
Concept explainers
Block A is released from rest and slides down the frictionless surface of B until it hits a bumper on the right end of B. Block A has a mass of 10 kg and object B has a mass of 30 kg and B can roll freely on the ground. Determine the velocities of A and B immediately after impact when (a)
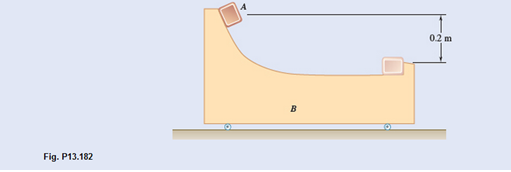
(a)
The velocities of A and B just after the impact if
Answer to Problem 13.182P
velocities of A and B just after the impact if :
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
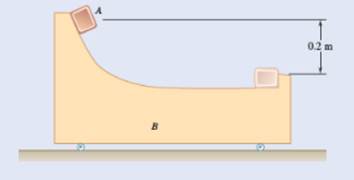
Mass of A is
Mass of B is
Conclusion:
The total linear momentum of two particles is conserved. Therefore:
The co-efficient of restitution is defined as:
The principle of conservation of energy is defined as.
When a particle moves under the action of conservation of forces. the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy of that particle remains constant.
Calculation:
Let
Apply conservation of linear momentum while block is sliding down.
Therefore.
Apply conservation of linear momentum at impact.
Therefore.
Assume.
According to conservation of energy.
The initial potential energy of A is equal to:
For B its zero.
Initial kinetic energy is zero.
And just before the impact.
Therefore, according to:
Substitute.
Therefore.
Therefore. the velocities just before the impact.
Apply co-efficient of restitution equation.
Substitute.
Therefore:
But we know that:
As a result of it:
Conclusion:
The velocities of A and B just after the impact. if
(b)
The velocities of A and B just after the impact if
Answer to Problem 13.182P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
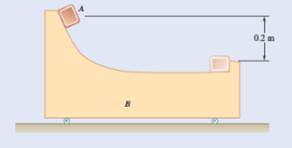
Mass of A is
Mass of B is
Conclusion:
According to sub part ‘a’ we have found.
Where.
Calculation:
Find the exact value of
For that.
Then.
But according to co-efficient of restitution equation.
Therefore.
Then.
Conclusion:
The velocities of A and B just after the impact. if
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
- 4. The 12-kg package A has a speed of 2.5 m/s when it enters the smooth ramp. As it slides down the ramp, it strikes the 34-kg package B which is initially at rest. If the coefficient of restitution between A and Bis = 0.65, determine the velocity of B just after the impact.arrow_forwardWhen the rope is at an angle of α = 35° the 0.5-kg sphere A has a speed vo = 1.5 m/s. The coefficient of restitution between A and the 0.9-kg wedge B is 0.7 and the length of rope l = 0.8 m. The spring constant has a value of 500 N/m and θ = 30°. Determine the velocities of A and B immediately after the impact.arrow_forwardBlock A of mass 5kg is moving with a velocity 5m/s. it then hit block B of mass 2kg moving at a rate of 2m/s moving in the same direction. If the coefficient of restitution between A and B is 0.2, determine the initial and final velocities of the blocksarrow_forward
- A ball of negligible size and mass m is given a velocity of v0 on the center of the cart which has a mass M and is originally at rest. If the coefficient of restitution between the ball and walls A and B is e, determine the velocity of the ball and the cart just after the ball strikes A. Also, determine the total time needed for the ball to strike A, rebound, then strike B, and rebound and then return to the center of the cart. Neglect frictionarrow_forwardDisks A and B have a mass of 6kg and 4kg, respectively. They are sliding on the smooth horizontal plane with the velocities shown. The coefficient of restitution is 0.6. a. Determine the velocity of A along the plane of contact before collision. b. Determine the velocity of A along the plane of contact after collision. c. Determine the velocity of B along the plane of contact after collision.arrow_forwardTwo identical frictionless balls have its magnitude and direction of velocities before they strike each other as shown in the figure. If the coefficient of restitution e =90. a) determine the magnitude of the velocity of ball A after the impact b) determine the direction of the velocity of ball A after the impact c) determine the magnitude of the velocity of ball B after the impact.arrow_forward
- The 4-kg masses A and B slide on the smooth horizontal bar with the velocities shown. Determine their velocities after they collide if their coefficient of restitution is e = 0.8arrow_forward: The Balls A and B are of the same size and each is attached to a 1 m cable as shown. The mass of A is 2 kg and the mass of B is 1 kg. The Ball A is released from rest with a 40o angle with the vertical direction as shown. Determine the speed of the Ball B right after the impact if the coefficient of restitution is e = 0.5. Assume the Ball B is at rest before the Ball A hits it.arrow_forwardThe 10-lb collar B is at rest, and when it is in the position shown the spring is unstretched. If another 1-lb collar A strikes it so that B slides 4 ft on the smooth rod before momentarily stopping, determine the velocity of A just after impact, and the average force exerted between A and B during the impact if the impact occurs in 0.002 s. The coefficient of restitution between A and B is e = 0.5arrow_forward
- Two identical 1350-kg automobiles A and B are at rest with their brakes released when B is struck by a 5400-kg truck C that is moving to the left at 8 km/h. A second collision then occurs when B strikes A. Assuming the first collision is perfectly plastic and the second collision is perfectly elastic, determine the velocities of the three vehicles just after the second collision.arrow_forwardDisk A and B have a mass if 6kg and 4kg respectively. They are sliding down on the smooth hoeizontal plane with the velocities shown. the coefficient of the restitution is 0.6. a. Determine the angle between velocity of A and the line of impact after collision b. Determine the angle between velocity of B and line of impact after collisionarrow_forwardThe 15-Mg tank car A and 25-Mg freight car Btravel toward each other with the velocities shown. If the coefficient of restitution between the bumpers is e = 0.6,determine the velocity of each car just after the collisionarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





