
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The C atom in the
Answer to Problem 19.1P
The product of the given reaction is
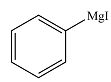
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
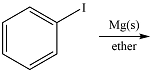
Magnesium is an active metal and reacts with the polar
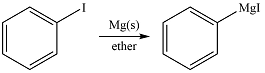
Thus, the product of the reaction is phenyl magensium iodide:

The structure of the product was drawn based on reversal of the charge on the carbon atom from the
(b)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The C atom in the
Answer to Problem 19.1P
The product of the given reaction is
![]()
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
![]()
The
![]()
In essence, the reaction inserts the metal atom between the C and Br atoms and leads to a reversal of the charge on the carbon atom.
Thus, the product of the reaction is
![]()
The product of the reaction was drawn based on the reversal of charge on the C atom bonded to bromine.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The C atom in the
Answer to Problem 19.1P
The product of the reaction is
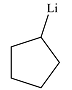
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
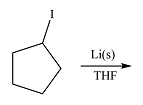
Li is a very active metal and will extract the iodine atom from the substrate. The
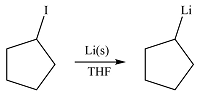
Effectively, the reaction results in the replacement of the iodine atom by Li atom, therefore, the product will be

The product of the reaction was drawn based on the reversal of the charge on the carbon atom initially bonded to iodine.
(d)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The C atom in the
This reverses the initial polarity (charge) of the carbon, allowing it to form a bond with an electron-poor carbon from say a carbonyl carbon.
Answer to Problem 19.1P
The product of the given reaction is
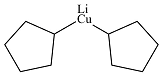
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
![]()
The product from part (c) is cyclopentyllithium. Two moles of this compound will react with one of copper(I) iodide to form
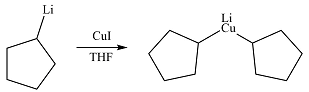
The carbon atom in the
The product of the reactio is, therefore,

The product of the reaction was drawn based formation of a bond between the relatively electron-rich carbon atoms and the copper atom.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
ORG.CHEM W/TEXT+SOLU.MANUAL
- Predict the major product of each of the following reactions and provide the complete, detailed mechanismarrow_forwardDraw the complete, detailed mechanism for each of the following reactions and predict the major products.arrow_forwardSolve correctly please. With explanation also. (Answer only if sure) What is the major product of the following reaction?arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism and the major organic product for each of the following reactions.arrow_forwardPredict the major product of each of the reactions shown here and provide the complete, detailed mechanism.arrow_forwardDraw the complete mechanism and the major organic product for each of the following reactions.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
