Concept explainers
Devise a synthesis of each compound using
a.
![]() e.
e.![]()
(a)
Interpretation: The synthesis of given compound from
Concept introduction: Alkynes acts as a nucleophile by removing its terminal proton. This brings negative charge on terminal carbon atom. The negatively charged alkyne is known as acetylide anion.
Answer to Problem 15.64P
The synthesis of given compound from
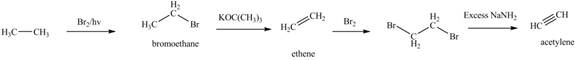
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of acetylene
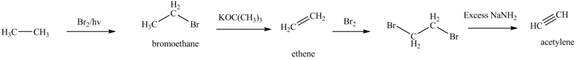
Figure 1
The synthesis of given compound from
(b)
Interpretation: The synthesis of given compound from
Concept introduction: Alkynes acts as a nucleophile by removing its terminal proton. This brings negative charge on terminal carbon atom. The negatively charged alkyne is known as acetylide anion.
Answer to Problem 15.64P
The synthesis of given compound from
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of acetylene
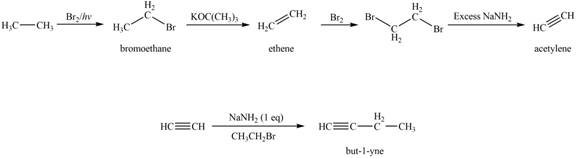
Figure 2
The synthesis of given compound from
(c)
Interpretation: The synthesis of given compound from
Concept introduction: Alkynes acts as a nucleophile by removing its terminal proton. This brings negative charge on terminal carbon atom. The negatively charged alkyne is known as acetylide anion.
Answer to Problem 15.64P
The synthesis of given compound from
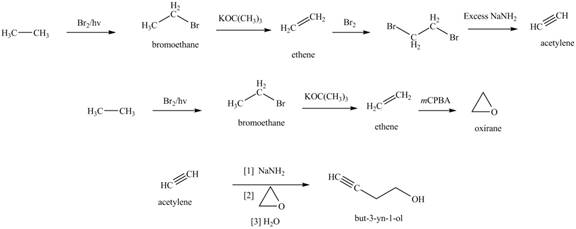
Explanation of Solution
The epoxidation of ethene, which is obtained from ethane, in the presence of m-chloroperbenzoic acid
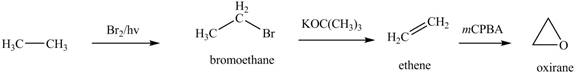
Figure 3
The synthesis of acetylene is shown in Figure 1. Acetylene undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction with oxirane in the presence of base to yield desired product as shown in Figure 4.
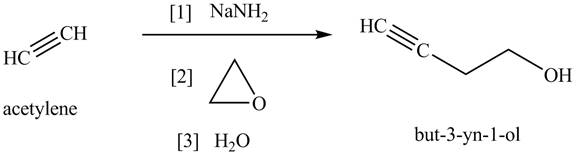
Figure 4
The synthesis of given compound from
(d)
Interpretation: The synthesis of given compound from
Concept introduction: Alkynes acts as a nucleophile by removing its terminal proton. This brings negative charge on terminal carbon atom. The negatively charged alkyne is known as acetylide anion.
Answer to Problem 15.64P
The synthesis of given compound from
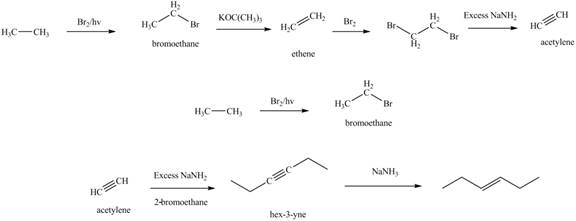
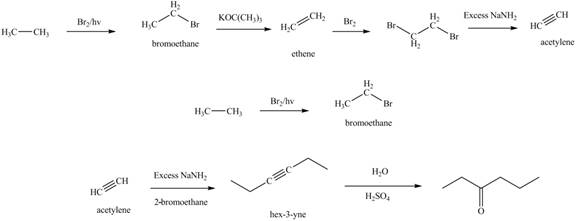
Explanation of Solution
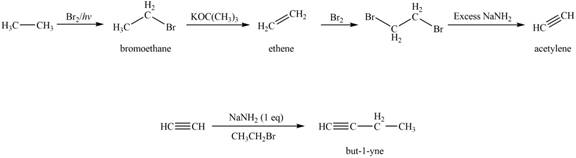
The synthesis of acetylene and bromoethane is shown in Figure 1. Acetylene undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction with two molecules of bromoethane to form symmetrical alkyne. The triple bond of symmetrical alkyne is reduced to double bond on reaction with
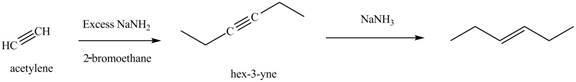
Figure 5
The synthesis of given compound from
(e)
Interpretation: The synthesis of given compound from
Concept introduction: Alkynes acts as a nucleophile by removing its terminal proton. This brings negative charge on terminal carbon atom. The negatively charged alkyne is known as acetylide anion.
Answer to Problem 15.64P
The synthesis of given compound from
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of acetylene and bromoethane is shown in Figure 1. Acetylene undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction with two molecules of bromoethane to form symmetrical alkyne. The symmetrical alkyne converts into ketone on reaction with
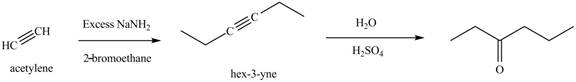
Figure 6
The synthesis of given compound from
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- A. OsO4 and NMO B. Br2 and H20 C. Hg(OAc)2, H2O and NaBH4, NaOH D. RCO3H E. BH3-THF and H2O2, NaOH Which reagent will complete this reaction?arrow_forwardWhat kind of reagent is KmnO4? Draw the possible reactions of this reagent with the specific compounds tested in the following reaction?arrow_forwardWhat reagent can be used from compound F to G? (NaH / NaOH / LiAlH4+hydronium quench / CrO3 Jones)arrow_forward
- What reagents are used in this reaction?arrow_forwardDevise a synthesis of each substituted cyclopropane. Use acetylene (HC=CH) as a starting material in part (a) and cyclohexanone as a starting material in part (b). You may use any other organic compounds and any needed reagents.arrow_forwardDraw the missing starting material. Reagent 1 is benzene and AlCl3. Reagent B is Zn(Hg) and HCl.arrow_forward
- Convert benzene into each compound. You may also use any inorganic reagents and organic alcohols having four or fewer carbons. One step of the synthesis must use a Grignard reagent.arrow_forwardConvert benzene into each compound. You may also use any inorganic reagents and organic alcohols having three carbons or fewer. One step of the synthesis must use a Grignard reagent.arrow_forwardHow Wittig reagents are synthesized by a two-step procedure ?arrow_forward
- Convert benzene into attached compound. You may also use any inorganic reagents and organic alcohols having four or fewer carbons. One step of the synthesis must use a Grignard reagent.arrow_forwardDraw the product formed by treating each compound with excess CH3I, followed by Ag2O, and then heat.arrow_forwardProvide all needed reagents and conditions for each step.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





