
Concept explainers
Interpretation: The total project completion time is to be calculated along with the lowest cost solution if the project is to be completed
Concept Introduction:
Project
Explanation of Solution
The activity with their immediate predecessor and estimated time, crash time, crash cost and normal cost is tabulated below.
| Activity | Immediate Predecessor | Estimated Normal Time | Crash Time | Normal Cost | Crash Cost |
| A | - | ||||
| B | A | ||||
| C | A | ||||
| D | - | ||||
| E | B, D, C | ||||
| F | D | ||||
| G | D | ||||
| H | E | ||||
| I | F, G, H |
Table (1)
The network diagram for the activity shown in table (1) is shown below.
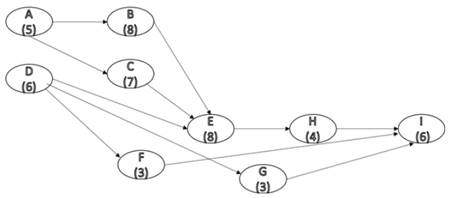
Figure (1)
Therefore, the network diagram of the given project is shown in Figure (1).
The expression for the cost slope is given by,
The cost slope for each activity is tabulated below.
| Activity | Immediate Predecessor | Estimated Normal Time | Crash Time | Normal Cost | Crash Cost | Cost Slope |
| A | - | |||||
| B | A | |||||
| C | A | |||||
| D | - | |||||
| E | B, D, C | |||||
| F | D | |||||
| G | D | |||||
| H | E | |||||
| I | F, G, H |
Table (2)
Consider figure (1), the different paths and their completion times is tabulated below.
| Path | Completion time (weeks) |
Table (3)
From Table (3), the maximum completion time is taken by path
Therefore, the critical path is
Now the project is to be completed
Consider the critical path activities.
The lowest crash cost per week is of activity B and activity H.
Crash Activity B by
And,
Thus, the additional cost of crashing the activity by
The new network diagram is shown in figure below.
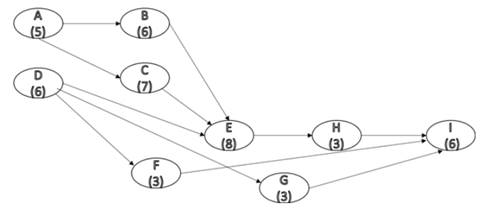
Figure (2)
Consider figure (2), the different paths and their completion times is tabulated below.
| Path | Completion time (weeks) |
Table (4)
From Table (4), the maximum completion time is taken by path
Therefore, the critical path is
But the desired project duration is
Try different option.
Crash Activity B by
And,
And,
Thus, the additional cost of crashing the activity by
The new network diagram is shown in figure below.
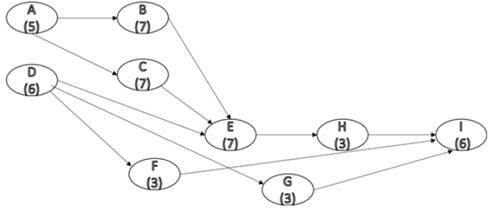
Figure (3)
Consider figure (3), the different paths and their completion times is tabulated below.
| Path | Completion time (weeks) |
Table (4)
From Table (4), the maximum completion time is taken by path
Therefore, the critical path are
Therefore, the crashing cost of the project is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- The table below contains data for the installation of new equipment in a manufacturing process for a steel corporation. Your company is responsible for the installation project. Indirect costs are $6,000 per week, and a penalty cost of $10,000 per week will be incurred by your company for every week the project is delayed beyond week 15. Activity Immediate Predecessor(s) Normal Time (weeks) Crash Time (weeks) Normal Cost ($) Crash Cost ($) A None 2 1 7,000 10,000 B None 2 2 3,000 3,000 C A 3 1 12,000 40,000 D B 3 2 12,000 28,000 E C 1 1 8,000 8,000 F D, E 5 3 5,000 15,000 G E 3 2 9,000 18,000 H F, G 8 6 14,000 32,000 Construct a network diagram for the project. What are the project completion time and the total cost under normal conditions? What is the shortest time duration for this project regardless of cost? What is the resulting total cost? What is the…arrow_forwardPlease do not give solution in image formate thanku. There are four critical paths in a network. A-B-C-D-E, A-F-E, A-B-H-J-K-E and A-S-T-E. Each activity in this network can be crashed by a maximum of 4 weeks. The crashing cost (per week), for the first week (crashing first time), for activity A is: $400, E is $415 and all other activities is : $100 (per week per activity). The crashing cost, second week and onwards(crashing second time), for activity A is $1000 per week, E is $1200 per week and for all other activities is $200 per activity per week. You have a maximum crashing budget of $2505. The maximum possible reduction in the project duration will be: a. 2 weeks b. 3 weeks c. 4 weeks d. 5 weeks e. 6 weeksarrow_forwardThe client of a project has requested the project team to crash 8 hours of time. The table below provides the necessary information about the possible project crashing. (a) What is the crash cost for 8 hours of time-savings? (b) Assume the team calls the client and asks for a project extension, reducing the amount of time they need to crash. The project team has a $20 crash budget. Is the budget sufficient to crash 4 hours of time? Activity Normal Duration (hours) Normal Cost ($) Crash Duration (hours) Crash Cost (S) Immediate Predecessors A 2 10 2 0 None B 3 15 2 23 A C 5 25 4 30 B D 3 20 1 24 C E 6 30 4 45 C F 1 5 1 0 E G 7 35 6 50 F H 10 50 7 80 D, Garrow_forward
