Draw the structure corresponding to each name.
a. propyl formate
b. butibutanoate
c. heptyl benzoate
d. N-ethylhexanamide
e. N-ethyl-N-methylheptanamide
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of propyl formate should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.55P
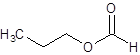
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H. When -H of the carboxylic acid is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group (-R') then it results in the formation of an ester having general formula RCOOR'.
The reaction which results in the formation of at least one ester along with water on heating acids with alcohols is said to be esterification.
So, in order to give the IUPAC name to the esters, the following steps are followed:
- The alkyl substituent from the alcohol is named first.
- The name of the parent chain from carboxylic acid part is replaced as carboxylate.
In order to write the common name of the esters, the common of acids are written from which the ester has been formed.
The given name is propyl formate where propyl name is derived from propanol and formate is derived from the name formic acid. So, the structure of propyl formate is:
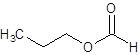
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of butyl butanoate should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.55P
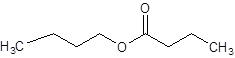
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H. When -H of the carboxylic acid is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group (-R') then it results in the formation of an ester having general formula RCOOR'.
The reaction which results in the formation of at least one ester along with water on heating acids with alcohols is said to be esterification.
So, in order to give the IUPAC name to the esters, the following steps are followed:
- The alkyl substituent from the alcohol is named first.
- The name of the parent chain from carboxylic acid part is replaced as carboxylate.
In order to write the common name of the esters, the common of acids are written from which the ester has been formed.
The given name is butyl butanoate where butyl name is derived from butanol and butanoate is derived from the name butanoic acid. So, the structure of butyl butanoate is:
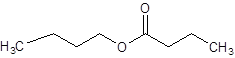
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of heptyl benzoate should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.55P
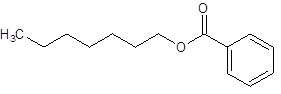
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H. When -H of the carboxylic acid is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group (-R') then it results in the formation of an ester having general formula RCOOR'.
The reaction which results in the formation of at least one ester along with water on heating acids with alcohols is said to be esterification.
So, in order to give the IUPAC name to the esters, the following steps are followed:
- The alkyl substituent from the alcohol is named first.
- The name of the parent chain from carboxylic acid part is replaced as carboxylate.
In order to write the common name of the esters, the common of acids are written from which the ester has been formed.
The given name is heptyl benzoate where heptyl name is derived from heptanol and benzoate is derived from the name benzoic acid. So, the structure of heptyl benzoate is:
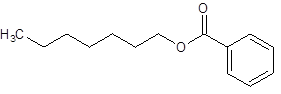
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of N-ethylhexanamide should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.55P
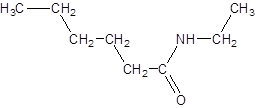
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H. When -OH (hydroxyl group) of the carboxylic acid is replaced by nitrogen (-N) then it results in the formation of an amide.
The reaction which results in the formation of amide along with water on heating acids with amine or ammonia is said to be amidation.
So, in order to give the IUPAC name to the amides, the rules for naming carboxylic acid is followed and -oic acid of the carboxylic acid is replaced by amide.
In order to give the name to the amide group, the following steps are followed:
- The parent (longest) alkane chain is named as for carboxylic acids.
- The -oic acid in the name is changed to -amide.
- The numbering of the chain is done in such a way that amide group and substituents gets the smaller number.
- N-alkyl is used to show each alkyl group bonded to -N atom in the name for secondary and tertiary amides.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
In order to write the common name of the amides, the common of acids are written from which the amide has been formed by replacing -oic acid in name from -amide.
The given name is N-ethylhexanamide where hex represents 6 carbon atoms parent chain and N-ethyl represents ethyl substituted N atom. So, the structure of N-ethylheptanamide is:
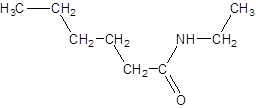
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure of N-ethyl-N-methylheptanamide should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.55P
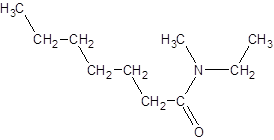
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H. When -OH (hydroxyl group) of the carboxylic acid is replaced by nitrogen (-N) then it results in the formation of an amide.
The reaction which results in the formation of amide along with water on heating acids with amine or ammonia is said to be amidation.
So, in order to give the IUPAC name to the amides, the rules for naming carboxylic acid is followed and -oic acid of the carboxylic acid is replaced by amide.
In order to give the name to the amide group, the following steps are followed:
- The parent (longest) alkane chain is named as for carboxylic acids.
- The -oic acid in the name is changed to -amide.
- The numbering of the chain is done in such a way that amide group and substituents gets the smaller number.
- N-alkyl is used to show each alkyl group bonded to -N atom in the name for secondary and tertiary amides.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
In order to write the common name of the amides, the common of acids are written from which the amide has been formed by replacing -oic acid in name from -amide.
The given name is N-ethyl-N-methylheptanamide where hept represents 7 carbon atoms parent chain, N-ethyl represents ethyl substituted N atom and N-methyl represents methyl substituted N atom. So, the structure of N-ethyl-N-methylheptanamide is:
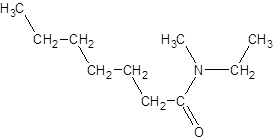
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Connect 2-Year Access Card for General, Organic and Biological Chemistry
- explain Furaneol that are found in strawberryarrow_forwardWhat polyamide is formed from each monomer or pair of monomers?arrow_forwarda) Draw the structure for ethyl 3-methyl butanoate. b) Which functional group(s) does this molecule contain? c) Which type of reaction could be used to synthesize this molecule?arrow_forward
- Draw all isomers of pentanol.arrow_forwardWhat kind of solvent ingredients is widely is usually used in mouthwash, perfumes and spray A. Ethly acetate B. Aliphatic alcohols C. Fragrant esters D. Phenols and phenol derivativesarrow_forwarda. What is the chemical structure of biphenyl, circle functional groupsdifferent than alkane, alkene, alkyne? b. Is it polar or nonpolar? _______________________ c. What is its water solubility in g/L? __________________________arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

