., is considering opening a new warehouse to serve the Southwest region. Darnell Moore, controller for Global Reach, has been reading about the advantages of foreign trade zones. He wonders if locating in one would be of benefit to his company, which imports about 90 percent of its merchandise (e.g., chess sets from the Philippines, jewelry from Thailand, pottery from Mexico, etc.). Darnell estimates that the new warehouse will store imported merchandise costing about 16.78 million per year. Inventory shrinkage at the warehouse (due to breakage and mishandling) is about 8 percent of the total. The average tariff rate on these imports is 5.5 percent. Required: 1. If Global Reach locates the warehouse in a foreign trade zone, how much will be saved in tariffs? Why? (Round your answer to the nearest dollar.) 2. Suppose that, on average, the merchandise stays in a Global Reach warehouse for nine months before shipment to retailers. Carrying cost for Global Reach is 6 percent per year. If Global Reach locates the warehouse in a foreign trade zone, how much will be saved in carrying costs? What will the total tariff-related savings be? (Round your answers to the nearest dollar.) 3. Suppose that the shifting economic situation leads to a new tariff rate of 13 percent, and a new carrying cost of 6.5 percent per year. To combat these increases, Global Reach has instituted a total quality program emphasizing reducing shrinkage. The new shrinkage rate is 7 percent. Given this new information, if Global Reach locates the warehouse in a foreign trade zone, how much will be saved in carrying costs? What will the total tariff-related savings be? (Round your answers to the nearest dollar.)arrow_forwardPaterson Company, a U.S.-based company, manufactures and sells electronic components worldwide. Virtually all its manufacturing takes place in the United States. The company has marketing divisions throughout Europe, including France. Debbie Kishimoto, manager of this division, was hired from a competitor 3 years ago. Debbie, recently informed of a price increase in one of the major product lines, requested a meeting with Jeff Phillips, marketing vice president. Their conversation follows. Debbie: Jeff, I simply dont understand why the price of our main product has increased from 5.00 to 5.50 per unit. We negotiated an agreement earlier in the year with our manufacturing division in Philadelphia for a price of 5.00 for the entire year. I called the manager of that division. He said that the original price was still acceptablethat the increase was a directive from headquarters. Thats why I wanted to meet with you. I need some explanations. When I was hired, I was told that pricing decisions were made by the divisions. This directive interferes with this decentralized philosophy and will lower my divisions profits. Given current market conditions, there is no way we can pass on the cost increase. Profits for my division will drop at least 600,000 if this price is maintained. I think a midyear increase of this magnitude is unfair to my division. Jeff: Under normal operating conditions, headquarters would not interfere with divisional decisions. But as a company, we are having some problems. What you just told me is exactly why the price of your product has been increased. We want the profits of all our European marketing divisions to drop. Debbie: What do you mean that you want the profits to drop? That doesnt make any sense. Arent we in business to make money? Jeff: Debbie, what you lack is corporate perspective. We are in business to make money, and thats why we want European profits to decrease. Our U.S. divisions are not doing well this year. Projections show significant losses. At the same time, projections for European operations show good profitability. By increasing the cost of key products transferred to Europeto your division, for examplewe increase revenues and profits in the United States. By decreasing your profits, we avoid paying taxes in France. With losses on other U.S. operations to offset the corresponding increase in domestic profits, we avoid paying taxes in the United States as well. The net effect is a much-needed increase in our cash flow. Besides, you know how hard it is in some of these European countries to transfer out capital. This is a clean way of doing it. Debbie: Im not so sure that its clean. I cant imagine the tax laws permitting this type of scheme. There is another problem, too. You know that the companys bonus plans are tied to a divisions profits. This plan could cost all of the European managers a lot of money. Jeff: Debbie, you have no reason to worry about the effect on your bonusor on our evaluation of your performance. Corporate management has already taken steps to ensure no loss of compensation. The plan is to compute what income would have been if the old price had prevailed and base bonuses on that figure. Ill meet with the other divisional managers and explain the situation to them as well. Debbie: The bonus adjustment seems fair, although I wonder if the reasons for the drop in