
A 15-ft beam weighing 500 Ib is lowered by mean of two cables unwinding from overhead cranes. As the beam approaches the ground, the crane operators apply brakes to slow the unwinding motion. Knowing that the deceleration of cable A is 20 ft/s2 and the deceleration of cable B is 2 ft/s2, determine the tension in each cable.
The tension in each cable.
Answer to Problem 16.60P
The tension in cable
The tension in cable
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of the beam is
The below figure represent the kinetics of the beam.
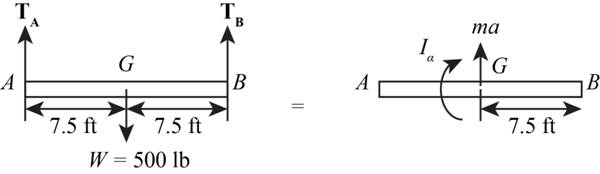
Figure-(1)
Write the expression of total force applied on the beam.
Here, the mass of the beam is
Consider the tension in the cable
Write the expression of deceleration of cable
Here, the acceleration of cable
Write the expression of total acceleration on the beam.
Here, the acceleration of the cable
Write the expression of moment of inertia of beam.
Here, the mass of the slender rod is
Write the expression of mass of the rod.
Here, the weight of the beam is
Write the expression of total moment about point
Here, the effective moment is
Write the expression of moment about point
Here, the tension in the cable
Write the expression of effective moment about point
Here, the angular acceleration of the rod is
Write the expression of generated torque in the beam.
Here, the of inertia of beam is
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Write the expression of total force applied on the beam by equilibrium of the beam as shown in Figure-(1).
Substitute
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The tension in cable
The tension in cable
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Package: Vector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics With 1 Semester Connect Access Card
- A 500-ft-long aerial tramway cable having a weight per unit length of 2.8 lb/ft is suspended between two points at the same elevation. Knowing that the sag is 125 ft, find (a) the horizontal distance between the supports, (b) the maximum tension in the cable.arrow_forwardA 40-m cable is strung as shown between two buildings. The maximum tension is found to be 350 N, and the lowest point of the cable is observed to be 6 m above the ground. Determine (a) the horizontal distance between the buildings, (b) the total mass of the cable.arrow_forwardUsing two ropes and a roller chute, two workers are unloading a 200-lb cast-iron counterweight from a truck. Knowing that at the instant shown the counterweight is kept from moving and that the positions of points A, B, and C are, respectively, A(0, –20 in., 40 in.), B(–40 in., 50 in., 0), and C(45 in., 40 in., 0), and assuming that no friction exists between the counterweight and the chute, determine the tension in each rope. (Hint: Because there is no friction, the force exerted by the chute on the counterweight must be perpendicular to the chute.)arrow_forward
- Pin B weighs 0.1kg and is free to slide in a horizontal plane along therotating arm OC and along the circular slot DE of radius b=500mm.Neglecting friction and assuming that θ= 15 rad/s andθ=250 rad/s2 for the position θ= 20o , determine for that position(a) the radial and transverse components of the resultant forceexerted on pin B, (b) the forces P and Q exerted on pin B,respectively, by rod OC and the wall of slot DE.arrow_forwardThe system shown is at rest when a constant 150-N force is applied to collar B. Neglecting the effect of friction, determine (a) the time at which the velocity of collar B will be 2.5 m/s to the left, (b) the corresponding tension in the cable.arrow_forwardA 25-kg block A rests on an inclined surface, and a 15-kg counterweight B is attached to a cable as shown. Neglecting friction, determine the acceleration of A and the tension in the cable immediately after the system is released from rest.arrow_forward
- A spring scale A and a lever scale B having equal lever arms are fastened to the roof of an elevator, and identical packages are attached to the scales as shown. Knowing that when the elevator moves downward with an acceleration of 1 m/s2 the spring scale indicates a load of 60 N, determine (b) the load indicated by the spring scale and the mass needed to balance the lever scale when the elevator moves upward with an acceleration of 1 m/s2.arrow_forwardA thin circular rod is supported in a vertical plane by a bracket at A. Attached to the bracket and loosely wound around the rod is a spring of constant k= 3 lb/ft and undeformed length equal to the arc of circle AB. An 8-oz collar C , not attached to the spring, can slide without friction along the rod. Knowing that the collar is released from rest at an angle 0 with the vertical, determine (a) the smallest value of 0 for which the collar will pass through D and reach point A, (b) the velocity of the collar as it reaches point A.arrow_forwardThe double pulley shown in the figure has a mass of 3 kg and a radius of 100 mm rotation. Knowing that when the pulley is at rest, it is applied to the cable in B, a force P of magnitude equal to 24N, determine the speed of the center of the pulley after 1.5 s and the tensile force on cable C.arrow_forward
- Help!!!!! A 500-lb box B is suspended from a cable attached to a 40-lb truck A mounted on an I-beam inclined in the form that shows. If at the indicated time the truck accelerates 1.2 ft / s2 up and to the right, determine (a) the acceleration of B in relation to A and b) the tension in the CD cable.arrow_forwardA small 250-g collar C can slide on a semicircular rod which is made to rotate about the vertical AB at a constant rate of 7.5 rad/s. Determine the three values of 0 for which the collar will not slide on the rod, assuming no friction between the collar and the rod.arrow_forwardGreek engineers had the unenviable task of moving large columns from the quarries to the city. One engineer, Chersiphron, tried several different techniques to do this. One method was to cut pivot holes into the ends of the stone and then use oxen to pull the column. The 4-ft diameter column weighs 12,000 lbs, and the team of oxen generates a constant pull force of 1500 lbs on the center of the cylinder G. Knowing that the column starts from rest and rolls without slipping, determine (a) the velocity of its center G after it has moved 5 ft, (b) the minimum static coefficient of friction that will keep it from slipping.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





