
Concept explainers
Draw the structure corresponding to each name.
a. 3-methyihexanoic acid
b. 3-hydroxy-4-methylheptanoic acid
c. p-nitrobenzoic acid
d. sodium hexanoate
e. m-ethylbenzoic acid
f. propyl decanoate
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of 3-methylhexanoic acid should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 44P
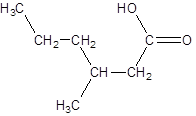
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H.
The IUPAC names are given to the carboxylic acid according to the following steps:
1. The parent (longest) alkane chain is identified.
2. The ending of the parent chain from alkane (-e) is changed to -oic acid for a carboxylic acid group.
3. The numbering is of the chain is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets the smaller number.
4. Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
The given name is 3-methylhexanoic acid where the parent chain is hexane that is 6 carbon atom chain having a methyl substituent at carbon-3. So, the structure of 3-methylhexanoic acid is:
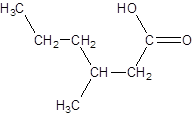
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of 3-hydroxy-4-methylheptanoic acid should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 44P
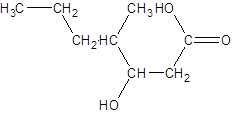
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H.
The IUPAC names are given to the carboxylic acid according to the following steps:
1. The parent (longest) alkane chain is identified.
2. The ending of the parent chain from alkane (-e) is changed to -oic acid for a carboxylic acid group.
3. The numbering is of the chain is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets the smaller number.
4. Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
The given name is 3-hydroxy-4-methylheptanoic acid where the parent chain is heptane that is 7 carbon atom chain having a hydroxy substituent at carbon-3 and a methyl substituent at carbon-4. So, the structure of 3-hydroxy-4-methylheptanoic acid is:
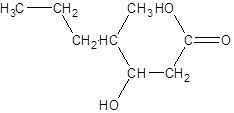
(c)
Interpretation:
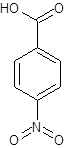
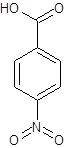
The structure of p-nitrobenzoic acid should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 44P
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H.
The IUPAC names are given to the carboxylic acid according to the following steps:
1. The parent (longest) alkane chain is identified.
2. The ending of the parent chain from alkane (-e) is changed to -oic acid for a carboxylic acid group.
3. The numbering is of the chain is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets the smaller number.
4. Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
The given name is p-nitrobenzoic acid where the parent chain is benzene having a nitro substituent at carbon-4. So, the structure of p-nitrobenzoic acid is:
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of sodium hexanoate should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 44P
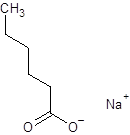
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H. When H of hydroxyl group present in carboxylic acid is replaced by an atom then it results in the formation of respective salt.
The IUPAC names are given to the carboxylic acid salt according to the following steps:
- The parent (longest) carbon chain is identified.
- The name of metal is written first from which the salt is made up of.
- The ending of the for a carboxylic acid group is changed to -oate for naming salt of carboxylic acid.
- The numbering is of the chain is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets the smaller number.
- Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
The given name is sodium hexanoate where the parent chain is hexane having 6 carbon atoms and metal is sodium. So, the structure of sodium hexanoate is:
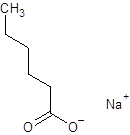
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure of m-ethylbenzoic acid should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 44P
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H.
The IUPAC names are given to the carboxylic acid according to the following steps:
1. The parent (longest) alkane chain is identified.
2. The ending of the parent chain from alkane (-e) is changed to -oic acid for a carboxylic acid group.
3. The numbering is of the chain is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets the smaller number.
4. Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
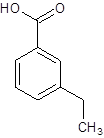
The given name is m-ethylbenzoic acid where the parent chain is benzene having an ethyl substituent at carbon-3. So, the structure of m-ethylbenzoic acid is:
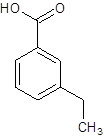
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure of propyl decanoate should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 44P
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H. When -H of the carboxylic acid is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group (-R') then it results in the formation of an ester having general formula RCOOR'.
The reaction which results in the formation of at least one ester along with water on heating acids with alcohols is said to be esterification.
So, in order to give the IUPAC name to the esters, the following steps are followed:
- The alkyl substituent from the alcohol is named first.
- The name of the parent chain from carboxylic acid part is replaced as carboxylate.
In order to write the common name of the esters, the common of acids are written from which the ester has been formed.
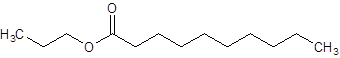
The given name is propyl decanoate where propyl name is derived from propanol and decanoate is derived from the name decanoic acid. So, the structure of propyl decanoate is:
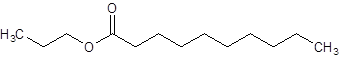
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
GENERAL, ORGANIC & BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY
- what reagent to use?arrow_forwardThis carboxylic salts are effective ingredient against yeast and molds in beverages, jams, pie fillings and ketchup a. benzoates b. sorbates c. acetates d. propionatesarrow_forwardDraw an example a) an aromatic heterocycle b) benzyne. c) an aromatic cation d) an aromatic anionarrow_forward
- Draw the structure corresponding to each name. a. 2-hydroxyheptanoic acid b. 4-chlorononanoic acid c. 3,4-dibromobenzoic acid d. lithium propanoate e. 2,2-dibromobutanoic acid f. ethyl 2-methylpropanoatearrow_forwardComplete what reagents are needed to produce the productsarrow_forwardEsterfication is the reaction of carboxylic acid with Select one: a. water b. alcohol c. alkyl halide d. ammoniaarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

