
Concept explainers
How many
a. 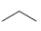 c.
c. 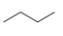 e.
e. 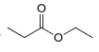 g.
g. 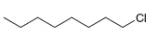
b. 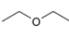 d.
d. 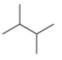 f.
f. 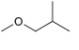 h.
h. 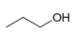
(a)
Interpretation: The number of
Concept introduction: The number of NMR signal in a compound is equal to the number of chemically non-equivalent protons present in that compound. Protons which are present in the same chemical environment that is between the same group of atoms are known as chemically equivalent protons and in
Answer to Problem 14.3P
The given compound, propane shows two signals in
Explanation of Solution
The number of signals in each compound is equal to the number of hydrogen atoms present in a different chemical environment. The given compound is propane that consists of two non-equivalent hydrogen groups. Therefore, the number of
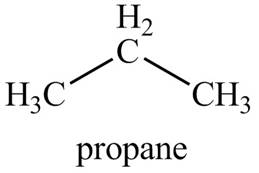
Figure 1
The given compound, propane shows two signals in
(b)
Interpretation: The number of
Concept introduction: The number of NMR signal in a compound is equal to the number of chemically non-equivalent protons present in that compound. Protons which are present in the same chemical environment that is between the same group of atoms are known as chemically equivalent protons and in
Answer to Problem 14.3P
The given compound, ethoxyethane shows two signals in
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is ethoxyethane that consists of two non-equivalent hydrogen groups. Therefore, the number of
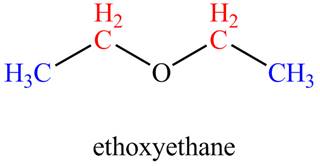
Figure 2
The given compound, ethoxyethane shows two signals in
(c)
Interpretation: The number of
Concept introduction: The number of NMR signal in a compound is equal to the number of chemically non-equivalent protons present in that compound. Protons which are present in the same chemical environment that is between the same group of atoms are known as chemically equivalent protons and in
Answer to Problem 14.3P
The given compound, butane shows two signals in
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is butane that consists of two non-equivalent hydrogen groups. Therefore, the number of
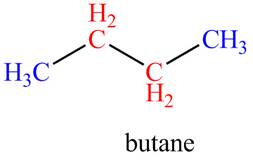
Figure 3
The given compound, butane shows two signals in
(d)
Interpretation: The number of
Concept introduction: The number of NMR signal in a compound is equal to the number of chemically non-equivalent protons present in that compound. Protons which are present in the same chemical environment that is between the same group of atoms are known as chemically equivalent protons and in
Answer to Problem 14.3P
The given compound,
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
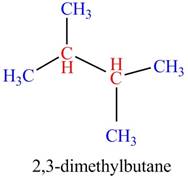
Figure 4
The given compound,
(e)
Interpretation: The number of
Concept introduction: The number of NMR signal in a compound is equal to the number of chemically non-equivalent protons present in that compound. Protons which are present in the same chemical environment that is between the same group of atoms are known as chemically equivalent protons and in
Answer to Problem 14.3P
The given compound, ethyl propanoate shows four signals in
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is ethyl propanoate that consists of four non-equivalent hydrogen groups. Therefore, the number of
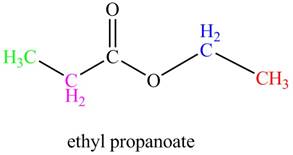
Figure 5
The given compound, ethyl propanoate shows four signals in
(f)
Interpretation: The number of
Concept introduction: The number of NMR signal in a compound is equal to the number of chemically non-equivalent protons present in that compound. Protons which are present in the same chemical environment that is between the same group of atoms are known as chemically equivalent protons and in
Answer to Problem 14.3P
The given compound,
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
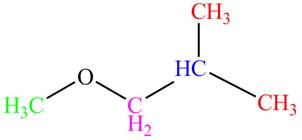
Figure 6
The given compound,
(g)
Interpretation: The number of
Concept introduction: The number of NMR signal in a compound is equal to the number of chemically non-equivalent protons present in that compound. Protons which are present in the same chemical environment that is between the same group of atoms are known as chemically equivalent protons and in
Answer to Problem 14.3P
The given compound,
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
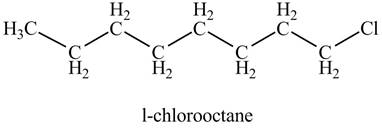
Figure 7
The given compound,
(h)
Interpretation: The number of
Concept introduction: The number of NMR signal in a compound is equal to the number of chemically non-equivalent protons present in that compound. Protons which are present in the same chemical environment that is between the same group of atoms are known as chemically equivalent protons and in
Answer to Problem 14.3P
The given compound,
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
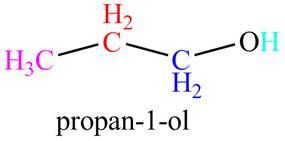
Figure 8
The given compound,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Loose Leaf for SG/Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications (11th Edition)
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry For Changing Times (14th Edition)
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- How many 1H NMR signals does each compound give?arrow_forwardExplain why the carbonyl carbon of an aldehyde or ketone absorbs farther downfield than the carbonyl carbon of an ester in a 13C NMR spectrum.arrow_forwardAn alcohol proton is deshielded as compared to a(n) __________ proton on an NMR spectrum. carboxylic acid aldehyde aromatic alkylarrow_forward
- Explain why the carbonyl carbon of an aldehyde or ketone absorbs farther downeld than the carbonyl carbon of an ester in a 13C NMR spectrum.arrow_forwardHow many 1H NMR Signals?arrow_forwardAnswer the following questions for each compound: a. How many signals are in its 13C NMR spectrum? b. Which signal is at the lowest frequency?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





