
(a)
The period of vibration.
Answer to Problem 19.41P
Period of vibration,
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
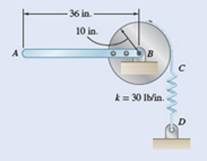
Weight of rod
Weight of disc
Spring constant
Length
Radius
The free body diagram of the given bar is as follows:
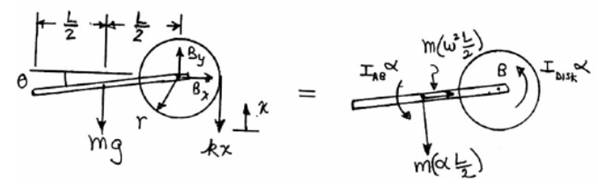
Now taking moment about point B,
Here,
And also from the statics of the diagram;
Assuming small angles
First we calculate the moment of inertia for AB,
Now, for disc the moment of inertia is,
By putting all the values in the above equation we get,
Compare the above equation with un-damped equation of vibration;
Then, Natural frequency:
And, Period
(b)
Maximum velocity at point A.
Answer to Problem 19.41P
Maximum velocity,
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
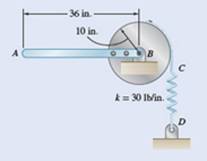
Weight of rod
Weight of disc
Spring constant
Length
Radius
The free body diagram of the given bar is as follows:
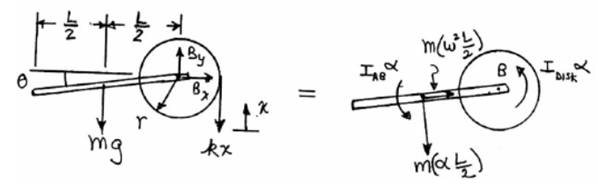
Now taking moment about point B,
Here,
And also, from the statics of the diagram;
Assuming small angles
First we calculate the moment of inertia for AB,
Now, for disc the moment of inertia is,
By putting all the values in the above equation we get,
Compare the above equation with un-damped equation of vibration;
Then, Natural frequency:
Maximum velocity:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Package: Vector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics With 1 Semester Connect Access Card
- A slender 10-kg bar AB with a length of l = 0.6 m is connected to two collars of negligible weight. Collar A is attached to a spring with a constant of k = 1.5 kN/m and can slide on a horizontal rod, while collar B can slide freely on a vertical rod. Knowing that the system is in equilibrium when bar AB is vertical and that collar A is given a small displacement and released, determine the period of the resulting vibrations.arrow_forwardTwo 12-lb uniform disks are attached to the 20-lb rod AB as shown. Knowing that the constant of the spring is 30 lb/in. and that the disks roll without sliding, determine the frequency of vibration of the system.arrow_forwardA 3-kg slender rod AB is bolted to a 5-kg uniform disk. A spring of constant 280 N/m is attached to the disk and is unstretched in the position shown. If end B of the rod is given a small displacement and released, determine the period of vibration of the system.arrow_forward
- A uniform disk of radius r = 120 mm is welded at its center to two elastic rods of equal length with fixed ends at A and B. Knowing that the disk rotates through an 8° angle when a 500-mN.m couple is applied to the disk and that it oscillates with a period of 1.3 s when the couple is removed, determine (a) the mass of the disk, (b) the period of vibration if one of the rods is removed.arrow_forwardA 6-kg uniform cylinder can roll without sliding on a horizontal surface and is attached by a pin at point C to the 4-kg horizontal bar AB. The bar is attached to two springs, each having a constant of k = 4.2 kN/m, as shown. The bar is moved 12 mm to the right of the equilibrium position and released. Determine the period of vibration of the system. (Round the final answer to three decimal places.) The period of vibration of the system is ___s.arrow_forwardTwo uniform rods, each of weight W = 1.2 lb and length l = 8 in., are welded together to form the assembly shown. Knowing that the constant of each spring is k = 0.6 lb/in. and that end A is given a small displacement and released, determine the frequency of the resulting motion.arrow_forward
- A 30-lb uniform cylinder can roll without sliding on a 15° incline. A belt is attached to the rim of the cylinder, and a spring holds the cylinder at rest in the position shown. If the center of the cylinder is moved 2 in. down the incline and released, determine (a) the period of vibration, (b) the maximum acceleration of the center of the cylinder.arrow_forwardAn 800-g rod AB is bolted to a 1.2-kg disk. A spring of constant k = 12 N/m is attached to the center of the disk at A and to the wall at C . Knowing that the disk rolls without sliding, determine the period of small oscillations of the system.arrow_forwardA 360-lb motor is supported by springs of total constant 12.5 kips/ft. The unbalance of the rotor is equivalent to a 0.9-oz weight located 7.5 in. from the axis of rotation. Determine the range of speeds of the motor for which the amplitude of the fluctuating force exerted on the foundation is less than 5 lb.arrow_forward
- A spring of stiffness 2 kN/m is suspended vertically and two equal masses of 4 kg each are attached to the lower end. One of these masses is suddenly removed and the system oscillates. Determine a) The amplitude of vibration, b) the frequency of vibration, and c) the velocity and acceleration of the mass when passing through half amplitude position.arrow_forwardAn 8-kg uniform disk of radius 200 mm is welded to a vertical shaft with a fixed end at B. The disk rotates through an angle of 3° when a static couple of magnitude 50N.m is applied to it. If the disk is acted upon by a periodic torsional couple of magnitude Tm=60N.m. determine the range of values of vf for which the amplitude of the vibration is less than the angle of rotation caused by a static couple of magnitude Tm.arrow_forwardTwo uniform rods AB and CD, each of length l and mass m, are attached to gears as shown. Knowing that the mass of gear C is m, are attached to gears as shown. Knowing that the mass of gear A is 4m, determine the period of small oscillations of the system.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





