
Concept explainers
Calen Company manufactures and sells three products in a factory of three departments. Both labor and machine time are applied to the products as they pass through each department. The nature of the machine processing and of the labor skills required in each department is such that neither machines nor labor can be switched from one department to another.
Calen’s management is attempting to plan its production schedule for the next several months. The planning is complicated by the fact that labor shortages exist in the community and some machines will be down several months for repairs.
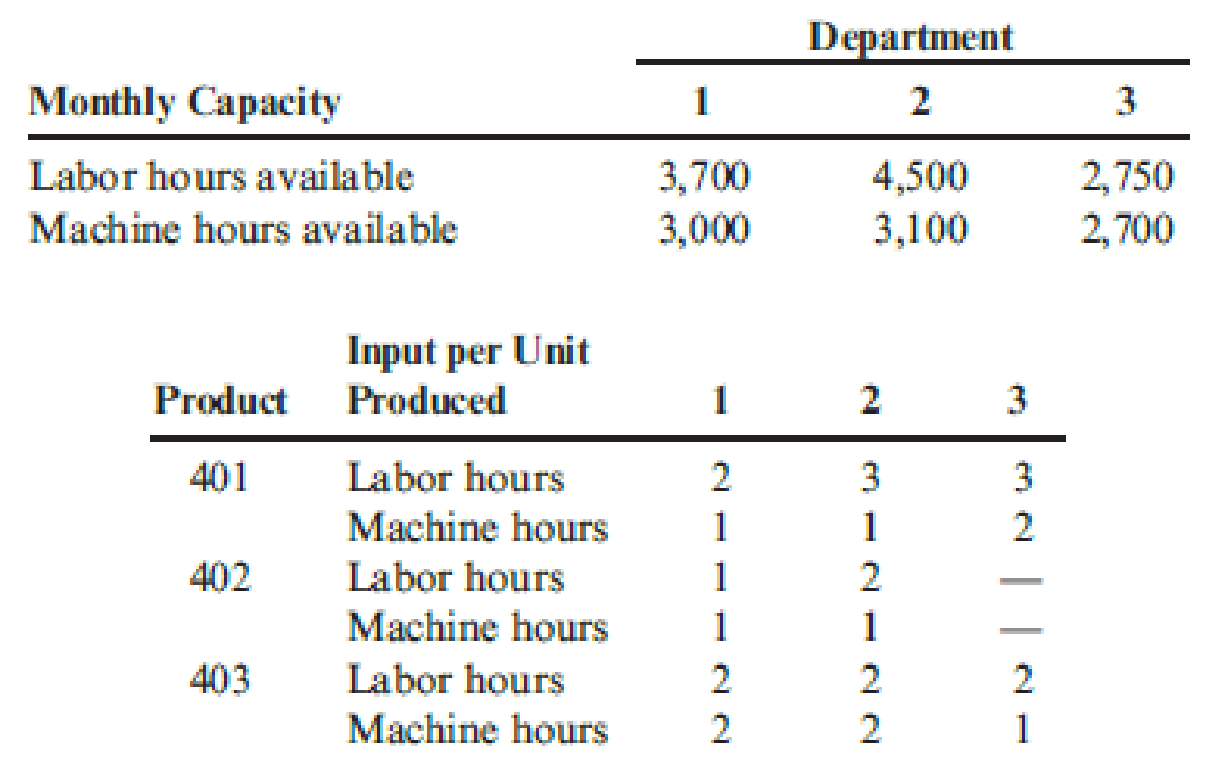
Following is information regarding available machine and labor time by department and the machine hours and direct labor hours required per unit of product. These data should be valid for at least the next six months.
