
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC naming of
- 1) The simplest aromatic carboxylic acid is benzoic acid.
- 2) Aromatic carboxylic acids are generally derivatives of benzoic acid.
- 3) The suffix –oic acid is used in IUPAC system and the suffix –ic acid is used in common system and is attached to the appropriate prefix.
- 4) The phenyl group is treated as substituent and the name is obtained from the appropriate alkanoic acid parent chain.
(a)
Answer to Problem 14.3PP
The structure of the given compound is,
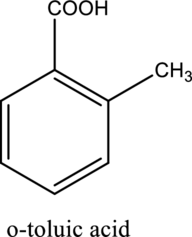
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The structure of the given compound is,
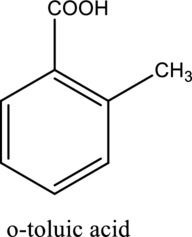
This compound is
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC naming of Aromatic Carboxylic acids
- 1) The simplest aromatic carboxylic acid is benzoic acid.
- 2) Aromatic carboxylic acids are generally derivatives of benzoic acid.
- 3) The suffix –oic acid is used in IUPAC system and the suffix –ic acid is used in common system and is attached to the appropriate prefix.
- 4) The phenyl group is treated as substituent and the name is obtained from the appropriate alkanoic acid parent chain.
(b)
Answer to Problem 14.3PP
The structure of the given compound is,
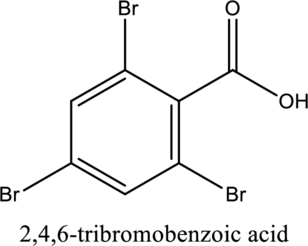
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The substituent
The structure of the given compound is,
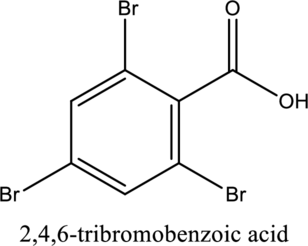
This compound is
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC naming of Aromatic Carboxylic acids
- 1) The simplest aromatic carboxylic acid is benzoic acid.
- 2) Aromatic carboxylic acids are generally derivatives of benzoic acid.
- 3) The suffix –oic acid is used in IUPAC system and the suffix –ic acid is used in common system and is attached to the appropriate prefix.
- 4) The phenyl group is treated as substituent and the name is obtained from the appropriate alkanoic acid parent chain.
(c)
Answer to Problem 14.3PP
The structure of the given compound is,
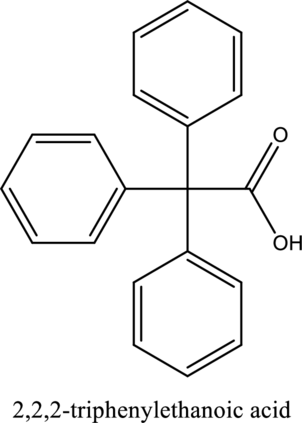
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The substituent phenyl is bonded to carbon
The structure of the given compound is,
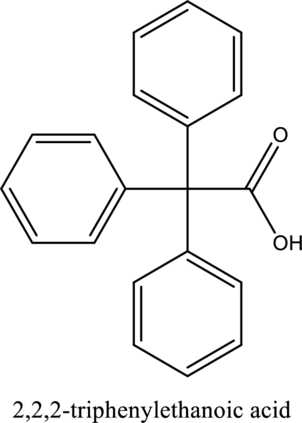
This compound is
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC naming of Aromatic Carboxylic acids
- 1) The simplest aromatic carboxylic acid is benzoic acid.
- 2) Aromatic carboxylic acids are generally derivatives of benzoic acid.
- 3) The suffix –oic acid is used in IUPAC system and the suffix –ic acid is used in common system and is attached to the appropriate prefix.
- 4) The phenyl group is treated as substituent and the name is obtained from the appropriate alkanoic acid parent chain.
(d)
Answer to Problem 14.3PP
The structure of the given compound is,
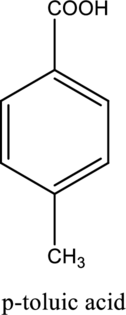
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The structure of the given compound is,
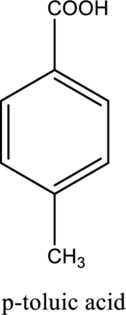
This compound is
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC naming of Aromatic Carboxylic acids
- 1) The simplest aromatic carboxylic acid is benzoic acid.
- 2) Aromatic carboxylic acids are generally derivatives of benzoic acid.
- 3) The suffix –oic acid is used in IUPAC system and the suffix –ic acid is used in common system and is attached to the appropriate prefix.
- 4) The phenyl group is treated as substituent and the name is obtained from the appropriate alkanoic acid parent chain.
(e)
Answer to Problem 14.3PP
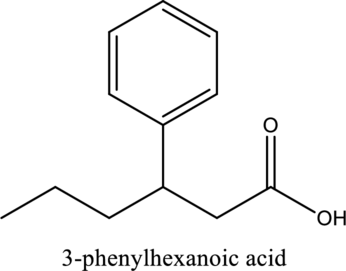
The structure of the given compound is,
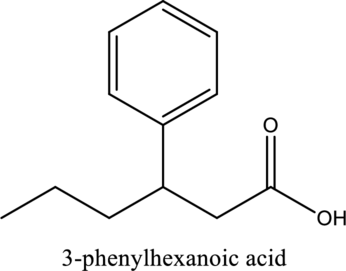
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The substituent phenyl is bonded to carbon
The structure of the given compound is,
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC naming of Aromatic Carboxylic acids
- 1) The simplest aromatic carboxylic acid is benzoic acid.
- 2) Aromatic carboxylic acids are generally derivatives of benzoic acid.
- 3) The suffix –oic acid is used in IUPAC system and the suffix –ic acid is used in common system and is attached to the appropriate prefix.
- 4) The phenyl group is treated as substituent and the name is obtained from the appropriate alkanoic acid parent chain.
(f)
Answer to Problem 14.3PP
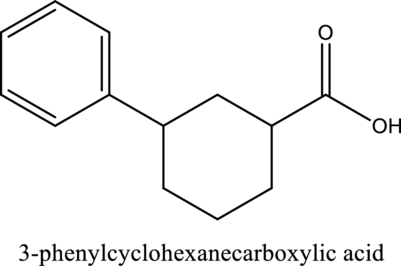
The structure of the given compound is,
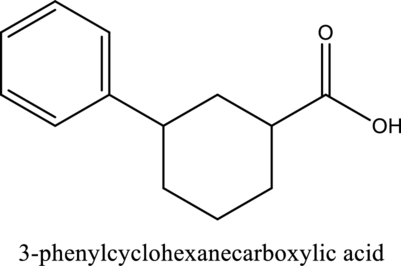
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
The substituent phenyl is bonded to carbon
The structure of the given compound is,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf General, Organic, And Biochemistry With Connect 2-semester Access Card
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





