
Interpretation:
Thegiven compounds are to be prepared by using the toluene, sodium cyanide, and carbon dioxide as the sources of the carbon atoms, along with any necessary inorganic reagents.
Concept introduction:
The oxidation of alkyl benzene using strong oxidizing agent
The hydroxyl group of
The condensation of alcohol with carboxylic acid forms an ester.
The primary amide can be prepared by the acylation of ammonia.
Electron donating groups activates the arenes and gives electrophilic substitution at ortho-para position.
Electron withdrawing groups deactivates the arenes and gives electrophilic substitution at meta position.
The treatment of Grignard’s reagent on carbon dioxide forms a carboxylic acid.
The alkyl cyanide (nitrile) on hydrolysis yields carboxylic acid.
Alkyl cyanide (nitrile) can be prepared by the nucleophilic substitution of
Aryl cyanide can be synthesized by using a Sandmeyer reaction where, the aryl diazonium salt is treated with
The aryl diazonium salt is a key intermediate in synthesis of
The aryl chlorides can be converted to acid anhydride by nucleophilic acyl substitution using carboxylic acid.
The nitration is the electrophilic substitution of aromatic compound using reagent nitric acid in concentrated sulfuric acid
The nitrobenzene on reduction with
The benzylic bromide can be synthesized from toluene using