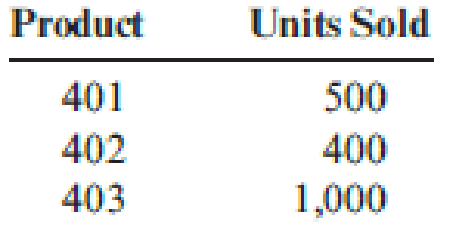
Calen believes that the monthly demand for the next six months will be as follows:
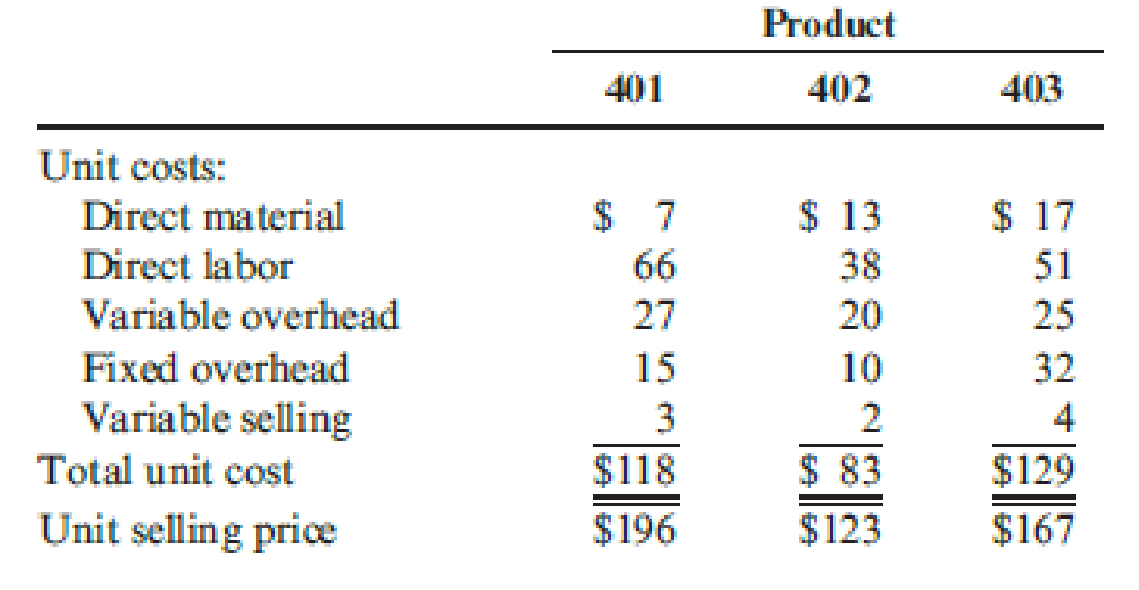
Inventory levels will not be increased or decreased during the next six months. The unit cost and price data for each product are as follows:
Required:
- 1. Calculate the monthly requirement for machine hours and direct labor hours for producing Products 401, 402, and 403 to determine whether or not the factory can meet the monthly sales demand.
- 2. Determine the quantities of 401, 402, and 403 that should be produced monthly to maximize profits. Prepare a schedule that shows the contribution to profits of your product mix.
- 3. Assume that the machine hours available in Department 3 are 1,500 instead of 2,700. Calculate the optimal monthly product mix using the graphing approach to linear programming. Prepare a schedule that shows the contribution to profits from this optimal mix. (CMA adapted)
1.
Calculate the monthly machine hours and direct labor hours for product 401, 402 and 403 and indicate whether the factory can meet monthly sales demand or not.
Explanation of Solution
Contribution margin: Contribution margin is a measurement of performance where only revenue and variable costs are taken into consideration. Hence, this measurement is useful in the evaluation of the probable outcomes of decisions including pricing decisions and other marketing strategies that affect primarily revenue and variable costs.
Calculate the monthly machine hours and direct labor hours for product 401, 402 and 403 and indicate whether the factory can meet monthly sales demand or not as follows:
Direct labor hours:
| Particulars | Department 1 | Department 2 | Department 3 | Total |
| Product 401: | ||||
| Labor hours per unit (A) | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Unit sold (B) | 500 units | 500 units | 500 units | |
| Labor hours for Product 401 | 1,000 | 1,500 | 1,500 | 4,000 hours |
| Product 402: | ||||
| Labor hours per unit (A) | 1 | 2 | 0 | |
| Unit sold (B) | 400 units | 400 units | 400 units | |
| Labor hours for Product 401 | 400 | 800 | 0 | 1,200 hours |
| Product 403: | ||||
| Labor hours per unit (A) | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Unit sold (B) | 1,000 units | 1,000 units | 1,000 units | |
| Labor hours for Product 401 | 2,000 | 2,000 | 2,000 | 6,000 hours |
| Totals | 3,400 hours | 4,300 hours | 3,500 hours | 11,200 hours |
Table (1)
Machine hours:
| Particulars | Department 1 | Department 2 | Department 3 | Total |
| Product 401: | ||||
| Machine hours per unit (A) | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Unit sold (B) | 500 units | 500 units | 500 units | |
| Machine hours for Product 401 | 500 | 500 | 1,000 | 2,000 hours |
| Product 402: | ||||
| Machine hours per unit (A) | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| Unit sold (B) | 400 units | 400 units | 400 units | |
| Machine hours for Product 401 | 400 | 400 | 0 | 800 hours |
| Product 403: | ||||
| Machine hours per unit (A) | 2 | 2 | 1 | |
| Unit sold (B) | 1,000 units | 1,000 units | 1,000 units | |
| Machine hours for Product 401 | 2,000 | 2,000 | 1,000 | 5,000 hours |
| Totals | 2,900 hours | 2,900 hours | 2,000 hours | 7,800 hours |
Table (2)
In this case, company can meet the demand in all departments expect Department 3, because available labor hours for department 3 (2,750 hours) is less than the monthly requirement of 3,500 hours.