profits will be remembered in a couple of years when Im being considered for promotion. Anyway, I still have some strong ethical concerns about this. How does this scheme relate to the tax laws? Jeff: We will be in technical compliance with the tax laws. In the United States, Section 482 of the Internal Revenue Code governs this type of transaction. The key to this law, as well as most European laws, is evidence of an arms-length price. Since youre a distributor, we can use the resale price method to determine such a price. Essentially, the arms-length price for the transferred good is backed into by starting with the price at which you sell the product and then adjusting that price for the markup and other legitimate differences, such as tariffs and transportation. Debbie: If I were a French tax auditor, I would wonder why the markup dropped from last year to this year. Are we being good citizens and meeting the fiscal responsibilities imposed on us by each country in which we operate? Jeff: Well, a French tax auditor might wonder about the drop in markup. But, the markup is still within reason, and we can make a good argument for increased costs. In fact, weve already instructed the managers of our manufacturing divisions to legitimately reassign as many costs as they can to the European product lines. So far, they have been very successful. I think our records will support the increase that you are receiving. You really do not need to be concerned with the tax authorities. Our tax department assures me that this has been carefully researchedits unlikely that a tax audit will create any difficulties. Itll all be legal and above board. Weve done this several times in the past with total success. Required: 1. Do you think that the tax-minimization scheme described to Debbie Kishimoto is in harmony with the ethical behavior that should be displayed by top corporate executives? Why or why not? What would you do if you were Debbie? 2. Apparently, the tax department of Paterson Company has been strongly involved in developing the tax-minimization scheme. Assume that the accountants responsible for the decision are CMAs and members of the IMA, subject to the IMA standards of ethical conduct. Review the IMA standards for ethical conduct in Chapter 1. Are any of these standards being violated by the accountants in Patersons tax department? If so, identify them. What should these tax accountants do if requested to develop a questionable taxminimization scheme?arrow_forward
- Embraer of Brazil is one of the two leading global manufacturers of regional jets (Bombbardler of Canada is the other). Regional jets are smaller than the traditional civilian airliners produced by Airbus and Boeing, seating between 50 and 100 people on average. Embraer has concluded an agreement with a regional U S airline to produce and deliver four aircraft one year from now for $78 Million. Although Embraer will be paid in U.S. Dollars. It also possesses a currency exposure of inputs- it must pay foreign suppliers $15 million for inputsone year from now (but they will be delivering the subcomponents throughtout the year). The cuurent spot rate on the Brazilian real (R$) is R$1.87/$, but it has been steadily appreciating against the US dollar over the past three years. Forward contracts are difficult to acquire and are considered expensive. Citibank Brasil has not explicity provided Embraer a forward rate quote, but has stated that it will probably be pricing a forward off the…arrow_forwardDavao has a potential foreign customer that has offered to buy 1,500 tons at P450 per ton. Assume that all of Davao’s costs would be at the same levels and rates as last year. What net income after taxes would Davao make if it took this order and rejected some business from regular customers so as not to exceed capacity? Without prejudice to your answers to previous questions, and assume that Davao plans to market its product in a new territory. Davao estimates that an advertising and promotion program costing P61,500 annually would need to be undertaken for the next two or three years. In addition, a P25 per ton sales commission over and above the current commission to the sales force in the new territory would be required. How many tons would have to be sold in the new territory to maintain Davao’s current after-tax income of P94,500? If the sales volume is estimated to be 2,100 tons in the next year, and if the prices and costs stay at the same levels and amounts next year, the…arrow_forwardNashville Co. presently incurs costs of about 12 million Australian dollars (A$) per year for research and development expenses in Australia. It sells the products that are designed each year, and all of the products sold each year are invoiced in U.S. dollars. Nashville anticipates revenue of about $20 million per year, and about half of the revenue will be from sales to customers in Australia. The Australian dollar is presently valued at $1 (1 U.S. dollar), but it fluctuates a lot over time. Nashville Co. is planning a new project that will expand its sales to other regions within the United States, and the sales will be invoiced in dollars. Nashville can finance this project with a 5-year loan by (1) borrowing only Australian dollars, or (2) borrowing only U.S. dollars, or (3) borrowing one-half of the funds from each of these sources. The 5-year interest rates on an Australian dollar loan and a U.S. dollar loan are the same. If Nashville wants to use the form of financing that will…arrow_forward
- Mama Mia Inc and Wonderful Inc are European-based companies with subsidiaries located in Kuala Lumpur. Both companies distribute chemical supplies (produced in Europe) to customers throughout Asia. Both subsidiaries purchase the products at cost and sell the products at 90 percent markup. The other operating costs of the subsidiaries are very low. Mama Mia Inc has a research and development centre in Europe that focuses on improving its medical technology. Wonderful Inc. has a similar centre based in Kuala Lumpur. The parent of each firm subsidizes its respective research and development centre on an annual basis. Which company is subject to a higher degree of economic exposure? Justify your answer with thorough explanation on both companies.arrow_forwardBillabong Fashion is based in Melbourne, Australia. Billabong Fashion has a subsidiary in Shanghai that generates RMB85 million in annual sales. Any earnings generated by the subsidiary are reinvested to support its operations. Belle Fashion is the close competitor of Billabong Fashion. Belle Fashion is a local Australian company located in Japan with annual export sale to Malaysia of about MYR 45 million. Based on the information provided, which firm is subject to a higher degree of translation exposure? Justify your answer with thorough explanation on both companies.arrow_forwardGermano Products, Incorporated, has a Pump Division that manufactures and sells a number of products, including a standard pump that could be used by another division in the company, the Pool Products Division, in one of its products. Data concerning that pump appear below: Capacity in units 70,000 Selling price to outside customers $ 77 Variable cost per unit $ 27 Fixed cost per unit (based on capacity) $ 31 The Pool Products Division is currently purchasing 16,000 of these pumps per year from an overseas supplier at a cost of $72 per pump. Assume that the Pump Division is selling all of the pumps it can produce to outside customers. Does there exist a transfer price that would make both the Pump and Pool Products Division financially better off than if the Pool Products Division were to continue buying its pumps from the outside supplier? Multiple Choice Yes, both divisions are always better off regardless of whether the selling division has enough idle…arrow_forward
- Lobby Company produces and sells its only product XT-300. The company has been approached by a new customer from the USA with an offer to purchase 15,000 units of XT-300 for $11.50 each. Selling to the US will not affect the company’s other customers, and existing sales would not be affected. Lobby normally produces 110,000 units per year but only plans to produce and sell 90,000 in the coming year. Exporting the product to the USA will require a further packaging cost of $0.30 per unit. The normal sales price is $16 per unit. Unit cost information for the normal level of activity is as follows: Direct materials $4.50 Direct labour 4.20 Variable overhead 1.65 Fixed overhead 2.00 Total $12.35 Required: A). What are the relevant costs and benefits of this special order? B). Will operating income increase or decrease if the order from this new customer is accepted – if so, by how much? C). Suppose the new customer wants to buy 25,000 units, should…arrow_forwardLobby Company produces and sells its only product XT-300. The company has been approached by a new customer from the USA with an offer to purchase 15,000 units of XT-300 for $11.50 each. Selling to the US will not affect the company’s other customers, and existing sales would not be affected. Lobby normally produces 110,000 units per year but only plans to produce and sell 90,000 in the coming year. Exporting the product to the USA will require a further packaging cost of $0.30 per unit. The normal sales price is $16 per unit. Unit cost information for the normal level of activity is as follows: Direct materials $4.50 Direct labour 4.20 Variable overhead 1.65 Fixed overhead 2.00 Total $12.35 Required: A). What are the relevant costs and benefits of this special order? B). Will operating income increase or decrease if the order from this new customer is accepted – if so, by how much?arrow_forwardKhan Ltd. has two divisions, Europe and Asia. Europe produces a ball bearing that Asia uses in its production. Europe's variable cost is $2 per unit and the fixed cost per unit is $1.50. Ball bearings sell on the open market for $6 each. If Europe has excess capacity, what would be the minimum transfer price if Asia currently is purchasing 100,000 units on the open market?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning

