
(a)
Sketch
(a)
Answer to Problem 9E
The plot
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure 17.29 in the textbook.
Formula used:
Write the general expression for Fourier series expansion.
Write the general expression for Fourier series coefficient
Write the general expression for Fourier series coefficient
Write the general expression for Fourier series coefficient
Write the expression to calculate the fundamental angular frequency.
Here,
Calculation:s
In the given Figure 17.29, the time period is
The function
Substitute 4 for T in equation (5) to find
Applying equation (6) in equation (2) to find
Simplify the above equation as follows,
Applying equation (6) in equation (3) to finding the Fourier coefficient
Equation (8) is simplified as,
Therefore, equation (8) becomes,
Consider the function,
Consider the following integration formula.
Compare the equations (10) and (11) to simplify the equation (10).
Using the equation (11), the equation (10) can be reduced as,
Simplify the above equation as follows,
Consider the function,
Compare the equations (12) and (11) to simplify the equation (12).
Using the equation (11), the equation (12) can be reduced as,
Substitute the value of x and y in equation (9) as follows,
The above equation becomes,
Applying equation (6) in equation (4) to finding the Fourier coefficient
Equation (14) is simplified as,
Therefore, equation (14) becomes,
Consider the function,
Consider the following integration formula.
Compare the equations (17) and (16) to simplify the equation (16).
Using the equation (17), the equation (16) can be reduced as,
Simplify the above equation as follows,
Consider the function,
Compare the equations (17) and (18) to simplify the equation (18).
Using the equation (17), the equation (18) can be reduced as,
Substitute the values of m and n in equation (15) as follows,
The above equation becomes,
Substitute the values of
The above equation becomes,
For
Therefore, equation (19) will be as follows,
For
Therefore, equation (19) will be as follows,
For
Therefore, equation (19) will be as follows,
Similarly, for
Therefore, equation (19) will be as follows,
Write the MATLAB Code to plot
t=linspace(-3,5,1000);
g0=0;
N=40;
for i=1:1000;
y3=0.193*cos(pi*t/2) + 0.419*cos(pi*t) - 0.167*cos(3*pi*t/2);
y5=0.193*cos(pi*t/2) + 0.419*cos(pi*t) - 0.167*cos(3*pi*t/2) + 0.184*cos(2*pi*t) - 0.143*cos(5*pi*t/2);
end
for i=1:1000;
sum=0;
for n=1:N;
sum=sum+((6*(-1)^n - 2*cos(3*n*pi))/(n*pi)^2)*cos(n*pi*t(i)/2) + (((-1)^n + cos(3*n*pi))/(n*pi))*cos(n*pi*t(i)/2);
end
gt(i)=g0+sum;
end
plot(t,y3,'b', t,y5,'r', t,gt,'g')
legend({'y3','y5','gt'},'Location','best')
xlabel('Time t in sec')
ylabel('The values y3, y5, and gt')
title('Plots for y3, y5, and gt')
Matlab output:
Figure 1 shows the plot
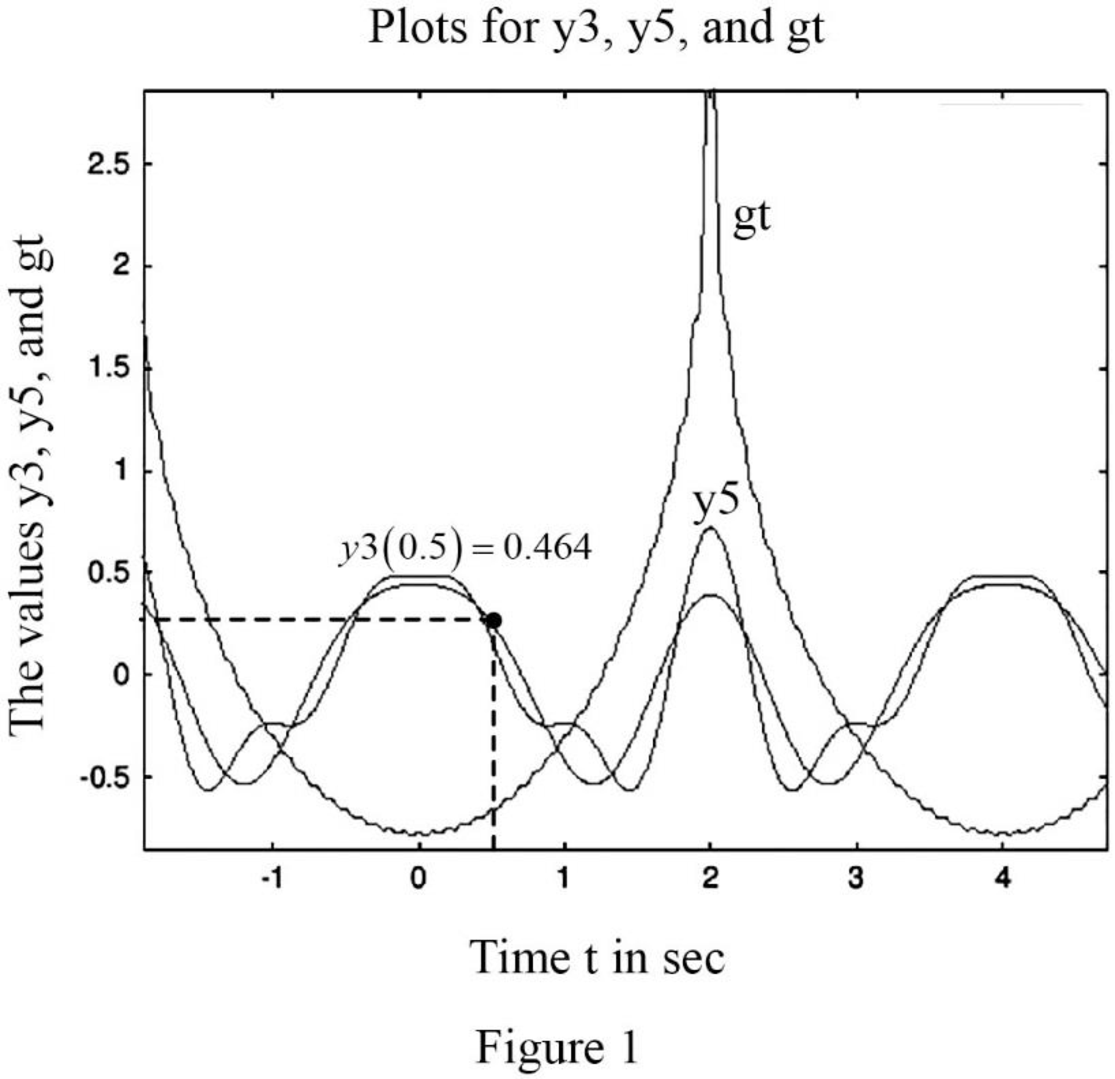
Conclusion:
Thus, the plot
(b)
Find the values of
(b)
Answer to Problem 9E
The values of
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure 17.29 in the textbook.
Calculation:
From Part (a), the function
Finding
The value of
From Part (a),
Finding
From Part (a),
Finding
From part (a),
Finding
The value of
Finding
Conclusion:
Thus, the values of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
- Be able to calculate the Fourier transform of a function Find the Fourier transform of each function. In each case, a is a positive real constant. f(t)=te−at,t≥0,f(t)=teat,t≤0.arrow_forwardType using Kepord or will dislike can anyone explain what the discussion could be make from the graphs respectively ? question : the fourier transform of the rectangular function numerically by sampling it 256 times over the time interval 0<= t < 0.2.arrow_forwardIt is given that f(t)=4t2 over the interval –2<t<2 s. Construct a periodic function that satisfies this f(t) between −2 sand +2 s, has a period of 8 s, and has half-wave symmetry.arrow_forward
- Given the finite-duration sequence below, x[n]={-4,1,2,0,3} where -4 is when n=0, if it has a fourier transform of X(w) , what is the value of X(0)?arrow_forwardobtain the Fourier transform of the signal as a single expressionarrow_forwardRegarding Signals and Systems, given a signal x(t) = |cos(ωt)| for ω>0. Find the Fourier transform of x(t). Please do not ignore the absolute value operator (that is what I am struggling with.arrow_forward
- The signal X(t)=(e^-bt) u(t) is given as input to a system with a unit impulse response h(t)=(e^-at) u(t). if a=2,b=1, Find the y(t) signal obtained at the output by the following methods.a. find by calculating the convolution of x(t) and h(t) in the form y(t) = x(t) ∗ h(t).b. find y(t) = F^-1{H(jw) X(jw)} by calculating the inverse Fourier Transform of the product of the Fourier transforms of x(t) and h(t). I used the ^ symbol for an exponential expressionarrow_forwardSignals and Systems Calculate the fourier transform of y(n) in terms of x(t)'s fourier transforms (X (jw).) Note : Substitute t for n for the range in the piecewise function. (misspelled as n in the ımage)arrow_forwardLet's examine the function g(t)= {Go for - π < t < -( π/2), {-Go for -( π/2) < t < ( π/2), {Go for ( π/2) < t < π, which is characterized by being 2 π-periodic. Firstly, without mathematical calculations, clarify why every bn value must be 0. Secondly, sketch the g(t) graph within the range of [-4 π,4 π]. Thirdly, express the Fourier expansion of g(t). Lastly, plot the g(t) using the first 3, 5, 10, 15, 20, and 25 terms of the series. At what point does the graph start resembling your initial sketch in the first question?arrow_forward
- Obtain the Fourier series expansion of the periodic function f(t) of period 2π defined by the given. Show your solution.arrow_forward1. Discrete Fourier Transform: Use the Fast Fourier Transform algorithm to compute the 8-point Dis- crete Fourier Transforms of sequences (1,0,1,0,1,0, 1,0) and (1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0). Provide detailed calculations with intermediate steps rather than just the results.arrow_forwardAn audio signal processing system has the following periodic sequence x[n]={…4,3,2,1,4,3,2,1,4,3,2,1…}. Determine the period and Fourier series coefficients of x[n].Model Short AnswerPeriod: 5Coefficients: 1,2 ,3,4,5,6,7arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