2.
Prepare a schedule of contribution to profits for the given product mix.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a schedule of contribution to profit for the given product mix as follows:
In this case, department 3 in product 401 has more labor hour than the actual available hours. Hence, after meeting the demand the additional labor hours of Department 3 is used to produce the product 1 as a subsidy of department 1. Thus, department 1 would produce only 250 units
| Particulars | Optimal output (A) | Contribution margin per unit (B) |
Total contribution |
| Product 401 | 250 units | $93 (1) | $23,250 |
| Product 402 | 400 units | $50 (2) | $20,000 |
| Product 403 | 1,000 units | $70 (3) | $70,000 |
| Total contribution margin | $113,250 | ||
Table (3)
Working note (1):
Calculate the contribution margin per unit for product 401.
Working note (2):
Calculate the contribution margin per unit for product 402.
Working note (3):
Calculate the contribution margin per unit for product 403.
3.
Compute the optimal monthly product mix using the graphical approach to linear program and calculate the contribution profit for the optimal mix.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the optimal monthly product mix using the graphical approach to linear program and calculate the contribution profit for the optimal mix as follows:
Machine constraint:
Direct labor constraint:
Demand constraint for each product:
Note: X denotes number of product produced in Product 401, Y denotes number of product produced in Product 402, and Z denotes number of product produced in Product 403.
| Corner point | X-value | Y-value | W-value | |
| A | 0 | 0 | 400 | $20,000 |
| B | 500 | 0 | 400 | $66,500 |
| C | 500 | 500 | 400 | $101,500 |
| D | 250 | 1,000 | 400 | $113,250 |
| E | 0 | 1,000 | 400 | $90,000 |
Table (1)
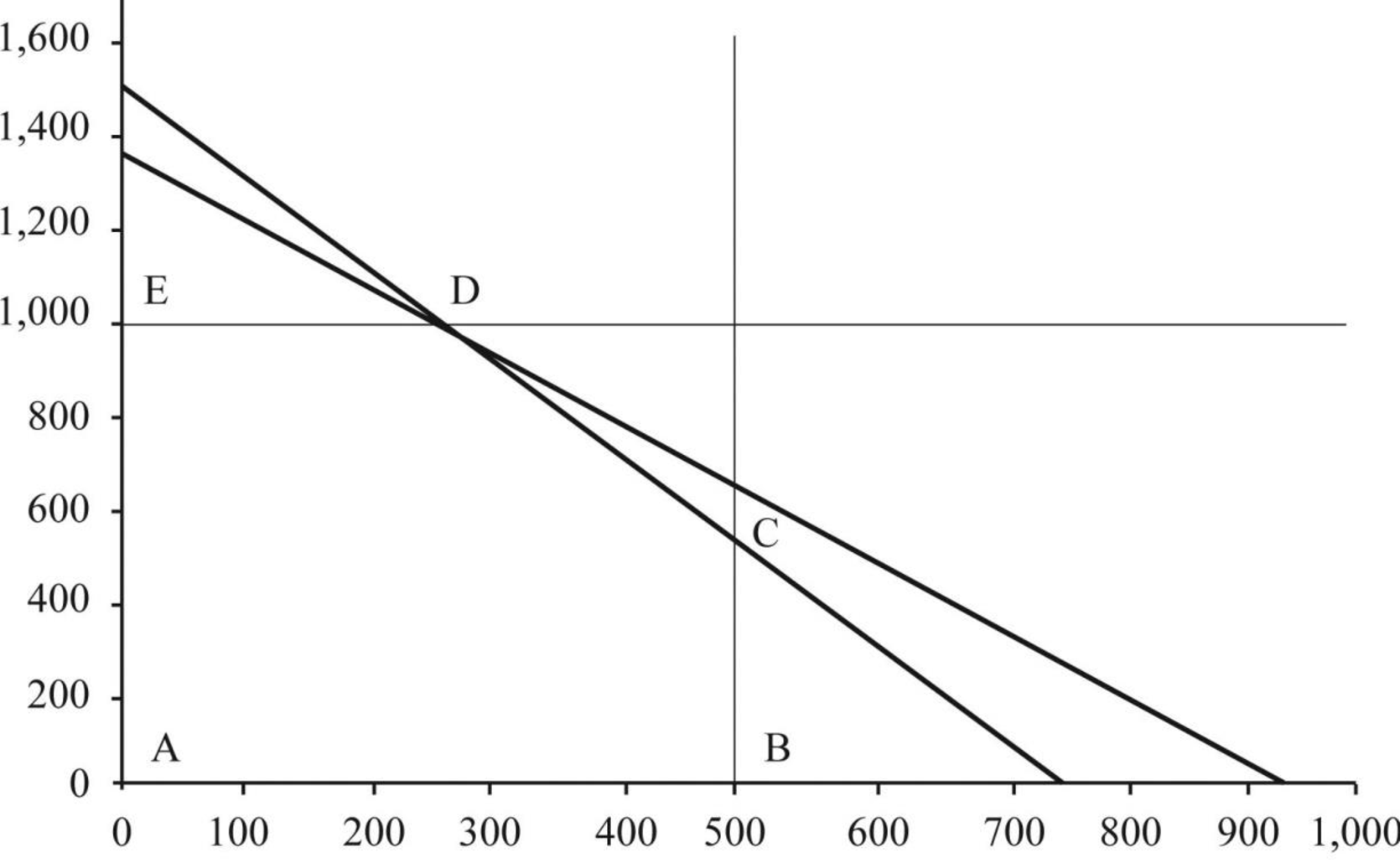
Figure (1)
Hence, contribution margin under optimal output is $113,250.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
CengageNOWv2, 1 term Printed Access Card for Hansen/Mowen’s Cornerstones of Cost Management, 4th
- Anderson Company has the following departmental manufacturing structure for one of its products: After some study, the production manager of Anderson recommended the following revised cellular manufacturing approach: Required: 1. Calculate the total time it takes to produce a batch of 20 units using Andersons traditional departmental structure. 2. Using cellular manufacturing, how much time is saved producing the same batch of 20 units? Assuming the cell operates continuously, what is the production rate? Which process controls this production rate? 3. What if the processing times of molding, welding, and assembly are all reduced to six minutes each? What is the production rate now, and how long will it take to produce a batch of 20 units?arrow_forwardBig Mikes, a large hardware store, has gathered data on its overhead activities and associated costs for the past 10 months. Nizam Sanjay, a member of the controllers department, believes that overhead activities and costs should be classified into groups that have the same driver. He has decided that unloading incoming goods, counting goods, and inspecting goods can be grouped together as a more general receiving activity, since these three activities are all driven by the number of receiving orders. The 10 months of data shown below have been gathered for the receiving activity. Required: 1. Prepare a scattergraph, plotting the receiving costs against the number of purchase orders. Use the vertical axis for costs and the horizontal axis for orders. 2. Select two points that make the best fit, and compute a cost formula for receiving costs. 3. Using the high-low method, prepare a cost formula for the receiving activity. 4. Using the method of least squares, prepare a cost formula for the receiving activity. What is the coefficient of determination?arrow_forwardVargas, Inc., produces industrial machinery. Vargas has a machining department and a group of direct laborers called machinists. Each machinist is paid 25,000 and can machine up to 500 units per year. Vargas also hires supervisors to develop machine specification plans and to oversee production within the machining department. Given the planning and supervisory work, a supervisor can oversee three machinists, at most. Vargass accounting and production history reveal the following relationships between units produced and the costs of direct labor and supervision (measured on an annual basis): Required: 1. Prepare two graphs: one that illustrates the relationship between direct labor cost and units produced, and one that illustrates the relationship between the cost of supervision and units produced. Let cost be the vertical axis and units produced the horizontal axis. 2. How would you classify each cost? Why? 3. Suppose that the normal range of activity is between 2,400 and 2,450 units and that the exact number of machinists is currently hired to support this level of activity. Further suppose that production for the next year is expected to increase by an additional 400 units. How much will the cost of direct labor increase (and how will this increase be realized)? Cost of supervision?arrow_forward
- Ingles Corporation is a manufacturer of tables sold to schools, restaurants, hotels, and other institutions. The table tops are manufactured by Ingles, but the table legs are purchased from an outside supplier. The Assembly Department takes a manufactured table top and attaches the four purchased table legs. It takes 16 minutes of labor to assemble a table. The company follows a policy of producing enough tables to ensure that 40 percent of next months sales are in the finished goods inventory. Ingles also purchases sufficient materials to ensure that materials inventory is 60 percent of the following months scheduled production. Ingless sales budget in units for the next quarter is as follows: Ingless ending inventories in units for July 31 are as follows: Required: 1. Calculate the number of tables to be produced during August. 2. Disregarding your response to Requirement 1, assume the required production units for August and September are 2,100 and 1,900, respectively, and the July 31 materials inventory is 4,000 units. Compute the number of table legs to be purchased in August. 3. Assume that Ingles Corporation will produce 2,340 units in September. How many employees will be required for the Assembly Department in September? (Fractional employees are acceptable since employees can be hired on a part-time basis. Assume a 40-hour week and a 4-week month.) (CMA adapted)arrow_forwardMott Company recently implemented a JIT manufacturing system. After one year of operation, Heidi Burrows, president of the company, wanted to compare product cost under the JIT system with product cost under the old system. Motts two products are weed eaters and lawn edgers. The unit prime costs under the old system are as follows: Under the old manufacturing system, the company operated three service centers and two production departments. Overhead was applied using departmental overhead rates. The direct overhead costs associated with each department for the year preceding the installation of JIT are as follows: Under the old system, the overhead costs of the service departments were allocated directly to the producing departments and then to the products passing through them. (Both products passed through each producing department.) The overhead rate for the Machining Department was based on machine hours, and the overhead rate for assembly was based on direct labor hours. During the last year of operations for the old system, the Machining Department used 80,000 machine hours, and the Assembly Department used 20,000 direct labor hours. Each weed eater required 1.0 machine hour in Machining and 0.25 direct labor hour in Assembly. Each lawn edger required 2.0 machine hours in Machining and 0.5 hour in Assembly. Bases for allocation of the service costs are as follows: Upon implementing JIT, a manufacturing cell for each product was created to replace the departmental structure. Each cell occupied 40,000 square feet. Maintenance and materials handling were both decentralized to the cell level. Essentially, cell workers were trained to operate the machines in each cell, assemble the components, maintain the machines, and move the partially completed units from one point to the next within the cell. During the first year of the JIT system, the company produced and sold 20,000 weed eaters and 30,000 lawn edgers. This output was identical to that for the last year of operations under the old system. The following costs have been assigned to the manufacturing cells: Required: 1. Compute the unit cost for each product under the old manufacturing system. 2. Compute the unit cost for each product under the JIT system. 3. Which of the unit costs is more accurate? Explain. Include in your explanation a discussion of how the computational approaches differ. 4. Calculate the decrease in overhead costs under JIT, and provide some possible reasons that explain the decrease.arrow_forwardBienestar Inc., has the following departmental structure for producing a well-known multivitamin: A consultant designed the following cellular manufacturing structure for the same product: The times above the processes represent the time required to process one unit of product. Required: 1. Calculate the time required to produce a batch of 15 bottles using a batch-processing departmental structure. 2. Calculate the time to process 15 units using cellular manufacturing. 3. How much manufacturing time will the cellular manufacturing structure save for a batch of 15 units?arrow_forward
- A dedicated pharmaceutical plant uses the theory of constraints and has three processes: Mixing, Encapsulating, and Packaging. For Mixing, sufficient materials are released to produce 4,000 packages of product per day. Encapsulating has a buffer inventory of 8,000 units (work in process from Mixing). Packaging produces 4,000 units per day. Which of the three processes sets the production rate of 4,000 units per day? a. The Mixing Department b. The Encapsulating Department c. The Packaging Department d. Cannot be determinedarrow_forwardYoung Company is beginning operations and is considering three alternatives to allocate manufacturing overhead to individual units produced. Young can use a plantwide rate, departmental rates, or activity-based costing. Young will produce many types of products in its single plant, and not all products will be processed through all departments. In which one of the following independent situations would reported net income for the first year be the same regardless of which overhead allocation method had been selected? a. All production costs approach those costs that were budgeted. b. The sales mix does not vary from the mix that was budgeted. c. All manufacturing overhead is a fixed cost. d. All ending inventory balances are zero.arrow_forwardBrees, Inc., a manufacturer of golf carts, has just received an offer from a supplier to provide 2,600 units of a component used in its main product. The component is a track assembly that is currently produced internally. The supplier has offered to sell the track assembly for 66 per unit. Brees is currently using a traditional, unit-based costing system that assigns overhead to jobs on the basis of direct labor hours. The estimated traditional full cost of producing the track assembly is as follows: Prior to making a decision, the companys CEO commissioned a special study to see whether there would be any decrease in the fixed overhead costs. The results of the study revealed the following: 3 setups1,160 each (The setups would be avoided, and total spending could be reduced by 1,160 per setup.) One half-time inspector is needed. The company already uses part-time inspectors hired through a temporary employment agency. The yearly cost of the part-time inspectors for the track assembly operation is 12,300 and could be totally avoided if the part were purchased. Engineering work: 470 hours, 45/hour. (Although the work decreases by 470 hours, the engineer assigned to the track assembly line also spends time on other products, and there would be no reduction in his salary.) 