The benzoic acid on heating with calcium oxide reduced to benzene.
Answer to Problem 37P
Solution:
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
f)
g)
h)
i)
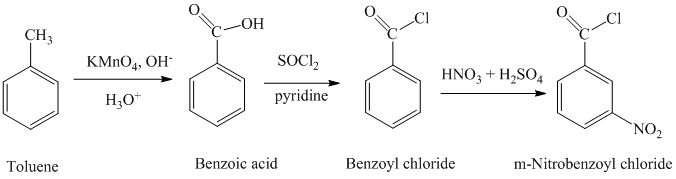
Explanation of Solution
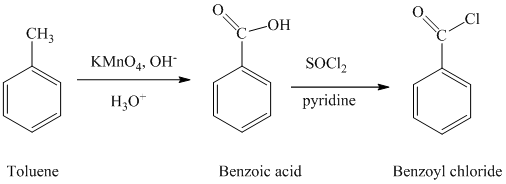
a) Benzoyl chloride
The benzoyl chloride can be synthesized starting with toluene.
The reaction sequence is shown below:
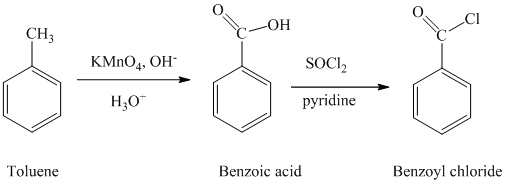
The toluene is oxidized to benzoic acid using a strong oxidizing agent
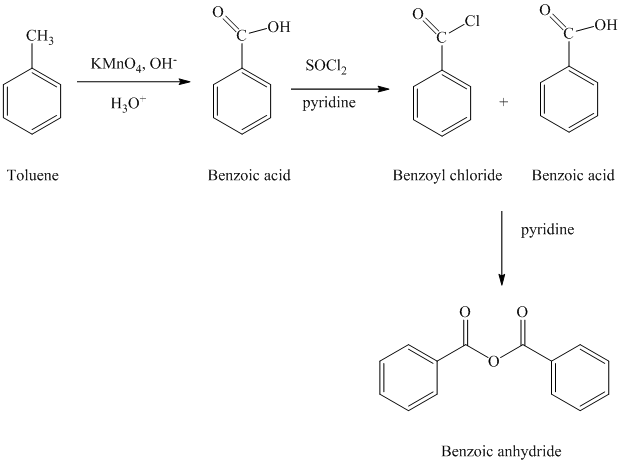
b) Benzoic anhydride
The reaction sequence for the synthesis of Benzoic anhydride is shown below:
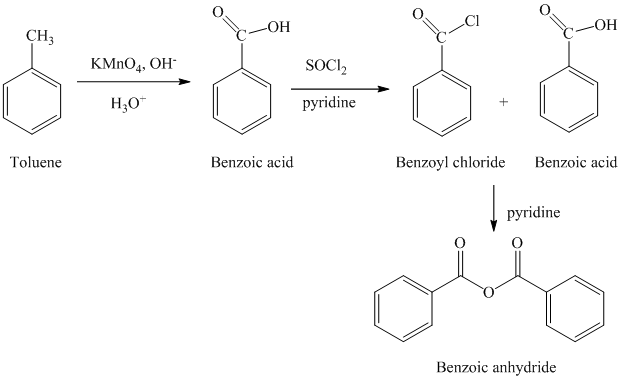
The toluene is first converted to benzoic acid using strong oxidizing agent
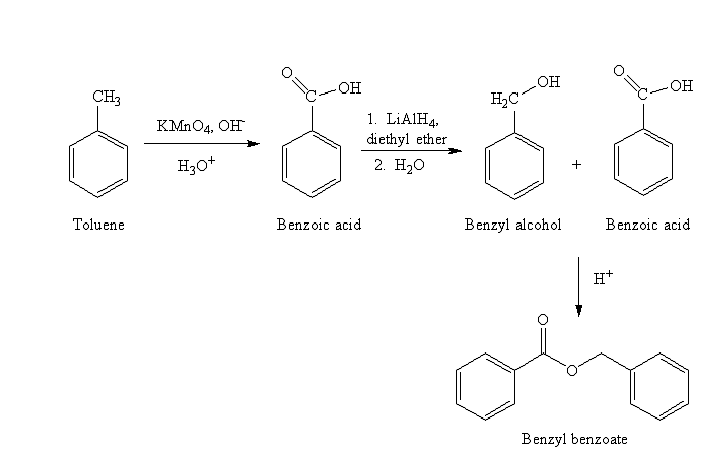
c) Benzyl benzoate
The reaction sequence for the synthesis of benzyl benzoate is shown below:
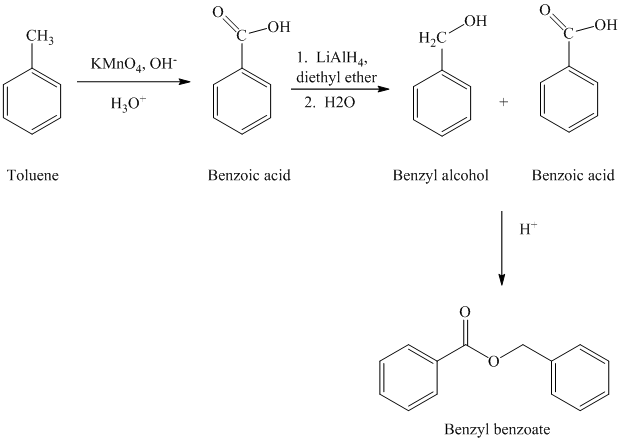
The benzyl benzoate is an ester prepared by reacting the benzyl alcohol and benzoic acid. The benzoic acid is prepared by oxidizing toluene by using strong oxidizing agent
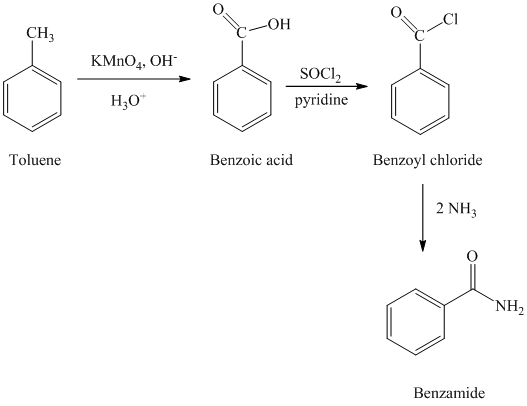
d) Benzamide
The benzamide is synthesized by the reaction of benzoyl chloride with ammonia. The benzoyl chloride is prepared by starting with toluene. The toluene is first converted to benzoic acid using strong oxidizing agent
The reaction sequence for the synthesis of benzamide is shown below:
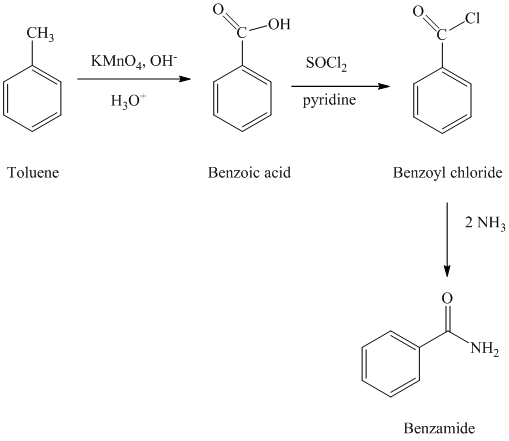
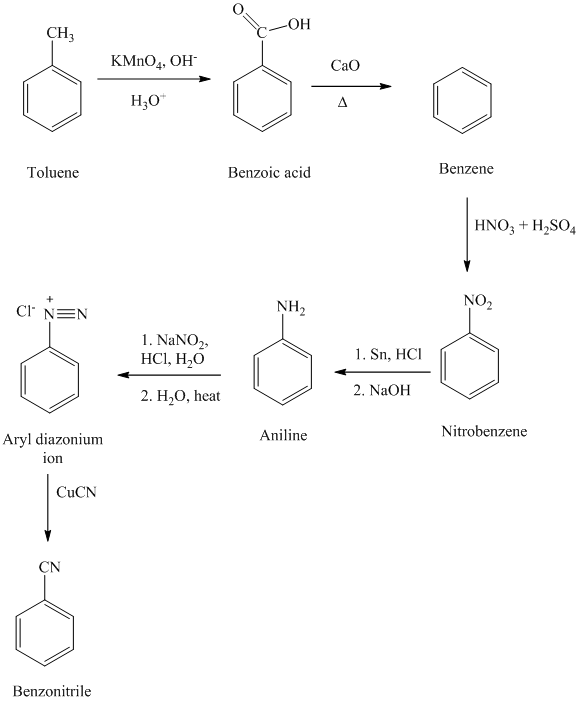
e) Benzonitrile
In the first step, the toluene is converted to benzoic acid using a strong oxidizing agent
The reaction sequence for the synthesis of benzonitrile is shown below:
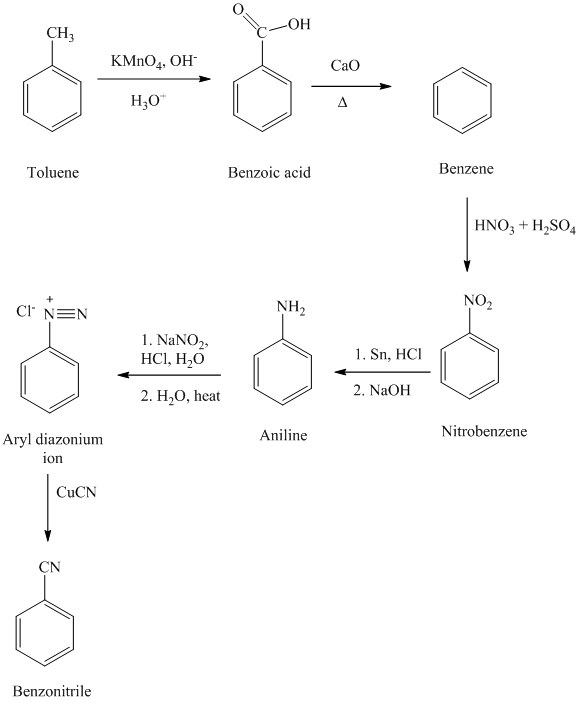
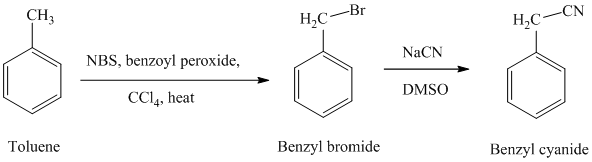
f) Benzyl cyanide
The reaction sequence for the synthesis of benzyl cyanide is shown below:
In the first step, the toluene is converted to benzyl bromide using a reagent
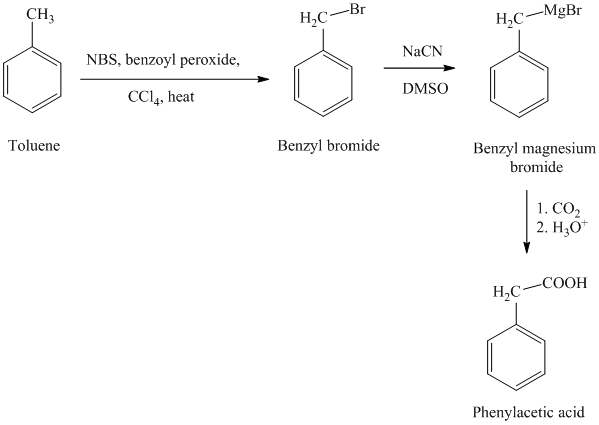
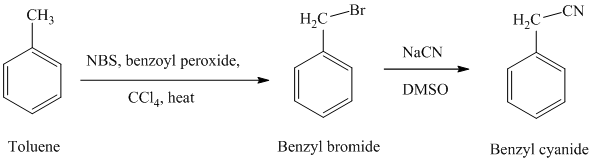
g) Phenylacetic acid
The reaction sequence for the synthesis of phenylacetic acid is shown below:
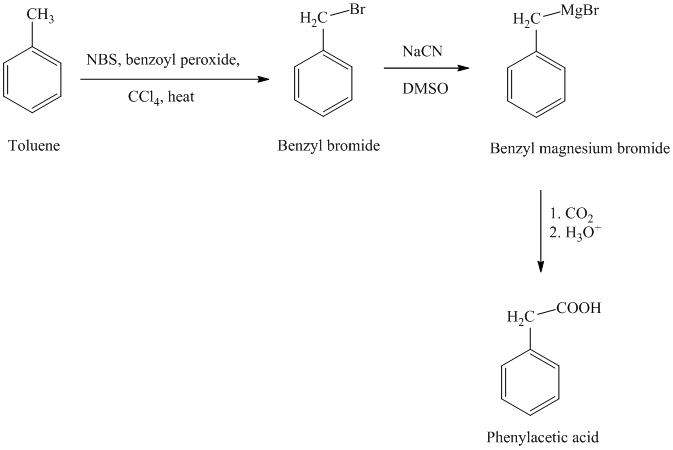
In the first step, the toluene is converted to benzyl bromide using a reagent
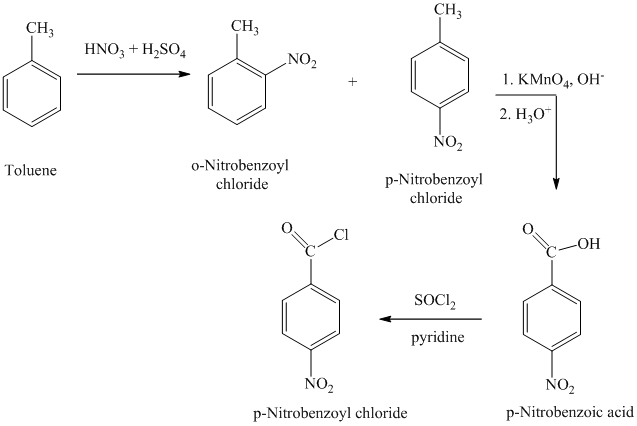
h)
The reaction sequence for the synthesis of
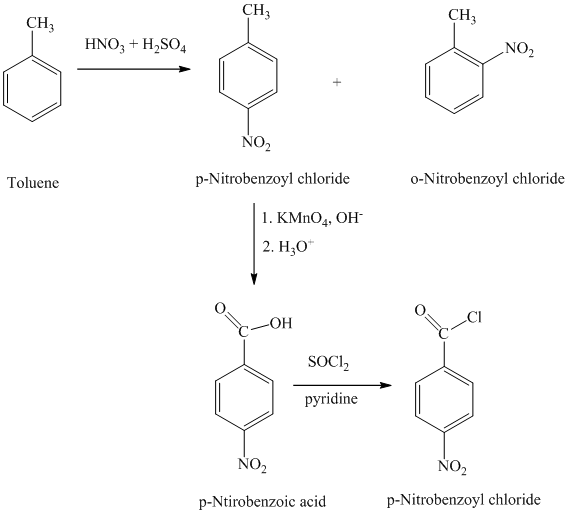
The toluene on nitration gave the mixture of ortho-nitro toluene and para-nitro toluene. The para-nitro toluene is then oxidized using a strong oxidizing agent
i)
The reaction sequence for the synthesis of
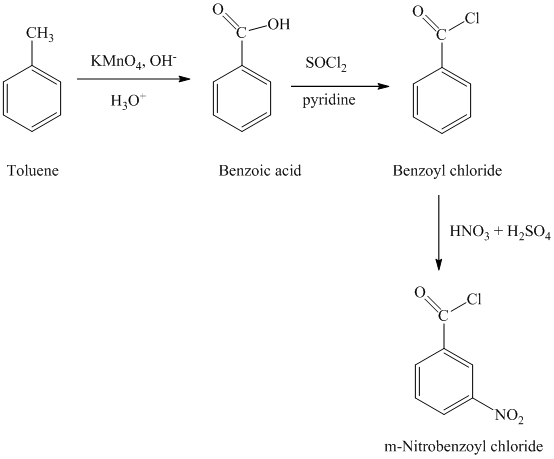
In first step, the toluene is oxidized to benzoic acid using a strong oxidizing agent
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
- Following is a synthesis for toremifene, a nonsteroidal estrogen antagonist whose structure is closely related to that of tamoxifen. (a) This synthesis makes use of two blocking groups, the benzyl (Bn) group and the tetrahydropyranyl (THP) group. Draw a structural formula of each group and describe the experimental conditions under which it is attached and removed. (b) Discuss the chemical logic behind the use of each blocking group in this synthesis. (c) Propose a mechanism for the conversion of D to E. (d) Propose a mechanism for the conversion of F to toremifene. (e) Is toremifene chiral? If so, which of the possible stereoisomers are formed in this synthesis?arrow_forwardPredict the products of reactions of ketones and aldehydes with the followingtypes of compounds, and give mechanisms where appropriate: (a) hydridereducing agents; (b) Clemmensen and Wolff-Kishner reagents; (c) Grignard andorganolithium reagents; (d) phosphorus ylides; (e) water; (f) hydrogen cyanide;(g) ammonia and primary amines; (h) hydroxylamine and hydrazine derivatives;(i) alcohols; and (j) oxidizing agents.arrow_forwardFollowing is an outline of a synthesis of the bronchodilator carbuterol, a beta-2 adrenergic blocker with high selectivity for airway smooth muscle receptors. Q. Propose reagents to bring about each step.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
