
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
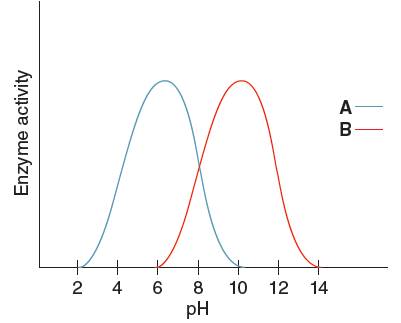
The optimum pH for enzyme 'A' needs to be determined, using the given pH versus enzyme activity graph for enzyme A and B.
Concept Introduction:
Enzymes are defined as a biological catalyst for various reactions in the living organisms. Enzymes are like all catalyst as it also increases the rate reaction but they themselves do not changed permanently during the process. Enzyme does not alter the position of equilibrium and the relative energy of both the reactant and the products. Reaction when catalyzed by an enzyme increases the
Answer to Problem 77P
Optimum pH for enzyme 'A' is
Explanation of Solution
The activity of enzyme is affected by both the temperature and pH. By increasing temperature, rate of reaction also increases until its maximum activity occurs that is at
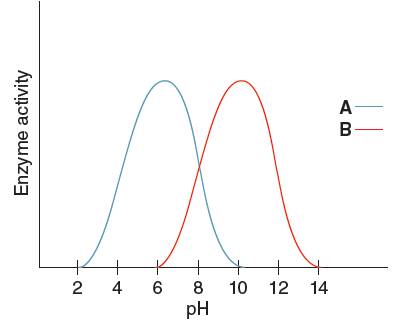
Optimum pH is the pH at which the activity of an enzyme is maximum. So, from the given graph, the activity of enzyme A is maximum at pH 6. Hence the optimum pH of enzyme A is 6.
(b)
Interpretation:
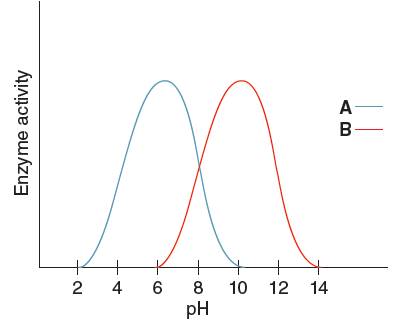
The optimum pH for enzyme 'B' needs to be determined, using the given pH versus enzyme activity graph for enzyme A and B.
Concept Introduction:
Enzymes are defined as a biological catalyst for various reactions in the living organisms. Enzymes are like all catalyst as it also increases the rate reaction but they themselves do not changed permanently during the process. Enzyme does not alter the position of equilibrium and the relative energy of both the reactant and the products. Reaction when catalyzed by an enzyme increases the rate of reaction by
Answer to Problem 77P
Optimum pH for enzyme 'B' is
Explanation of Solution
The activity of enzyme is affected by both the temperature and pH. By increasing temperature, rate of reaction also increases until its maximum activity occurs that is at
Optimum pH is the pH at which the activity of an enzyme is maximum. So, from the given graph, the activity of enzyme B is maximum at pH 10.
Hence, the optimum pH of enzyme B is 10.
(c)
Interpretation:
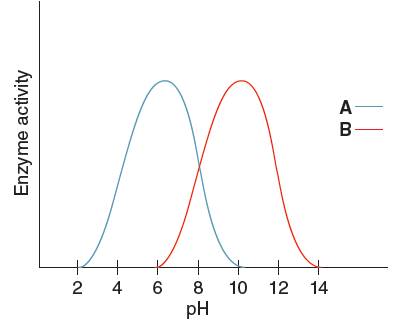
The enzyme having the higher activity when pH is
Concept Introduction:
Enzymes are defined as a biological catalyst for various reactions in the living organisms. Enzymes are like all catalyst as it also increases the rate reaction but they themselves do not changed permanently during the process. Enzyme does not alter the position of equilibrium and the relative energy of both the reactant and the products. Reaction when catalyzed by an enzyme increases the rate of reaction by
Answer to Problem 77P
Enzyme 'A' will have higher pH at
Explanation of Solution
The activity of enzyme is affected by both the temperature and pH. Optimum pH is the pH value at which the enzyme is most active. The rate of enzyme catalyzed reaction is maximum at optimum pH
The graph shown below clearly explains the activity of an enzyme with change in pH values:
From the given graph, it can be seen that the activity of enzyme B starts from pH 6 onwards and activity of enzyme A starts from pH 2 onwards. So, before pH 2 enzyme A is inactive and before pH 6 enzyme B is inactive. Therefore, at pH 4 the activity of enzyme A is higher than that of enzyme B.
(d)
Interpretation:
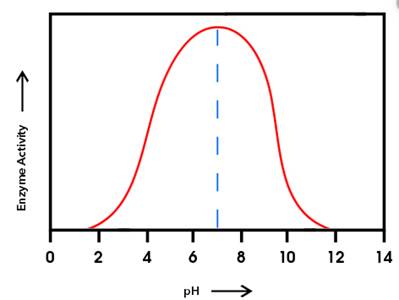
The enzyme having the higher activity at pH
Concept Introduction:
Enzymes are defined as a biological catalyst for various reactions in the living organisms. Enzymes are like all catalyst as it also increases the rate reaction but they themselves do not changed permanently during the process. Enzyme does not alter the position of equilibrium and the relative energy of both the reactant and the products. Reaction when catalyzed by an enzyme increases the rate of reaction by
Answer to Problem 77P
Enzyme 'B' will have the higher activity at pH
Explanation of Solution
The activity of enzyme is affected by both the temperature and pH. Optimum pH is the pH value at which the enzyme is most active. The rate of enzyme catalyzed reaction is maximum at optimum pH
The graph shown below clearly explains the activity of an enzyme with change in pH values:
From the given graph, it can be seen that the activity of enzyme B starts from pH 6 onwards and becomes maximum at pH 10and then activity of enzyme starts decreasing. And activity of enzyme A starts from pH 2 onwards and becomes maximum at pH 6 and then starts decreasing.
At pH 9, activity of enzyme A is decreasing and that of enzyme B is increasing. Hence, at pH 9 activity of enzyme B is higher than that of enzyme A.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
GENERAL ORGANIC & BIOCHEMISTRY >ACCESS<
- Describe the importance of zymogens in the body. Give an example of an enzyme that has a zymogen.arrow_forwardThe human body has an average pH of about 7 and a temperature of about 37C. Use graphs to illustrate enzyme activity in the human body as a function of the following: a. Substrate concentration b. Enzyme concentration c. pH include pH optimum value d. Temperature include temperature optimum valuearrow_forward. How does the efficiency of an enzyme compare with that of inorganic catalysts? Are enzymes more or less efficient?arrow_forward
- Based on the graphical information in Problem 21-41 about enzymes A and B indicate whether the enzyme activity of enzyme B increases or decreases when the following changes in reaction conditions are made. a. pH decreases from 7.6 to 7.2 b. pH increases from 7.2 to 7.4 c. temperature decreases from 37.8C to 37.6C d. temperature increases from 38.2C to 38.4Carrow_forwardDraw a graph that shows the effect of increasing substrate concentration on the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction (at constant temperature, pH, and enzyme concentration).arrow_forwardExplain how the pasteurization of milk utilizes one of the factors that influence enzyme activity.arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