- The client of a project has requested the project team to crash 8 hours of time. The table below provides the necessary information about the possible project crashing. (a) What is the crash cost for 8 hours of time-savings?(b) Assume the team calls the client and asks for a project extension, reducing the amount of time they need to crash. The project team has a $20 crash budget. Is the budget sufficient to crash 4 hours of time?arrow_forwardEnvironment Recycling, Inc. must clean up a large automobile tire dump under a state environmental cleanup contract. Suppose that some of the activities in the Environment Recycling, Inc. project can be crashed.The table below shows the crash times and costs associated with performing the activities at their original (normal) times and also for the crash times (all times are in weeks). Normal Crash Normal Crash Activity Predecessor(s) Time Time Cost Cost A — 6 5 $490 $640 B A 9 7 1,800 2,400 C A 8 7 860 1,060 D — 7 6 620 920 E B, C, D 9 7 1,900 2,300 F D 4 2 820 1,320 G D 4 3 620 870 H E 5 4 500 710 I F, G, H 7 5 950 1,550 Choose the correct network for the project. The correct network is C . Identify the critical path. The critical path is A-B-E-H-I. What is the total project completion time? Round your answer to the nearest whole number. ___ weeks What is the lowest cost solution if…arrow_forwardAn IT project manager of ABC Company has developed an activity list for the purpose oftracking employees’ daily activities on the project. The project’s schedule is considered to be ofhigh risk due to the possibility of sabotage by some of the employees. In addition, the IT projectmanager has gathered time information for each activity, as shown in the table below. Considerthe following project’s tasks and their identified best, likely, and worst case estimates of taskduration. Assume the organization computes PERT weight average based on the standardformula.Activity Optimistic MostlikelyPessimisticA 5 5 25B 3 5 8C 7 5 8D 4 4 5E 10 19 34F 3 14 18G 6 16 20H 32 44 65I 12 17 25J 2 8 18The dependencies between the 10 activities listed in the table above are as follows: The project starts with two activities—A, and B—which can be done concurrently. When activity A is finished, activity C can start When activity B is finished, activities D and E can start When both activities C and D are…arrow_forward
- In making a forward pass through a network, three activities are immediate predecessors for activity T and one following activity. What is the late start time for activity T? Group of answer choices: - the LS of the following activity plus the activity time of T - the smallest EF for the three activities that are immediate predecessors for activity T - the LF of the following activity minus the activity time of T - the LS of the following activity minus the activity time of T - the largest EF for the three activities that are immediate predecessors for activity Tarrow_forwardGiven problem: A contractor has a job which should be completed in 120 days. At present, he has 80 men on the job and it is estimated that they will finish the work in 150 days. Of the 80 men, 50 are each paid Php 150.00 a day, 25 at Php 210.00, and 5 at Php 280.00. For each day beyond the original 120 days, the contractor has to pay Php 1,500.00 liquidated damages. How many more men should the contractor add so that he can complete the work on time? *Do show solution. Round off final answer in 2 decimal places. Thank you.arrow_forwardA 4-year financial project has net cash flows of $20,000; $25,000; $30,000; and $50,000 in the next 4 years. It will cost $75,000 to implement the project. If the required rate of return is 0.2, conduct a discounted cash flow calculation to determine the NPV.arrow_forward
- Consider the project network pictured. Assume that the timesattached to each node are the means and the variances of the project completion times, respectively.a. Identify all paths from nodes 1 to 6.b. Which path is critical based on the expected completion times?c. Determine the probability that the project is completed within 20 weeksassuming that the path identified in part (b) is critical.d. Using independence of paths A–C–E and B–F–G only, recompute the answer to part (c).e. Recompute the answer to part (c) assuming independence of the paths identified in part (a).f. Which answer, (c), (d), or (e), is probably the most accurate?arrow_forwardThe City of Rockland is planning to build a new fire station. A project manager and the project team have been selected. The project team is interested in selecting a project scheduling technique that will be used to complete the project. The criteria for the process of selecting the project scheduling technique has been established as follows: easy to use, and shows the following – task durations, milestones, flow of work, sequence of events, which tasks can be undertaken at the same time, and how far tasks are from completion. The City Manager favors the Gantt chart, the Fire Chief likes Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT), and the project manager prefers the Critical Path Method (CPM). Assume you are the project manager; which project scheduling technique would you choose? Discuss the rationale for your decision.arrow_forwardUse the following network and the data to perform the following: a) Prepare the manpower loaded Gantt chart with total floats of this project using early start and late times. Plot the manpower resource profile that shows the total number of laborers per day over the course of the project. Prepare the Gantt chart and the resource profile using the early start and finish dates of activities (not necessary to produce the late start and finish charts). b) Level the manpower resource given the constraint that the owner has only 14 workers to allocate to this project per day. Please try to do in excel. Thannksarrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.
Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.





