
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The class of given compound is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 43E
The class of compound
Explanation of Solution
The given organic compound is
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia. The formula of ammonia is
When the hydrogen of the ammonia is replaced by alkyl group amines is formed. The general formula of amines is shown below.
Therefore, the class of compound
The class of given has been rightfully identified.
(b)
Interpretation:
The class of given compound is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The functional groups are atoms or the group of atoms that acts as substituents in the molecules and are responsible for their characteristic reactions. The functional group containing oxygen atoms are alcohol group, carboxylic acid group, aldehyde group, ketone group, phenols, ethers, and their derivatives.
Answer to Problem 43E
The class of compound
Explanation of Solution
The given organic compound is
Halogen is the elements that belong to the seventeenth group of the periodic table. When a halogen is combined with a hydrocarbon, then organic halides are formed. Fluorine is halogen.
Therefore, the class of compound
The class of given has been rightfully identified.
(c)
Interpretation:
The class of given compound is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The functional groups are atoms or the group of atoms that acts as substituents in the molecules and are responsible for their characteristic reactions. The functional group containing oxygen atoms are alcohol group, carboxylic acid group, aldehyde group, ketone group, phenols, ethers, and their derivatives.
Answer to Problem 43E
The class of the given compound is ester.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given compounds is shown below.
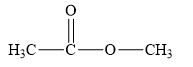
Figure 1
Esters are the derivatives of carboxylic acid. The general structure of carboxylic acid is shown below.
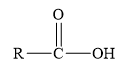
Figure 2
When the hydrogen of the hydroxyl group of carboxylic acid is replaced by another alkyl group, then ester is formed.
Therefore, the class of the given compound is ester.
The class of given has been rightfully identified.
(d)
Interpretation:
The class of given compound is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The functional groups are atoms or the group of atoms that acts as substituents in the molecules and are responsible for their characteristic reactions. The functional group containing oxygen atoms are alcohol group, carboxylic acid group, aldehyde group, ketone group, phenols, ethers, and their derivatives.
Answer to Problem 43E
The class of the given compound is a carboxylic acid.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given organic compound is shown below.
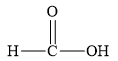
Figure 3
The given compound can release
The given compound is an organic acid.
Therefore, the class of the given compound is carboxylic acid.
The class of given has been rightfully identified.
(e)
Interpretation:
The class of given compound is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The functional groups are atoms or the group of atoms that acts as substituents in the molecules and are responsible for their characteristic reactions. The functional group containing oxygen atoms are alcohol group, carboxylic acid group, aldehyde group, ketone group, phenols, ethers, and their derivatives.
Answer to Problem 43E
The class of the given compound is aldehyde.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given organic compound is shown below.
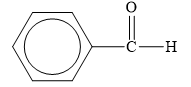
Figure 4
The carbonyl compounds are the compounds that contain
Therefore, the class of the given compound is aldehyde.
The class of given has been rightfully identified.
(f)
Interpretation:
The class of given compound is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The functional groups are atoms or the group of atoms that acts as substituents in the molecules and are responsible for their characteristic reactions. The functional group containing oxygen atoms are alcohol group, carboxylic acid group, aldehyde group, ketone group, phenols, ethers, and their derivatives.
Answer to Problem 43E
The class of given compound is ether.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given organic compound is shown below.
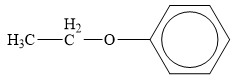
Figure 5
Ether is the derivatives of alcohol. The general formula of alcohols is shown below.
When the hydrogen of the alcohol is replaced by another alkyl group ether is formed.
Therefore, the class of given compound is ether.
The class of given has been rightfully identified.
(g)
Interpretation:
The class of given compound is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The functional groups are atoms or the group of atoms that acts as substituents in the molecules and are responsible for their characteristic reactions. The functional group containing oxygen atoms are alcohol group, carboxylic acid group, aldehyde group, ketone group, phenols, ethers, and their derivatives.
Answer to Problem 43E
The class of given compound is ketone.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given organic compound is shown below.
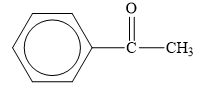
Figure 6
The carbonyl compounds are the compounds that contain
Therefore, the class of the given compound is ketone.
The class of given has been rightfully identified.
(h)
Interpretation:
The class of given compound is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The functional groups are atoms or the group of atoms that acts as substituents in the molecules and are responsible for their characteristic reactions. The functional group containing oxygen atoms are alcohol group, carboxylic acid group, aldehyde group, ketone group, phenols, ethers, and their derivatives.
Answer to Problem 43E
The class of the given compound is amide.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given compounds is shown below.
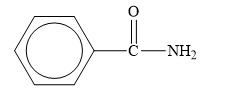
Figure 7
Amides are the derivatives of carboxylic acid. The general structure of carboxylic acid is shown below.
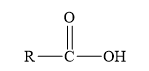
Figure 2
When the hydroxyl group of a carboxylic acid is replaced by amine group, then amide is formed.
Therefore, the class of the given compound is amide.
The class of given has been rightfully identified.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY-STD.GDE.+SOL.MAN
- Draw the condensed structures of the compounds formedfrom (a) butanoic acid and methanol, (b) benzoic acid and2-propanol, (c) propanoic acid and dimethylamine. Namethe compound in each case.arrow_forwardFor each of the following, state whether the two structural formulae show representconstitutional isomers or same compounds or different compounds.arrow_forwardWrite a condensed structural formula for an acid with the formula C4H8O2arrow_forward
- How many gauche interations are there in ethylcyclohexane?arrow_forwardSelect the functional groups that are PRESENTS in the compund. Choose between these options below. -Ketone, Aromatic, Amine, Carboxylic Acid, Amide, Aldehyde, Ether, Ester.arrow_forwardDraw the structural formula(s) for the constitutional isomer(s) with the molecular formula C7H16 that have an unbranched chain.arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
