
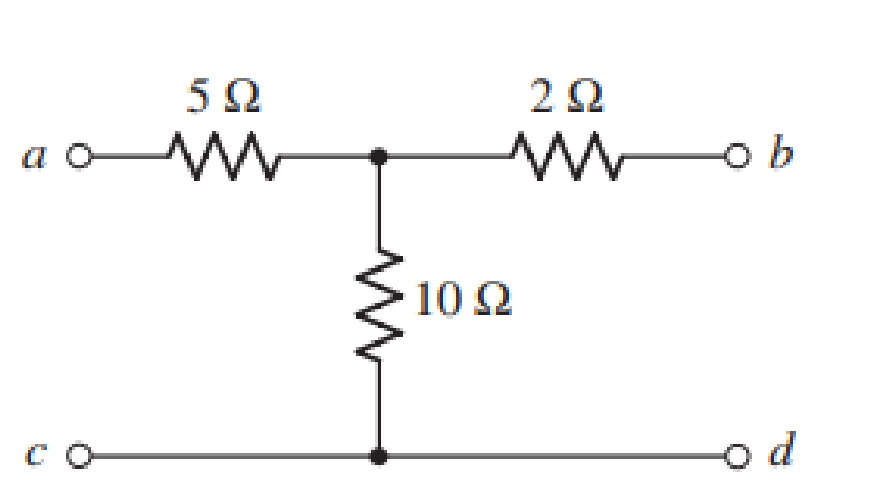
(a) Obtain y, z, h, and t parameters for the network shown in Fig. 16.67 using either the defining equations or mesh/nodal equations. (b) Verify your answers using the relationships in Table 16.1.
(a)
The
Answer to Problem 59E
The
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
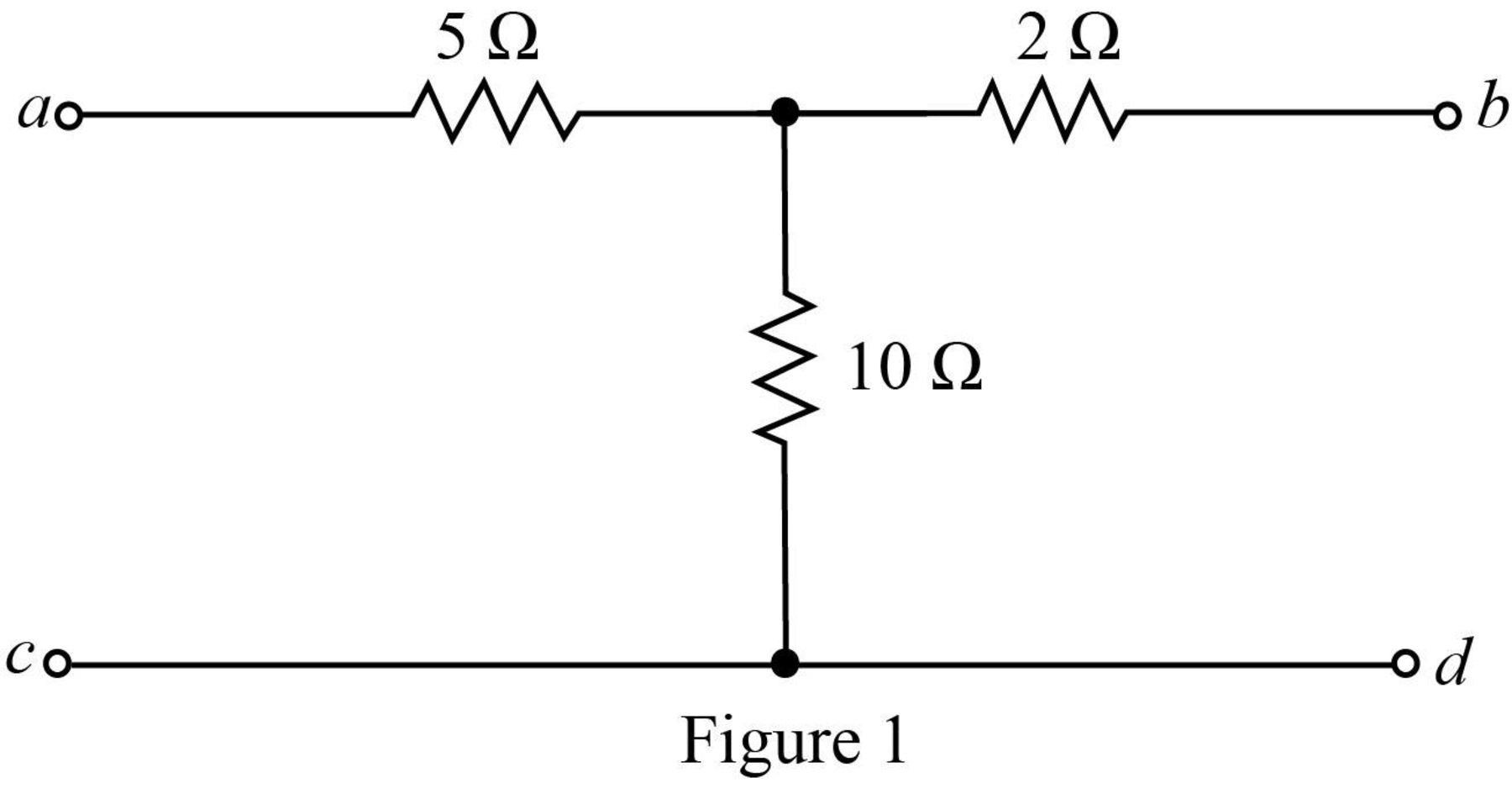
The given diagram is shown in Figure 1.
