Concept explainers
Draw the structure of each compound.
a.
b.
c.
d.
(a)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
The prefix
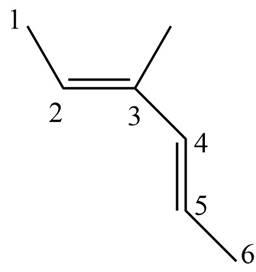
Answer to Problem 16.37P
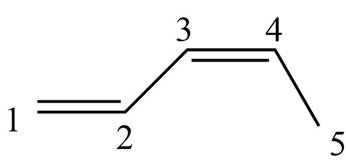
The structure corresponding to
Explanation of Solution
The given name is
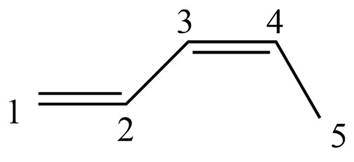
Figure 1
The structure corresponding to
(b)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
The prefix
Answer to Problem 16.37P
The structure corresponding to
Explanation of Solution
The given name is
Thus, the correct structure of
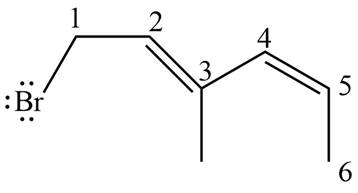
Figure 2
The structure corresponding to
(c)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
The prefix
Answer to Problem 16.37P
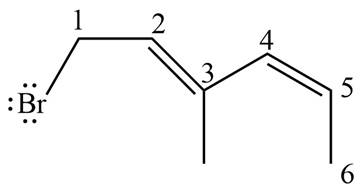
The structure corresponding to
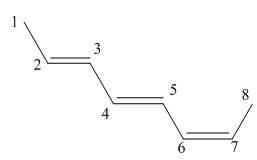
Explanation of Solution
The given name is
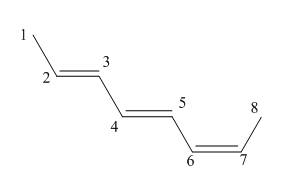
Figure 3
The structure corresponding to
(d)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
4. First identify the word root for the given compound.
5. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
6. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
The prefix
Answer to Problem 16.37P
The structure corresponding to
Explanation of Solution
The given name is
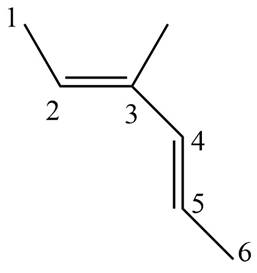
Figure 4
The structure corresponding to
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Package: Organic Chemistry with Connect 2-year Access Card
- Rank the following groups in order of decreasing priority. a.−COOH, −H, −NH2, −OH b.−H, −CH3, −Cl, −CH2Cl c. −CH2CH3, −CH3, −H, −CH(CH3)2 d.−CH=CH2, −CH3, −C≡CH, −Harrow_forwardConsidering both 5-methylcyclopenta-1,3-diene (A) and 7-methylcyclohepta-1,3,5-triene (B), which labeled H atom is most acidic?Which labeled H atom is least acidic? Explain your choices.arrow_forwardA compound of formala ( C20H29NO) absorbs 4 molar equivalents of hydrogen. How many rings does it contain ? select one : A) 3 B) 2 C) 1 D) 4arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