75 fewer material moves at 30 per move. Required: 1. Ignore the special study, and determine whether the track assembly should be produced internally or purchased from the supplier. 2. Now, using the special study data, repeat the analysis. 3. Discuss the qualitative factors that would affect the decision, including strategic implications. 4. After reviewing the special study, the controller made the following remark: This study ignores the additional activity demands that purchasing would cause. For example, although the demand for inspecting the part on the production floor decreases, we may need to inspect the incoming parts in the receiving area. Will we actually save any inspection costs? Is the controller right?arrow_forward
- Christmas Timber, Inc., produces Christmas trees. The trees are produced through a cutting and pruning process. Machine maintenance and janitorial labors are performed throughout the production process by nonproduction employees. Maintenance and janitorial costs are allocated based on machine hours used and the number of trees in each department, respectively. The company estimates that the cutting and pruning areas typically have about 20 and 60 trees, respectively, in them at one time. The company also estimates that the cutting process requires about 9 times as many machine hours as the pruning process. The total costs of each department are as follows: Using the direct method of support department cost allocation, determine the total cost of each production department after allocating all support costs to the production departments.arrow_forwardVollmer Manufacturing makes three components for sale to refrigeration companies. The components are processed on two machines: a shaper and a grinder. The times (in minutes) required on each machine are as follows: The shaper is available for 120 hours, and the grinder for 110 hours. No more than 200 units of component 3 can be sold, but up to 1,000 units of each of the other components can be sold. In fact, the company already has orders for 600 units of component 1 that must be satisfied. The profit contributions for components 1, 2, and 3 are 8, 6, and 9, respectively. a. Formulate and solve for the recommended production quantities. b. What are the objective coefficient ranges for the three components? Interpret these ranges for company management. c. What are the right-hand-side ranges? Interpret these ranges for company management. d. If more time could be made available on the grinder, how much would it be worth? e. If more units of component 3 can be sold by reducing the sales price by 4, should the company reduce the price?arrow_forwardMabbut Company has the following departmental manufacturing layout for one of its plants: A consulting firm recommended a value stream with the following manufacturing cell: Required: 1. Calculate the total time it takes to produce a batch of 10 units using the traditional departmental manufacturing layout. 2. Using cellular manufacturing, how much time is saved producing the same batch of 10 units? Assuming the cell operates continuously, what is the production rate? Which process controls this production rate? 3. Assume the processing time of Welding is reduced to 6 minutes, while the times of the other processes stay the same. What is the production rate now, and how long will it take to produce a batch of 10 units if the cell is in a continuous production mode?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning




