
Concept explainers
a)
To determine: The suitable outsourcing provider using factor- rating method.
Introduction:
Factor-rating method:
The factor-rating method is a quantitative approach to make a decision from various alternatives such that the decision is beneficial to the firm involved. This method is utilized to decide on new layout, new locations, best supplier, outsourcing providers etc.
a)
Answer to Problem 8P
The suitable outsourcing provider is Canada.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
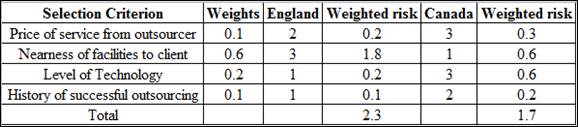
| Selection criterion | Weight | England | Canada |
| Price of service from outsourcer | 0.1 | 2 | 3 |
| Nearness of facilities to client | 0.6 | 3 | 1 |
| Level of technology | 0.2 | 1 | 3 |
| History of successful outsourcing | 0.1 | 1 | 2 |
Low Risk = 1
High Risk = 3
Formula to calculate weighted risk:
Formula to calculate Total weighted risk:
Excel Formula:
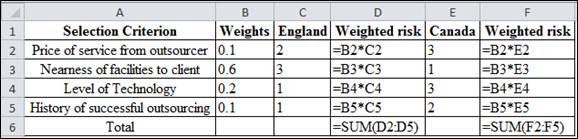
Calculation of weighted risk for England:
The weighted risk is calculated my multiplying the weights with risk rating of each criteria.
The weighted risk is calculated as follows:
Service from outsourcer:
The weighted risk for price of service from outsourcer is 0.2.
Nearness of facilities to client:
The weighted risk for Nearness of facilities to client is 1.8.
Level of Technology:
The weighted risk for Level of Technology is 0.2.
History of successful outsourcing:
The weighted risk for History of successful outsourcing is 0.1.
Calculation of Total weighted risk:
The total weighted risk is calculated be summing all the weighted risk values.
The total weighted risk for England is 2.3.
Calculation of weighted risk for Canada:
The weighted risk is calculated my multiplying the weights with risk rating of each criteria.
The weighted risk is calculated as follows:
Price of service from outsourcer:
The weighted risk for price of service from outsourcer is 0.3.
Nearness of facilities to client:
The weighted risk for nearness of facilities to client is 0.6.
Level of Technology:
The weighted risk for Level of Technology is 0.6.
History of successful outsourcing:
The weighted risk for History of successful outsourcing is 0.2.
Calculation of Total weighted risk:
The total weighted risk is calculated be summing all the weighted risk values.
The total weighted risk for Canada is 1.7.
The weighted risk value for England is 2.3. The weighted risk value for Canada is 1.7. Since, the risk value for Canada is less for England (1.7 < 2.3), Canada is selected.
The suitable outsourcing provider is Canada.
b)
To determine: The impact of doubling the weights used in part (a).
Introduction:
Factor-rating method:
The factor-rating method is a quantitative approach to make a decision from various alternatives such that the decision is beneficial to the firm involved. This method is utilized to decide on new layout, new locations, best supplier, outsourcing providers etc.
b)
Answer to Problem 8P
The Doubling of weights will have No Change.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
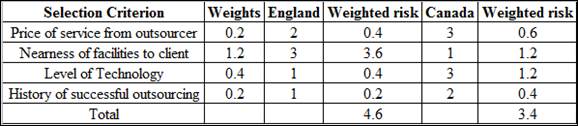
| Selection criterion | Weight | England | Canada |
| Price of service from outsourcer | 0.2 | 2 | 3 |
| Nearness of facilities to client | 1.2 | 3 | 1 |
| Level of technology | 0.4 | 1 | 3 |
| History of successful outsourcing | 0.2 | 1 | 2 |
Low Risk = 1
High Risk = 3
Formula to calculate weighted risk:
Formula to calculate Total weighted risk:
Excel Formula:
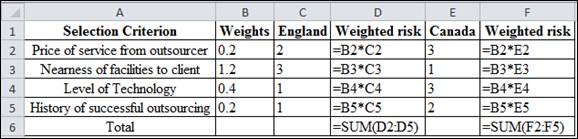
Calculation of weighted risk for England:
The weighted risk is calculated my multiplying the weights with risk rating of each criteria.
The weighted risk is calculated as follows:
Price of service from outsourcer:
The weighted risk for price of service from outsourcer is 0.4.
Nearness of facilities to client:
The weighted risk for nearness of facilities to client is 3.6.
Level of Technology:
The weighted risk for Level of Technology is 0.4.
History of successful outsourcing:
The weighted risk for History of successful outsourcing is 0.2.
Calculation of Total weighted risk:
The total weighted risk is calculated be summing all the weighted risk values.
The total weighted risk for England is 4.6.
Calculation of weighted risk for Canada:
The weighted risk is calculated my multiplying the weights with risk rating of each criteria.
The weighted risk is calculated as follows:
Price of service from outsourcer:
The weighted risk for price of service from outsourcer is 0.6.
Nearness of facilities to client:
The weighted risk for nearness of facilities to client is 1.2.
Level of Technology:
The weighted risk for Level of Technology is 1.2.
History of successful outsourcing:
The weighted risk for History of successful outsourcing is 0.4.
Calculation of Total weighted risk:
The total weighted risk is calculated be summing all the weighted risk values.
The total weighted risk for Canada is 3.4.
The weighted risk value for England is 4.6. The weighted risk value for Canada is 3.4. Since, the risk value for Canada is less for England (3.4 < 4.6), Canada is selected.
The doubling of weights of the risk avoidance criteria does not alter the result arrived at in part (a). The weighted risk value is doubled for England and Canada. But, the risk value of Canada is still lower than England. The result will not change irrespective of doubling the weights because the risk avoidance criterion value is unaltered.
Hence, the Doubling of weights will have No Change.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK PRINCIPLES OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
- The Global Sourcing Wire Harness Decision Sheila Austin, a buyer at Autolink, a Detroit-based producer of subassemblies for the automotive market, has sent out requests for quotations for a wiring harness to four prospective suppliers. Only two of the four suppliers indicated an interest in quoting the business: Original Wire (Auburn Hills, MI) and Happy Lucky Assemblies (HLA) of Guangdong Province, China. The estimated demand for the harnesses is 5,000 units a month. Both suppliers will incur some costs to retool for this particular harness. The harnesses will be prepackaged in 24 12 6-inch cartons. Each packaged unit weighs approximately 10 pounds. Quote 1 The first quote received is from Original Wire. Auburn Hills is about 20 miles from Autolinks corporate headquarters, so the quote was delivered in person. When Sheila went down to the lobby, she was greeted by the sales agent and an engineering representative. After the quote was handed over, the sales agent noted that engineering would be happy to work closely with Autolink in developing the unit and would also be interested in future business that might involve finding ways to reduce costs. The sales agent also noted that they were hungry for business, as they were losing a lot of customers to companies from China. The quote included unit price, tooling, and packaging. The quoted unit price does not include shipping costs. Original Wire requires no special warehousing of inventory, and daily deliveries from its manufacturing site directly to Autolinks assembly operations are possible. Original Wire Quote: Unit price = 30 Packing costs = 0.75 per unit Tooling = 6,000 one-time fixed charge Freight cost = 5.20 per hundred pounds Quote 2 The second quote received is from Happy Lucky Assemblies of Guangdong Province, China. The supplier must pack the harnesses in a container and ship via inland transportation to the port of Shanghai in China, have the shipment transferred to a container ship, ship material to Seattle, and then have material transported inland to Detroit. The quoted unit price does not include international shipping costs, which the buyer will assume. HLA Quote: Unit price = 19.50 Shipping lead time = Eight weeks Tooling = 3,000 In addition to the suppliers quote, Sheila must consider additional costs and information before preparing a comparison of the Chinese suppliers quotation: Each monthly shipment requires three 40-foot containers. Packing costs for containerization = 2 per unit. Cost of inland transportation to port of export = 200 per container. Freight forwarders fee = 100 per shipment (letter of credit, documentation, etc.). Cost