
a)
Interpretation: The products of the following reactions are to be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
The cleavage of ether below acidic conditions results in the formation of two
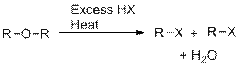
The cleavage of Phenyl ether below acidic conditions results in the formation of Phenol and Alkyl halide.
Phenol cannot be further used in the conversion of Halide, because either
Hydrogen iodide and Hydrogen bromide are used in the cleavage of Ethers. Hydrogen chloride is less significant and Hydrogen fluoride doesn’t cause acid cleavage of Ethers. The reactivity is a result of relative nucleophilicity of Halide ions.
b)
Interpretation: The products of the following reactions are to be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
The cleavage of ether below acidic conditions results in the formation of two Alkyl halides.
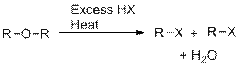
The cleavage of Phenyl ether below acidic conditions results in the formation of Phenol and Alkyl halide.
Phenol cannot be further used in the conversion of Halide, because either
Hydrogen iodide and Hydrogen bromide are used in the cleavage of Ethers. Hydrogen chloride is less significant and Hydrogen fluoride doesn’t cause acid cleavage of Ethers. The reactivity is a result of relative nucleophilicity of Halide ions.
c)
Interpretation: The products of the following reactions are to be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
The cleavage of ether below acidic conditions results in the formation of two Alkyl halides.
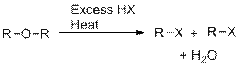
The cleavage of Phenyl ether below acidic conditions results in the formation of Phenol and Alkyl halide.
Phenol cannot be further used in the conversion of Halide, because either
Hydrogen iodide and Hydrogen bromide are used in the cleavage of Ethers. Hydrogen chloride is less significant and Hydrogen fluoride doesn’t cause acid cleavage of Ethers. The reactivity is a result of relative nucleophilicity of Halide ions.
d)
Interpretation: The products of the following reactions are to be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
The cleavage of ether below acidic conditions results in the formation of two Alkyl halides.
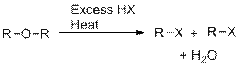
The cleavage of Phenyl ether below acidic conditions results in the formation of Phenol and Alkyl halide.
Phenol cannot be further used in the conversion of Halide, because either
Hydrogen iodide and Hydrogen bromide are used in the cleavage of Ethers. Hydrogen chloride is less significant and Hydrogen fluoride doesn’t cause acid cleavage of Ethers. The reactivity is a result of relative nucleophilicity of Halide ions.
e)
Interpretation: The products of the following reactions are to be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
The cleavage of ether below acidic conditions results in the formation of two Alkyl halides.
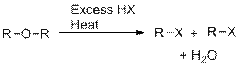
The cleavage of Phenyl ether below acidic conditions results in the formation of Phenol and Alkyl halide.
Phenol cannot be further used in the conversion of Halide, because either
Hydrogen iodide and Hydrogen bromide are used in the cleavage of Ethers. Hydrogen chloride is less significant and Hydrogen fluoride doesn’t cause acid cleavage of Ethers. The reactivity is a result of relative nucleophilicity of Halide ions.
f)
Interpretation: The products of the following reactions are to be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
The cleavage of ether below acidic conditions results in the formation of two Alkyl halides.
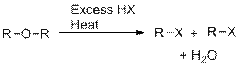
The cleavage of Phenyl ether below acidic conditions results in the formation of Phenol and Alkyl halide.
Phenol cannot be further used in the conversion of Halide, because either
Hydrogen iodide and Hydrogen bromide are used in the cleavage of Ethers. Hydrogen chloride is less significant and Hydrogen fluoride doesn’t cause acid cleavage of Ethers. The reactivity is a result of relative nucleophilicity of Halide ions.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





