
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
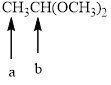
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “ a” split into doublet and “b” into quartet.
Explanation of Solution
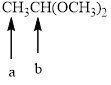
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow a and b are having nonequivalent protons. Thus methyl proton indicated by “ a” into doublet and “ b” into quartet.
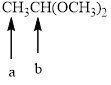
Thus in the given structure, for the indicated arrow “ a” split into doublet and “b” into quartet.
(b)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
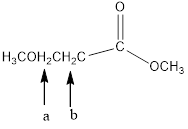
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “ a” and “b” split into doublet.
Explanation of Solution

Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow a and b are having equivalent protons. Thus proton indicated by “ a” and “b” split into doublet.

Thus in the given structure for the indicated arrow “ a” and “b” split into doublet.
(c)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
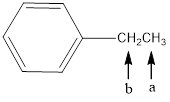
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “ a” split into triplet and “b” split into qaurtet.
Explanation of Solution

Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow a and b are having nonequivalent protons. Thus proton indicated by “ a” split into triplet and “b” split into qaurtet.

Thus in the given structure for the indicated arrow “ a” split into triplet and “b” split into qaurtet.
(d)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
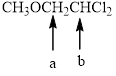
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “ a” split into doublet and “b” split into triplet.
Explanation of Solution
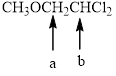
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow a and b are having nonequivalent protons. Thus proton indicated by “ a” split into doublet and “b” split into triplet.
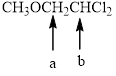
Thus in the given structure for the indicated arrow “ a” split into doublet and “b” split into triplet.
(e)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
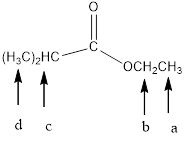
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “ a” split into triplet, “b” split into quartet,
“c” split into septet and “d” split into doublet.
Explanation of Solution
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow a, b, c and d are having nonequivalent protons. Thus proton indicated by “ a” split into triplet, “b” split into quartet, “c” split into septet and “d” split into doublet.


Thus in the given structure for the indicated arrow “ a” split into triplet, “b” split into quartet,
“c” split into septet and “d” split into doublet.
(f)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
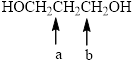
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “ a” split into quintet and “b” split into triplet.
Explanation of Solution
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow a and b are having nonequivalent protons. Thus proton indicated by “a” split into quintet and “b” split into triplet.
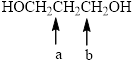
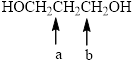
Thus in the given structure for the indicated “ a” split into quintet and “b” split into triplet.
(g)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
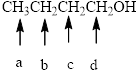
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “ a” split into triplet, “b” split into multiplet i.e it observe 5 peaks (12 peaks maximum), “c” split into multiplet i.e it observe 6 peaks (9 peaks maximum) and “d” split into triplet.
Explanation of Solution
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow protons are having nonequivalent protons. Thus proton indicated by “ a” split into triplet, “b” split into multiplet i.e it observe 5 peaks (12 peaks maximum), “c” split into multiplet i.e it observe 6 peaks (9 peaks maximum) and “d” split into triplet.
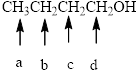
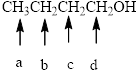
Thus in the given structure for the indicated “ a” split into triplet, “b” split into multiplet i.e it observe 5 peaks (12 peaks maximum), “c” split into multiplet i.e it observe 6 peaks (9 peaks maximum) and “d” split into triplet.
(h)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
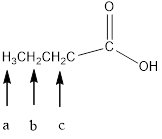
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “a” split into triplet, “b” split into multiplet i.e., it observe 6 peaks and “c” split into triplet.
Explanation of Solution
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow protons are having nonequivalent protons. Thus proton indicated by “a” split into triplet, “b” split into multiplet i.e., it observe 6 peaks and “c” split into triplet.

Thus in the given structure for the indicated “a” split into triplet, “b” split into multiplet i.e., it observe 6 peaks and “c” split into triplet.

(i)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
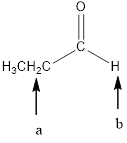
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “a” split into 8 peak (maximum) but observed singlet, “b” split into triplet.
Explanation of Solution
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow protons are having nonequivalent protons. Thus proton indicated by “a” split into 8 peak (maximum) but observed singlet, “b” split into triplet.

Thus in the given structure for the indicated “a” split into 8 peak (maximum) but observed singlet, “b” split into triplet.

(j)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
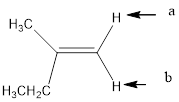
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “a” and “b” split into doublet.
Explanation of Solution
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow protons are having equivalent protons lie on the same carbon. Thus proton indicated by “a” and “b” split into doublet.
Thus in the given structure for the indicated “a” and “b” split into doublet.

(k)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
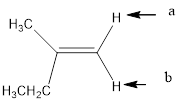
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “a” and “b” split into doublet.
Explanation of Solution
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow protons are having equivalent protons lie on the same carbon. Thus proton indicated by “a” and “b” split into doublet.
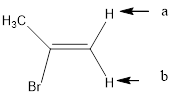
Thus in the given structure for the indicated “a” and “b” split into doublet.

(l)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
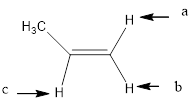
Answer to Problem 14.44P
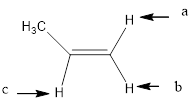
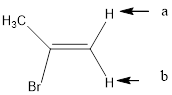
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “a” and “b” split into doublet of doublet and “c” split into maximum of 16 peaks.
Explanation of Solution
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow protons are having non-equivalent protons lie on the same carbon. Thus proton indicated by “a” and “b” split into doublet of doublet and “c” split into maximum of 16 peaks.

Thus in the given structure for the indicated “a” and “b” split into doublet of doublet and “c” split into maximum of 16 peaks.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- What is the main particularity of a MS signal for a molecule having: An adduct with sodium?arrow_forwardWhich underlined proton (or sets of protons) has the greater chemical shift (that is, the higher frequency signal)?arrow_forwarddraw fragment ion that corresponds to the Base peak in each spectra. compound given.arrow_forward
- In what ratios would the peaks of an sextet (a signal with six peaks) appear?arrow_forwardHow many peaks can you identify from the NMR spectrum? To which does each chemical shift peak corresponds?arrow_forwardHow many peaks can you identify from the NMR spectrum? To which does each chemical shift peak corresponds? Explain.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