of ocean transport = 4,000 per container. This has risen significantly in recent years due to a shortage of ocean freight capacity. Marine insurance = 0.50 per 100 of shipment. U.S. port handling charges = 1,200 per container. This fee has also risen considerably this year, due to increased security. Ports have also been complaining that the charges may increase in the future. Customs duty = 5% of unit cost. Customs broker fees per shipment = 300. Transportation from Seattle to Detroit = 18.60 per hundred pounds. Need to warehouse at least four weeks of inventory in Detroit at a warehousing cost of 1.00 per cubic foot per month, to compensate for lead time uncertainty. Sheila must also figure the costs associated with committing corporate capital for holding inventory. She has spoken to some accountants, who typically use a corporate cost of capital rate of 15%. Cost of hedging currencybroker fees = 400 per shipment Additional administrative time due to international shipping = 4 hours per shipment 25 per hour (estimated) At least two five-day visits per year to travel to China to meet with supplier and provide updates on performance and shipping = 20,000 per year (estimated) The international sourcing costs must be absorbed by Sheila, as the supplier does not assume any of the additional estimated costs and invoice Sheila later, or build the costs into a revised unit price. Sheila feels that the U.S. supplier is probably less expensive, even though it quoted a higher price. Sheila also knows that this is a standard technology that is unlikely to change during the next three years, but which could be a contract that extends multiple years out. There is also a lot of hall talk amongst the engineers on her floor about next-generation automotive electronics, which will completely eliminate the need for wire harnesses, which will be replaced by electronic components that are smaller, lighter, and more reliable. She is unsure about how to calculate the total costs for each option, and she is even more unsure about how to factor these other variables into the decision. Based on this case, do you think international purchasing is more or less complex than domestic purchasing? Why? Is it worth the additional effort?arrow_forwardThe Global Sourcing Wire Harness Decision Sheila Austin, a buyer at Autolink, a Detroit-based producer of subassemblies for the automotive market, has sent out requests for quotations for a wiring harness to four prospective suppliers. Only two of the four suppliers indicated an interest in quoting the business: Original Wire (Auburn Hills, MI) and Happy Lucky Assemblies (HLA) of Guangdong Province, China. The estimated demand for the harnesses is 5,000 units a month. Both suppliers will incur some costs to retool for this particular harness. The harnesses will be prepackaged in 24 12 6-inch cartons. Each packaged unit weighs approximately 10 pounds. Quote 1 The first quote received is from Original Wire. Auburn Hills is about 20 miles from Autolinks corporate headquarters, so the quote was delivered in person. When Sheila went down to the lobby, she was greeted by the sales agent and an engineering representative. After the quote was handed over, the sales agent noted that engineering would be happy to work closely with Autolink in developing the unit and would also be interested in future business that might involve finding ways to reduce costs. The sales agent also noted that they were hungry for business, as they were losing a lot of customers to companies from China. The quote included unit price, tooling, and packaging. The quoted unit price does not include shipping costs. Original Wire requires no special warehousing of inventory, and daily deliveries from its manufacturing site directly to Autolinks assembly operations are possible. Original Wire Quote: Unit price = 30 Packing costs = 0.75 per unit Tooling = 6,000 one-time fixed charge Freight cost = 5.20 per hundred pounds Quote 2 The second quote received is from Happy Lucky Assemblies of Guangdong Province, China. The supplier must pack the harnesses in a container and ship via inland transportation to the port of Shanghai in China, have the shipment transferred to a container ship, ship material to Seattle, and then have material transported inland to Detroit. The quoted unit price does not include international shipping costs, which the buyer will assume. HLA Quote: Unit price = 19.50 Shipping lead time = Eight weeks Tooling = 3,000 In addition to the suppliers quote, Sheila must consider additional costs and information before preparing a comparison of the Chinese suppliers quotation: Each monthly shipment requires three 40-foot containers. Packing costs for containerization = 2 per unit. Cost of inland transportation to port of export = 200 per container. Freight forwarders fee = 100 per shipment (letter of credit, documentation, etc.). Cost of ocean transport = 4,000 per container. This has risen significantly in recent years due to a shortage of ocean freight capacity. Marine insurance = 0.50 per 100 of shipment. U.S. port handling charges = 1,200 per container. This fee has also risen considerably this year, due to increased security. Ports have also been complaining that the charges may increase in the future. Customs duty = 5% of unit cost. Customs broker fees per shipment = 300. Transportation from Seattle to Detroit = 18.60 per hundred pounds. Need to warehouse at least four weeks of inventory in Detroit at a warehousing cost of 1.00 per cubic foot per month, to compensate for lead time uncertainty. Sheila must also figure the costs associated with committing corporate capital for holding inventory. She has spoken to some accountants, who typically use a corporate cost of capital rate of 15%. Cost of hedging currencybroker fees = 400 per shipment Additional administrative time due to international shipping = 4 hours per shipment 25 per hour (estimated) At least two five-day visits per year to travel to China to meet with supplier and provide updates on performance and shipping = 20,000 per year (estimated) The international sourcing costs must be absorbed by Sheila, as the supplier does not assume any of the additional estimated costs and invoice Sheila later, or build the costs into a revised unit price. Sheila feels that the U.S. supplier is probably less expensive, even though it quoted a higher price. Sheila also knows that this is a standard technology that is unlikely to change during the next three years, but which could be a contract that extends multiple years out. There is also a lot of hall talk amongst the engineers on her floor about next-generation automotive electronics, which will completely eliminate the need for wire harnesses, which will be replaced by electronic components that are smaller, lighter, and more reliable. She is unsure about how to calculate the total costs for each option, and she is even more unsure about how to factor these other variables into the decision. Calculate the total cost per unit of purchasing from Original Wire.arrow_forwardThe Global Sourcing Wire Harness Decision Sheila Austin, a buyer at Autolink, a Detroit-based producer of subassemblies for the automotive market, has sent out requests for quotations for a wiring harness to four prospective suppliers. Only two of the four suppliers indicated an interest in quoting the business: Original Wire (Auburn Hills, MI) and Happy Lucky Assemblies (HLA) of Guangdong Province, China. The estimated demand for the harnesses is 5,000 units a month. Both suppliers will incur some costs to retool for this particular harness. The harnesses will be prepackaged in 24 12 6-inch cartons. Each packaged unit weighs approximately 10 pounds. Quote 1 The first quote received is from Original Wire. Auburn Hills is about 20 miles from Autolinks corporate headquarters, so the quote was delivered in person. When Sheila went down to the lobby, she was greeted by the sales agent and an engineering representative. After the quote was handed over, the sales agent noted that engineering would be happy to work closely with Autolink in developing the unit and would also be interested in future business that might involve finding ways to reduce costs. The sales agent also noted that they were hungry for business, as they were losing a lot of customers to companies from China. The quote included unit price, tooling, and packaging. The quoted unit price does not include shipping costs. Original Wire requires no special warehousing of inventory, and daily deliveries from its manufacturing site directly to Autolinks assembly operations are possible. Original Wire Quote: Unit price = 30 Packing costs = 0.75 per unit Tooling = 6,000 one-time fixed charge Freight cost = 5.20 per hundred pounds Quote 2 The second quote received is from Happy Lucky Assemblies of Guangdong Province, China. The supplier must pack the harnesses in a container and ship via inland transportation to the port of Shanghai in China, have the shipment transferred to a container ship, ship material to Seattle, and then have material transported inland to Detroit. The quoted unit price does not include international shipping costs, which the buyer will assume. HLA Quote: Unit price = 19.50 Shipping lead time = Eight weeks Tooling = 3,000 In addition to the suppliers quote, Sheila must consider additional costs and information before preparing a comparison of the Chinese suppliers quotation: Each monthly shipment requires three 40-foot containers. Packing costs for containerization = 2 per unit. Cost of inland transportation to port of export = 200 per container. Freight forwarders fee = 100 per shipment (letter of credit, documentation, etc.). Cost of ocean transport = 4,000 per container. This has risen significantly in recent years due to a shortage of ocean freight capacity. Marine insurance = 0.50 per 100 of shipment. U.S. port handling charges = 1,200 per container. This fee has also risen considerably this year, due to increased security. Ports have also been complaining that the charges may increase in the future. Customs duty = 5% of unit cost. Customs broker fees per shipment = 300. Transportation from Seattle to Detroit = 18.60 per hundred pounds. Need to warehouse at least four weeks of inventory in Detroit at a warehousing cost of 1.00 per cubic foot per month, to compensate for lead time uncertainty. Sheila must also figure the costs associated with committing corporate capital for holding inventory. She has spoken to some accountants, who typically use a corporate cost of capital rate of 15%. Cost of hedging currencybroker fees = 400 per shipment Additional administrative time due to international shipping = 4 hours per shipment 25 per hour (estimated) At least two five-day visits per year to travel to China to meet with supplier and provide updates on performance and shipping = 20,000 per year (estimated) The international sourcing costs must be absorbed by Sheila, as the supplier does not assume any of the additional estimated costs and invoice Sheila later, or build the costs into a revised unit price. Sheila feels that the U.S. supplier is probably less expensive, even though it quoted a higher price. Sheila also knows that this is a standard technology that is unlikely to change during the next three years, but which could be a contract that extends multiple years out. There is also a lot of hall talk amongst the engineers on her floor about next-generation automotive electronics, which will completely eliminate the need for wire harnesses, which will be replaced by electronic components that are smaller, lighter, and more reliable. She is unsure about how to calculate the total costs for each option, and she is even more unsure about how to factor these other variables into the decision. Based on the total cost per unit, which supplier should Sheila recommend?arrow_forward
- The Global Sourcing Wire Harness Decision Sheila Austin, a buyer at Autolink, a Detroit-based producer of subassemblies for the automotive market, has sent out requests for quotations for a wiring harness to four prospective suppliers. Only two of the four suppliers indicated an interest in quoting the business: Original Wire (Auburn Hills, MI) and Happy Lucky Assemblies (HLA) of Guangdong Province, China. The estimated demand for the harnesses is 5,000 units a month. Both suppliers will incur some costs to retool for this particular harness. The harnesses will be prepackaged in 24 12 6-inch cartons. Each packaged unit weighs approximately 10 pounds. Quote 1 The first quote received is from Original Wire. Auburn Hills is about 20 miles from Autolinks corporate headquarters, so the quote was delivered in person. When Sheila went down to the lobby, she was greeted by the sales agent and an engineering representative. After the quote was handed over, the sales agent noted that engineering would be happy to work closely with Autolink in developing the unit and would also be interested in future business that might involve finding ways to reduce costs. The sales agent also noted that they were hungry for business, as they were losing a lot of customers to companies from China. The quote included unit price, tooling, and packaging. The quoted unit price does not include shipping costs. Original Wire requires no special warehousing of inventory, and daily deliveries from its manufacturing site directly to Autolinks assembly operations are possible. Original Wire Quote: Unit price = 30 Packing costs = 0.75 per unit Tooling = 6,000 one-time fixed charge Freight cost = 5.20 per hundred pounds Quote 2 The second quote received is from Happy Lucky Assemblies of Guangdong Province, China. The supplier must pack the harnesses in a container and ship via inland transportation to the port of Shanghai in China, have the shipment transferred to a container ship, ship material to Seattle, and then have material transported inland to Detroit. The quoted unit price does not include international shipping costs, which the buyer will assume. HLA Quote: Unit price = 19.50 Shipping lead time = Eight weeks Tooling = 3,000 In addition to the suppliers quote, Sheila must consider additional costs and information before preparing a comparison of the Chinese suppliers quotation: Each monthly shipment requires three 40-foot containers. Packing costs for containerization = 2 per unit. Cost of inland transportation to port of export = 200 per container. Freight forwarders fee = 100 per shipment (letter of credit, documentation, etc.). Cost of ocean transport = 4,000 per container. This has risen significantly in recent years due to a shortage of ocean freight capacity. Marine insurance = 0.50 per 100 of shipment. U.S. port handling charges = 1,200 per container. This fee has also risen considerably this year, due to increased security. Ports have also been complaining that the charges may increase in the future. Customs duty = 5% of unit cost. Customs broker fees per shipment = 300. Transportation from Seattle to Detroit = 18.60 per hundred pounds. Need to warehouse at least four weeks of inventory in Detroit at a warehousing cost of 1.00 per cubic foot per month, to compensate for lead time uncertainty. Sheila must also figure the costs associated with committing corporate capital for holding inventory. She has spoken to some accountants, who typically use a corporate cost of capital rate of 15%. Cost of hedging currencybroker fees = 400 per shipment Additional administrative time due to international shipping = 4 hours per shipment 25 per hour (estimated) At least two five-day visits per year to travel to China to meet with supplier and provide updates on performance and shipping = 20,000 per year (estimated) The international sourcing costs must be absorbed by Sheila, as the supplier does not assume any of the additional estimated costs and invoice Sheila later, or build the costs into a revised unit price. Sheila feels that the U.S. supplier is probably less expensive, even though it quoted a higher price. Sheila also knows that this is a standard technology that is unlikely to change during the next three years, but which could be a contract that extends multiple years out. There is also a lot of hall talk amongst the engineers on her floor about next-generation automotive electronics, which will completely eliminate the need for wire harnesses, which will be replaced by electronic components that are smaller, lighter, and more reliable. She is unsure about how to calculate the total costs for each option, and she is even more unsure about how to factor these other variables into the decision. Calculate the total cost per unit of purchasing from Happy Lucky Assemblies.arrow_forwardThe Global Sourcing Wire Harness Decision Sheila Austin, a buyer at Autolink, a Detroit-based producer of subassemblies for the automotive market, has sent out requests for quotations for a wiring harness to four prospective suppliers. Only two of the four suppliers indicated an interest in quoting the business: Original Wire (Auburn Hills, MI) and Happy Lucky Assemblies (HLA) of Guangdong Province, China. The estimated demand for the harnesses is 5,000 units a month. Both suppliers will incur some costs to retool for this particular harness. The harnesses will be prepackaged in 24 12 6-inch cartons. Each packaged unit weighs approximately 10 pounds. Quote 1 The first quote received is from Original Wire. Auburn Hills is about 20 miles from Autolinks corporate headquarters, so the quote was delivered in person. When Sheila went down to the lobby, she was greeted by the sales agent and an engineering representative. After the quote was handed over, the sales agent noted that engineering would be happy to work closely with Autolink in developing the unit and would also be interested in future business that might involve finding ways to reduce costs. The sales agent also noted that they were hungry for business, as they were losing a lot of customers to companies from China. The quote included unit price, tooling, and packaging. The quoted unit price does not include shipping costs. Original Wire requires no special warehousing of inventory, and daily deliveries from its manufacturing site directly to Autolinks assembly operations are possible. Original Wire Quote: Unit price = 30 Packing costs = 0.75 per unit Tooling = 6,000 one-time fixed charge Freight cost = 5.20 per hundred pounds Quote 2 The second quote received is from Happy Lucky Assemblies of Guangdong Province, China. The supplier must pack the harnesses in a container and ship via inland transportation to the port of Shanghai in China, have the shipment transferred to a container ship, ship material to Seattle, and then have material transported inland to Detroit. The quoted unit price does not include international shipping costs, which the buyer will assume. HLA Quote: Unit price = 19.50 Shipping lead time = Eight weeks Tooling = 3,000 In addition to the suppliers quote, Sheila must consider additional costs and information before preparing a comparison of the Chinese suppliers quotation: Each monthly shipment requires three 40-foot containers. Packing costs for containerization = 2 per unit. Cost of inland transportation to port of export = 200 per container. Freight forwarders fee = 100 per shipment (letter of credit, documentation, etc.). Cost of ocean transport = 4,000 per container. This has risen significantly in recent years due to a shortage of ocean freight capacity. Marine insurance = 0.50 per 100 of shipment. U.S. port handling charges = 1,200 per container. This fee has also risen considerably this year, due to increased security. Ports have also been complaining that the charges may increase in the future. Customs duty = 5% of unit cost. Customs broker fees per shipment = 300. Transportation from Seattle to Detroit = 18.60 per hundred pounds. Need to warehouse at least four weeks of inventory in Detroit at a warehousing cost of 1.00 per cubic foot per month, to compensate for lead time uncertainty. Sheila must also figure the costs associated with committing corporate capital for holding inventory. She has spoken to some accountants, who typically use a corporate cost of capital rate of 15%. Cost of hedging currencybroker fees = 400 per shipment Additional administrative time due to international shipping = 4 hours per shipment 25 per hour (estimated) At least two five-day visits per year to travel to China to meet with supplier and provide updates on performance and shipping = 20,000 per year (estimated) The international sourcing costs must be absorbed by Sheila, as the supplier does not assume any of the additional estimated costs and invoice Sheila later, or build the costs into a revised unit price. Sheila feels that the U.S. supplier is probably less expensive, even though it quoted a higher price. Sheila also knows that this is a standard technology that is unlikely to change during the next three years, but which could be a contract that extends multiple years out. There is also a lot of hall talk amongst the engineers on her floor about next-generation automotive electronics, which will completely eliminate the need for wire harnesses, which will be replaced by electronic components that are smaller, lighter, and more reliable. She is unsure about how to calculate the total costs for each option, and she is even more unsure about how to factor these other variables into the decision. Are there any other issues besides cost that Sheila should evaluate?arrow_forwardKantanka Limited is a family-owned automobile manufacturer with origin in Agona Swedru in the Central Region of Ghana. Kantanka Limited manufactures and sells saloon cars, trucks, SUVs, and trailers with related accessories. The Company is the current market leader, but is considering outsourcing their automobile production to increase margins. A large scale outsourcing move would be a first for the industry, and the Company wants to know if this is a worthwhile proposition. There are two options being explored: (i) full outsourcing an automobile manufacturing plant in China; (ii) outsourcing final production in Ivory Coast with parts provided from China. You are free to use relevant diagrams/frameworks/figures in supporting your answers to the questions below NOTE; PLEASE I NEED A DIFFERENT VIEW OR ANSWER APART FROM THE PREVIOUS ANSWER GIVEN. What could be the problem(s) justifying the outsourcing decision? Should the Company outsource their automobile production and why? Which…arrow_forward
- Kantanka Limited is a family-owned automobile manufacturer with origin in Agona Swedru in the Central Region of Ghana. Kantanka Limited manufactures and sells saloon cars, trucks, SUVs, and trailers with related accessories. The Company is the current market leader, but is considering outsourcing their automobile production to increase margins. A large scale outsourcing move would be a first for the industry, and the Company wants to know if this is a worthwhile proposition. There are two options being explored: (i) full outsourcing an automobile manufacturing plant in China; (ii) outsourcing final production in Ivory Coast with parts provided from China. You are free to use relevant diagrams/frameworks/figures in supporting your answers to the questions below a. What could be the problem(s) justifying the outsourcing decision? b. Should the Company outsource their automobile production and why? c. Which outsourcing option is the optimal choice? Your response should engage with the…arrow_forwardMany would argue that the TV manufacturing business has become largely a commodity business,and competition is based on price, with many good brands offered at low prices at retailers such asWalmart. The manufacturers of TVs are said to have a barrier to entry from other potential competitors because the existing manufacturers (Phillips, Sony, Samsung, etc.) have spent huge sumsto develop their brands and manufacturing facilities. In recent years, there has been a large growthin the number of contract manufacturers (such as Flextronics) that manufacture TVs for the largefirms. How does this affect the competition within the industry? Are there now new opportunities forsmaller manufacturers of TVs?arrow_forwardStrategic Planning, Core Competencies and OutsourcingClndia Pragram Technologies, Inc. , has narrowed its choice of outsourcing provider to two firms located in different countries. Pragram wants to decide which one of the two countries is the better choice, based on risk-avoidance criteria. She has polled her executives and established four criteria.The resulting ratings for the two countries are presented in the table below, where l is a lower risk and 3 is a higher risk. The executives have determined four criteria weightings: Price, with a weight of 0. 1; Nearness, with 0.6; Technology, with 0.2; and History, with 0.1.a) Using the factor-rating method, which country would you select?b) Double each of the weights used in part (a) (to 0.2, 1.2, 0.4, and 0.2, respectively). What effect does this have on your answer? Why?arrow_forward
- Aling Rosa is a sari-sari store owner. Along the street where she operates her store, there are three other stores offering similar products at similar prices. What should she do to allow her business to thrive in the next three to five years? Determine whether building good supplier relations will allow her to lower costs, and therefore provide lower prices. Determine whether selling hard-to-get items will allow her to attract customers. Identify a customer group within her barangay or street, particularly those with unsatisfied needs and wants in terms of product and service offerings, and consider changing the business model towards that buyer preference. All of the above.arrow_forwardMacrosoft Corporation is a software giant in personal computers (PCs). Although its flagship operating system ‘Meadow’ is still dominating in the PC market, the burgeoning of tablets and smartphones in recent years has been chewing up the PC market. In fact, the numbers of new Meadow users was shrinking every year. In view of this situation, Macrosoft is considering making an offer to purchase Oats Production, and upstart smartphone producer in China. The management of Macrosoft hopes that the acquisition could allow the company to explore the smartphone software market and bring in new revenue to the firm. The treasurer of Macrosoft has collected the following information: Macrosoft Corporation Oats Production Shares outstanding 1,500,000 800,000 Earnings $8,400,000 $2,400,000 Divdends $4,200,000 $1,800,000 Price-earnings ratio 18X 15X The treasurer also discovers that the earnings and dividends of Oats will grow at a constant rate of 6% every year. If the acquisition…arrow_forwardAssume that Trinbago is a small country that produces wine and motor vehicles, where motor vehicles are capital-intensive. Trinbago is also capital intensive, and the standard Heckscher -Ohlin (H-O) assumptions hold. The other country in the model is Vincyland. Question: Give a background on the Heckscher-Ohlin Trade model and then answer the following questions. (a) Based on the H-O assumptions, which good should Vincyland export, and why? (b) What trade pattern would occur if the Leontief Paradox holds? Which two (2) explanations of the Leontief Paradox most strongly support the H-O theory? Give the reasons. (c) In autarky, according to Ohlin, how does Trinbago’s relative price of labor compare to Vincyland’s?arrow_forward
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
