
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product should be identified when
Concept Introduction:
Reaction of alkene with
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 58P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule. When addition of
Refer to the below reaction;
(b)
Interpretation:
The product should be identified when
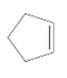 =
=
Concept Introduction:
Cyclic alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Answer to Problem 58P
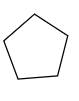
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated
Refer to the below reaction;
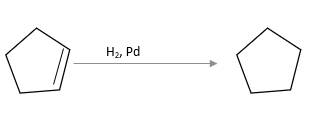
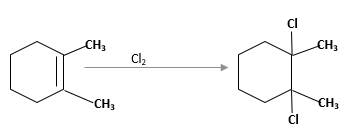
(c)
Interpretation:
The product should be identified when
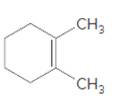 =
=
Concept Introduction:
Cyclic alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Answer to Problem 58P
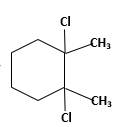
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated
(d)
Interpretation:
The product should be identified when
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Answer to Problem 58P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated
(e)
Interpretation:
The product should be identified when
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 58P
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule. When addition of
Refer to the below reaction;
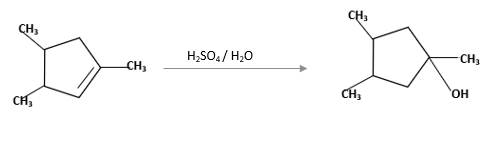
(f)
Interpretation:
The product should be identified when
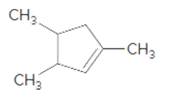 =
=
Concept Introduction:
Cyclic alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of alkene with
Hydration reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 58P
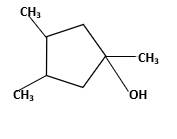
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
GENERAL ORGANIC & BIOCHEMISTRY >ACCESS<
- Calculate ∆H° for each step in this reaction CH3¬CH3 + Cl2 ¡hv CH3¬CH2Cl + HClarrow_forwardWhich reaction corresponds to the Kb for HSO4− ? a. H2SO4 ⇌ H+ + HSO4− b. SO42− + H2O ⇌ OH− + HSO4− c. HSO4− + H2O ⇌ OH− + H2SO4 d. HSO4− ⇌ H+ + SO42− e. HSO4− + OH− ⇌ H2O + SO42−arrow_forward#6r Daw a stepwise mechanism for the following reaction:arrow_forward
- (CH3)3CCH=CHCl (1)NaNH2 -----> (2)H2O Which of the following is the product for the given reaction? a) (CH3)3CCH≡CH b) (CH3)3CCH=CH2 c) (CH3)3CCH=CHOH d) (CH3)3CCH=CHNH2arrow_forwardWhen (CH3CH2)3CBr is added to CH3OH at room temperature, the major product is (CH3O)C(CH2CH3)3 and a minor product is CH3CH=C(CH2CH3)2. Propose a mechanism for the product that is formed by the substitution reaction. Use curved arrows to show the movement of electrons.arrow_forwardHi, Product the products of each reaction, H2 CO3 (aq) + LiOH (aq) ------>arrow_forward
- Which reagents are used for reaction 1? a NaN3, ethanol and NaBH4, ethanol, H3O+ b CH3CH2NH2, NaOH c NH3, NaOH d NH3, DCC Which reagent are used for reaction 2? a CH3COOH, DCC b CH3COCH3 and NaBH4, ethanol, H3O+ c CH3COH and NaBH4, ethanol, H3O+ d CH3CONH2 and CH3CH2NH2arrow_forwardDraw the products of the following reactions. Use curved arrows to show where the pair of electrons starts and where it ends up. a. ZnCl2 + CH3OH b. FeBr3 + Br c. AlCl3 + Cl−arrow_forward1. What reagents are necessary to carry out the reaction sequence shown? Determine the needed reaction to perform each conversion. Synthesis Step A B C OH A OH B Reagents Needed Type of Reactionarrow_forward
- Calculate ΔH° for each reaction. a. HO• + CH4 → •CH3 + H2O b. CH3OH + HBr → CH3Br + H2Oarrow_forwardDraw the products of each reaction and determine the direction of equilibrium. (see the Attached file)arrow_forwardThe major product formed by addition of HBr to (CH3)2C=CH– CH=C(CH3)2 is the same at low and high temperature. Draw the structure of the major product, and explain why the kinetic and thermodynamic products are the same in this reaction.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





