
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The alcohol should be identified as primary, secondary or tertiary alcohol.
Concept introduction:
Classification of alcohol:
Alcohols can be classified in to three types as
Primary alcohol,
Secondary alcohol,
Tertiary alcohol
Primary alcohol:
Hydroxyl group (
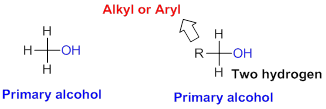
Secondary alcohol:
Hydroxyl group (
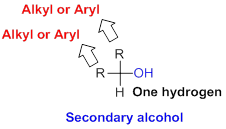
Tertiary alcohol:
Hydroxyl group (
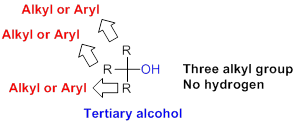
(b)
Interpretation:
The hydrophilic or hydrophobic part and solubility property in water should be identified for the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols have two different parts
- (1) Hydrophilic (water-loving),
- (2) Hydrophobic (water-fearing).
Hydrophilic (water-loving):
The compound has the hydroxyl group (

Hydrophobic (water-fearing):
The compound has alkyl chain group is called as hydrophilic.
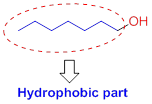
Solubility of the alcohol in water:
The solubility of the alcohol is mainly depends on the hydrophilic part as well as length of the alkyl chain. If the compound has more hydroxyl group or less number of carbon chain which is soluble in water. If the compound has hydroxyl group with more number of carbon which is insoluble in water because of hydrophobic part.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, Books a la Carte Edition; Modified Mastering Chemistry with Pearson eText -- ValuePack ... and Biological Chemistry (4th Edition)
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
