
Concept explainers
Three steel spheres of equal mass are suspended from the ceiling by cords of equal length that are spaced at a distance slightly greater than the diameter of the spheres. After being pulled back and released, sphere A hits sphere B, which then hits sphere C. Denoting the coefficient of restitution between the spheres by e and the velocity of A just before it hits B by v0, determine (a) the velocities of A and B immediately after the first collision, (b) the velocities of B and C immediately after the second collision. (c) Assuming now that n spheres are suspended from the ceiling and that the first sphere is pulled back and released as described here, determine the velocity of the last sphere after it is hit for the first time. (d) Use the result of part c to obtain the velocity of the last sphere when
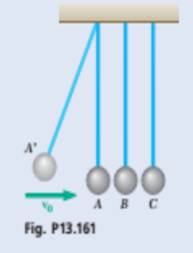
(a)
The velocities of sphere A and B immediately after the first collision.
Answer to Problem 13.161P
Explanation of Solution
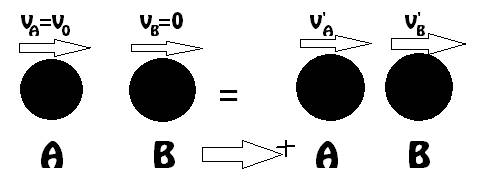
First collision between the sphere A and B :
The total momentum is conserved:
From the relation of coefficient of restitution of Relative velocities:
Solving Equations (1) and (2) simultaneously,
And, from equation (2)
Conclusion:
The velocities of sphere A and B immediately after collision is
(b)
The velocities of B and C, after the second collision.
Answer to Problem 13.161P
Explanation of Solution
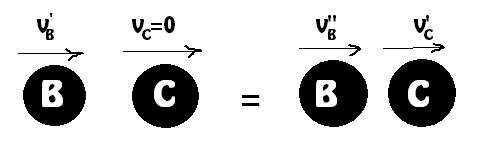
Second Collision (between sphere B and C ):
The total momentum is conserved:
Using the result from part (a) for
From the relation of coefficient of restitution of Relative velocities:
Substituting again for
Solving equations (3) and (4) simultaneously,
Substitute the value of
Again, put the value of
Conclusion:
The velocities of sphere B and C, after the second collision is
(c)
The velocity of the last sphere after it is hit for the first time if there is n number of spheres.
Answer to Problem 13.161P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
There are
Calculation:
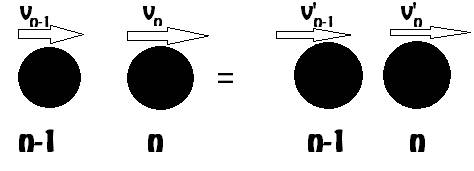
For n spheres there are (n) number of balls and
Sphere C is the 3 number of sphere and we can take the velocity of sphere C from the above part that is part (b). Thus,
Put n = 3 for
Thus, for (n) number of balls
Conclusion:
The velocity of the (n) number of sphere after it is hit for the first time is
(d)
The velocity of last sphere.
Answer to Problem 13.161P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
For
From the answer of part (c) with n=5
Conclusion:
The velocity of last sphere is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Package: Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics with 2 Semester Connect Access Card
- Two identical hockey pucks are moving on a hockey rink at the same speed of 3 m/s and in perpendicular directions when they strike each other as shown. Assuming a coefficient of restitution e= 0.9, determine the magnitude and direction of the velocity of each puck after impact.arrow_forwardAfter having been pushed by an airline employee, an empty 40-kg luggage carrier A hits with a velocity of 5 m/s an identical carrier B containing a 15-kg suitcase equipped with rollers. The impact causes the suitcase to roll into the left wall of carrier B. Knowing that the coefficient of restitution between the two carriers is 0.80 and that the coefficient of restitution between the suitcase and the wall of carrier B is 0.30, determine (a) the velocity of carrier B after the suitcase hits its wall for the first time, (b) the total energy lost in that impact.arrow_forwardPackages in an automobile parts supply house are transported to the loading dock by pushing them along on a roller track with very little friction. At the instant shown, packages B and c are at rest, and package A has a velocity of 2 m/s. Knowing that the coefficient of restitution between the packages is 0.3, determine (a) the velocity of package C after A hits B and B hits C, (b) the velocity of A after it hits B for the second time.arrow_forward
- The velocities of two steel blocks before impact are as shown. Knowing that the velocity of block B after the impact is observed to be 2.3 m/s to the right, determine the coefficient of restitution between the two blocks. The coefficient of restitution between the two blocks is ______?arrow_forwardTwo small balls A and B with masses 2m and m , respectively, are released from rest at a height h above the ground. Neglecting air resistance, which of the following statements is true when the two balls hit the ground? a. The kinetic energy of is the same as the kinetic energy of B.b. The kinetic energy of A is half the kinetic energy of B.c. The kinetic energy of A is twice the kinetic energy of B.d. The kinetic energy of A is four times the kinetic energy of B.arrow_forwardA test machine that kicks soccer balls has a 5-lb simulated foot attached to the end of a 6-ft long pendulum arm of negligible mass. Knowing that the arm is released from the horizontal position and that the coefficient of restitution between the foot and the 1-lb ball is 0.8, determine the exit velocity of the ball (a) if the ball is stationary, (b) if the ball is struck when it is rolling towards the foot with a velocity of 10 ft/s.arrow_forward
- (a). Two identical blocks A and B are at rest on a frictionless plane. Block C of the same weight hits block B with a velocity of 2.5 m/s. Knowing that the coefficient of restitution is 0.7 between block B and block C and 0.4 between block A and block B. (i) Determine the velocity of each block after all collisions have taken place. (ii) From your working in Q1(a)(i), predict whether there will be another collision after block B collides with block A? (iii) If the coefficient of restitution between block A and block B is changed to 0.7, explain with calculations whether there will be a collision between block B and block C after block B collides with block A?arrow_forwardDetermine the altitude reached by the spacecraft of Prob. 14.95 when all the fuel of its launching rocket has been consumed.Reference to Problem 14.95:A 540-kg spacecraft is mounted on top of a rocket with a mass of 19 Mg, including 17.8 Mg of fuel. Knowing that the fuel is consumed at a rate of 225 kg/s and ejected with a relative velocity of 3600 m/s, determine the maximum speed imparted to the spacecraft if the rocket is fired vertically from the ground.arrow_forwardThe two spheres shown collide. the weight of the first sphere (W1) is 40 N while that of the second is (W2) is 30N. assuming that the second sphere's velocity (v2) is 14 m/s and the first sphere's velocity (v1) is 16 m/s along the their respective angles. theta 1(θ1)=30 degrees and theta 2(θ2)=60 degrees. Assume velocities along y will be equal before and after impact. The coefficient of restitution is 0.57. A.) Determine the velocity of the 30N sphere after impact (m/s) B.) Determine the Velocity of the 40N sphere after impact (m/s) C.) Determine the angle of the velocity after impact of the 40N sphere with the horizontal (degrees) D.) Determine the angle of the velocity after impact for the 30N sphere with the vertical (degrees)arrow_forward
- A 600-g ball A is moving with a velocity of magnitude 6 m/s when it is hit as shown by a 1-kg ball B that has a velocity of magnitude 4 m/s. Knowing that the coefficient of restitution is 0.8 and assuming no friction, determine the velocity of each ball after impact.arrow_forwardTwo spheres, each of mass m, can slide freely on a frictionless, horizontal surface. Sphere A is moving at a speed v0 = 16 ft/s when it strikes sphere B which is at rest, and the impact causes sphere B to break into two pieces, each of mass m/2.a) Knowing that 0.7 s after the collision one piece reaches Point C and 1.17 s after the collision the other piece reaches Point D, determine the velocity of sphere A after the collision.b) Knowing that 0.7 s after the collision one piece reaches Point C and 1.17 s after the collision the other piece reaches Point D, determine the angle θ and the speeds of the two pieces after the collision.arrow_forwardSituation 01. A 4kg ball and 3kg ball move on a smooth plane along a straight path with speeds equivalent to 6m/s going to the right and 8 m/s going to the left, respectively a. Determine the speed of the 3kg ball after impact if the impact is elastic. b. Determine the speed of the 3kg ball after impact if the coefficient of restitution is 0.50. complete solution of impulse and momentumarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