Calculation:
Mark the branch currents and open circuit voltages.
The required diagram is shown in Figure 2.
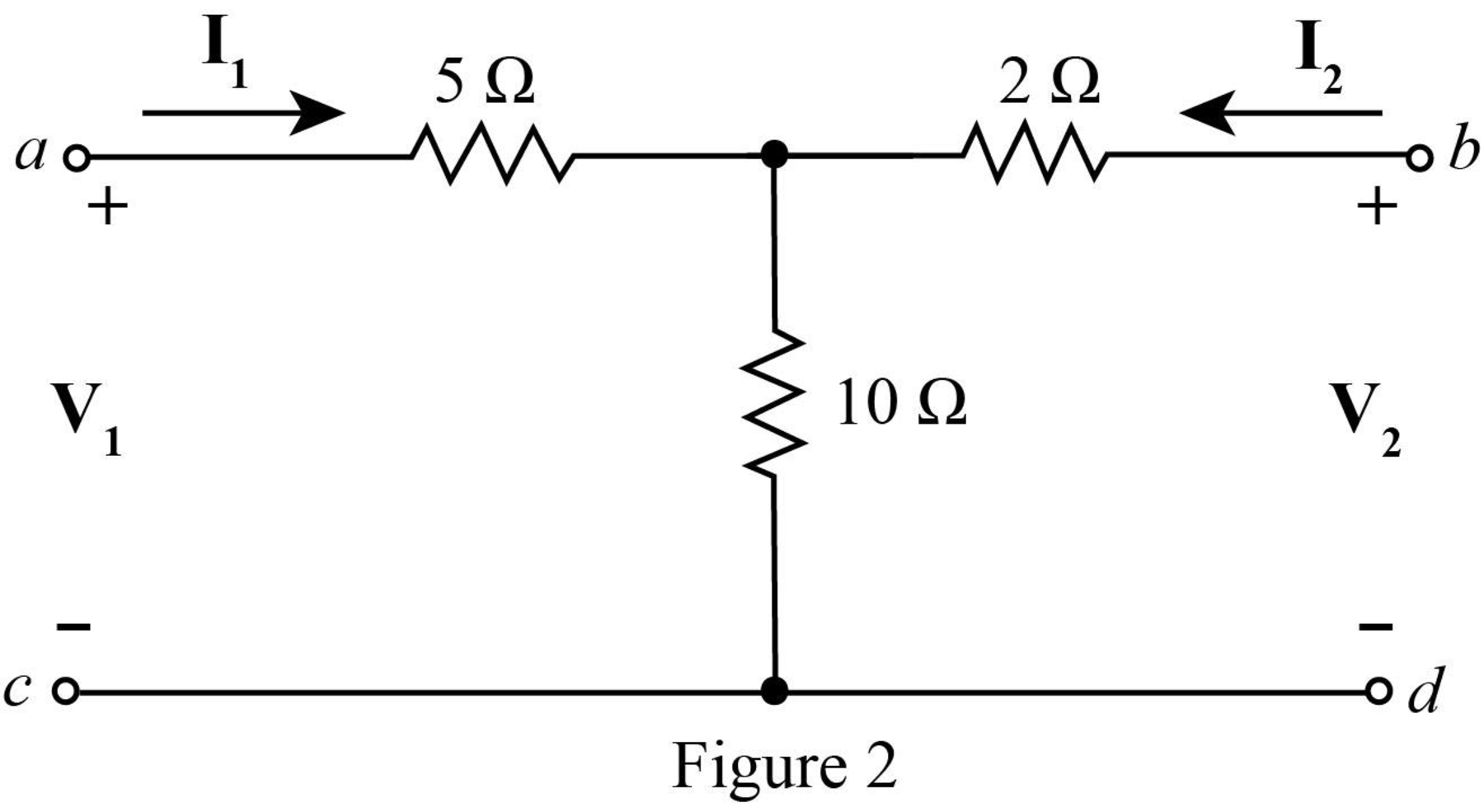
Apply KVL at the input side.
Apply KVL at the output side.
The standard equations for
Compare equation (1) with equation (3).
Compare equation (2) with equation (4).
The
Substitute
Rearrange equation (1) as,
Rearrange equation (2) as,
Substitute
Substitute
The standard equations for
Compare equation (7) with equation (9).
Compare equation (8) with equation (10).
The
Substitute
Substitute
The standard equations for
Compare equation (11) with equation (12).
Compare equation (6) with equation (13).
The
Substitute
Rearrange equation (6) as,
Substitute
The standard equations for
Compare equation (15) with equation (16).
Compare equation (14) with equation (17).
The
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the
(b)
To verify: The value of
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The relation between
The determinant
Substitute
The relation between
Substitute
The relation between
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, within the limits of error the value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Electric machinery fundamentals
Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Principles Of Electric Circuits
Fundamentals of Applied Electromagnetics (7th Edition)
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
- The relationship between input and output for an LTI system is defined by the following difference equation. Calculate the system output y[n] for system input x[n] = u[n] using z transformations (y[-1]=1 , y[-2] =2).arrow_forwardUse Norton's Theoremarrow_forwardShow all equations equations in the translation system shownarrow_forward
- Perform addition on the given base-r number systems. 5138+ 23058 CAFE16 + FACE16 CB013 + 7AB13arrow_forwardGiven: G(ABCD) = Σ (2,6,7,8,12,13) Derive the minimal SOP form of G using a K-map Derive the minimal POS form of G using a K-map Calculate the literal cost between the 2arrow_forwardUse mesh analysis to obtain Voarrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





