
Concept explainers
Astronauts on a distant planet toss a rock into the air. With the aid of a camera that takes pictures at a steady rate, they record the rock’s height as a function of time as given in the following table, (a) Find the rock’s average velocity in the time interval between each measurement and the next, (b) Using these average velocities to approximate instantaneous velocities at the midpoints of the lime intervals, make a graph of velocity as a function of time, (c) Does the rock move with constant acceleration? If so, plot a straight line of best fit on the graph and calculate its slope to find the acceleration.
(a)
The average velocity of rock in the time interval between each measurement and the next.
Answer to Problem 2.76AP
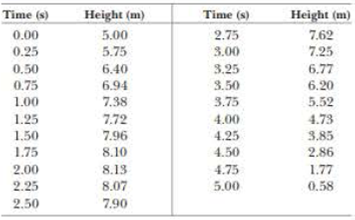
The rock’s height as a function of time is shown in below given table.
| Time (s) | Height (m) | Average velocity (
| Midpoint time (s) |
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table (1)
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The rock’s height as a function of time is shown in below given table.
| Time (s) | Height (m) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table (2)
The formula to calculate the average velocity is,
Here,
The formula to calculate the midpoint time is,
Here,
Substitute the values given in table (1) and calculate the average velocity and midpoint time as mentioned in the table.
| Time (s) | Height (m) | Average velocity (
| Midpoint time (s) |
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table (3)
Conclusion:
Therefore, the rock’s height as a function of time is shown in below given table.
| Time (s) | Height (m) | Average velocity (
| Midpoint time (s) |
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(b)
To draw: The velocity versus time graph.
Answer to Problem 2.76AP
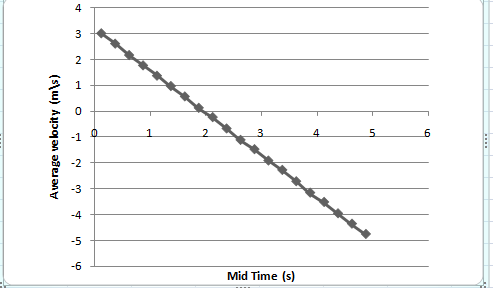
The average velocity versus mid time graph is,
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
The velocity is defined as rate of change of position of the object. The Midpoint time is the mean of the time interval taken for which position of the object is defined. Plot the difference of the position with respect to midpoint time to obtain velocity time graph.
From part (a) make a graph using values of average velocity and mid time from table (1) as shown below.

Figure (1)
Conclusion:
Therefore, the average velocity versus mid time graph is,

(c)
Whether the rock moves with constant acceleration and determine the acceleration.
Answer to Problem 2.76AP
The rock moves with constant acceleration and the acceleration is
Explanation of Solution
The formula to calculate speed of rock from its graph in figure (1) is,
Substitute
Thus the slope of curve is
Hence, the acceleration of rock is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the rock moves with constant acceleration and the acceleration is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update, Hybrid Edition (with Enhanced WebAssign Multi-Term LOE Printed Access Card for Physics)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
Essential University Physics: Volume 2 (3rd Edition)
College Physics
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
- The following table gives the position s1t2 of an object moving along a line at time t. Determine the average velocities over the time intervals 31, 1.014, 31, 1.0014, and 31, 1.00014. Then make a conjecture about the value of the instantaneous velocity at t = 1.arrow_forwardTrue or false-Consider an object that starts from rest and moves with constant acceleration. The plot of displacement versus time for such motion is a curved line while the plot of displacement versus time squared is a straight line.arrow_forwardIf a ball is thrown straight up into the air with an initial velocity of 70 ft/s, it height in feet after ? second is given by y=70t−16t^2. Find the average velocity for the time period begining when t=2 and lasting 0.1 seconds = 0.01 seconds= 0.001 seconds= Finally based on the above results, guess what the instantaneous velocity of the ball is when ?=2.arrow_forward
- A box was dropped from the top of a building. Which of the following is true regarding its displacement per second? (A) The distance covered by the falling box per second increases. (B) The distance covered by the falling box per second decreases. (C) The distance covered by the falling box per second remains constant. (D) I need more details to confirm any of these three statements.arrow_forwardPlot a graph using the values given in the table of distance and time. Determine the moving average velocity during the first 5.0 seconds. Determine the moving average velocity during the time interval of 2.0 to 13.0 seconds. Determine the time if the velocity is zero. Determine the velocity for each given time: 3.0 s 6.5 s 11.0 sarrow_forwardIf a drag racing motorcyclist has an initial speed of 10 m/s, and then he/she accelerates for 15 seconds at 15 m/s2, what is the velocity after 15 seconds? (do not include units in answer)arrow_forward
- Which of the following is the correct conversion of initial velocity in base SI units? Refer to the problem given below. Lamborghini Murcielago is one of the most iconic cars ever as it was featured as a Batmobile in the third installment of Batman Trilogy directed by Christopher Nolan. If it can go from 0 to 60 miles per hour in 3 seconds, what is its rate of change in velocity per unit time? (1 mile is equal to 1.61 kilometers)arrow_forwardFor an object, for example a car, which is constantly decelerating, which of the following would be an appropriate position versus time graph?arrow_forwardIf the average velocity of a car is nonzero for some time interval does this mean that the instantaneous velocity is never zero?arrow_forward
- If you divide the total distance traveled on a car trip (as determined by the odometer) by the time for the trip, are you calculating the average speed or the magnitude of the average velocity? Under what circumstances are these two quantities the same?arrow_forwardA Honda Jazz is stopped at a traffic light. It then travels along a straight road so that its distancefrom the light is given bya. Calculate the average velocity of the car from the time interval t =0 to t 10.0 sb. Calculate the instantaneous velocity of the car at t =0, t =5.0 s and t = 10.0 sarrow_forwardWhat expression in cartesian unit-vector notation for the average acceleration of the car during the given time period using the symbols be provided? And how does that help find the magnitude in m/s2 of the average acceleration of the car during the given time?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill





