
Concept explainers
Consider the following mRNA sequence:
- What amino acid sequence is coded for by this mRNA?
- What is the amino acid sequence if a mutation converts CAG to AAC?
- What is the amino acid sequence if a mutation converts CUU to CUC?
- What occurs when a mutation converts CAG to UAG?
- What occurs if CU is deleted from the beginning of the chain?
(a)
Interpretation:
Peptide synthesized by the 5' CUU CAG CAC 3' mRNA should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Answer to Problem 22.75P
Peptide − Leu-Gln-His
Explanation of Solution
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5) to 3 prime end (3) of mRNA. There is a unique triplet representation for a particular amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
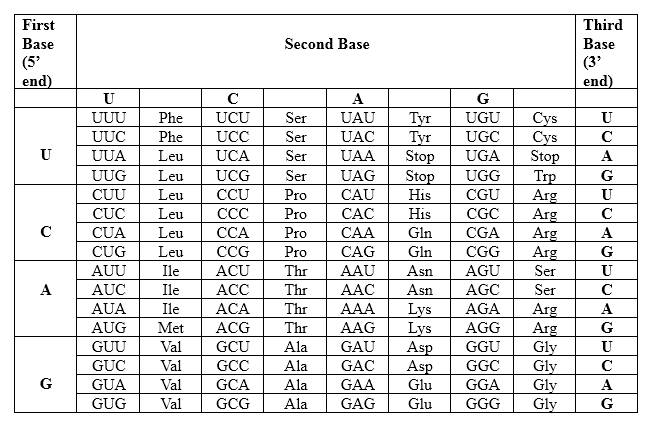
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. CUU triplet is unique for Leucine. CAG triplet is unique for Glutamine. CAC is unique for Histidine.
Therefore, Leu-Gln-His is the amino acid sequence for 5' CUU CAG CAC 3'.
(b)
Interpretation:
Peptide formed from mutated mRNA5' CUU CAG AAC3' should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule.
Answer to Problem 22.75P
Peptide − Leu-Gln-Asn
Explanation of Solution
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. When mutation happens at a particular position of a DNA molecule, that mutation goes through mRNA and translate a wrong peptide.
Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule. There are three types of mutations which can be classified as follows;
- Point mutations − A substitution of one nucleotide for another nucleotide.
- Deletion mutations − One or more nucleotides is lost from a particular DNA molecule.
- Insertion mutations − One or more nucleotides is added to a DNA molecule.
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
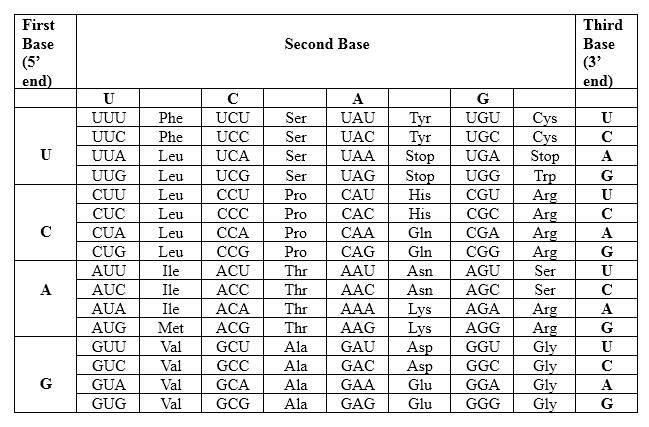
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. CUU triplet is unique for Leucine. CAG triplet is unique for Glutamine. AAC is unique for Asparagine. There is a point mutation in the mRNA strand, which CAC in the normal strand converts to AAC in the mutated strand. The resulting protein is different from the un-mutated one.
Therefore, Leu-Gln-Asn is the amino acid sequence for 5' CUU CAG AAC 3'.
(c)
Interpretation:
Peptide formed from mutated mRNA 5' CUC CAG CAC 3' should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule.
Answer to Problem 22.75P
Peptide − Leu-Gln-His.
Explanation of Solution
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. When mutation happens at a particular position of a DNA molecule, that mutation goes through mRNA and translate a wrong peptide.
Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule. There are three types of mutations which can be classified as follows;
- Point mutations − A substitution of one nucleotide for another nucleotide.
- Deletion mutations − One or more nucleotides is lost from a particular DNA molecule.
- Insertion mutations − One or more nucleotides is added to a DNA molecule.
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
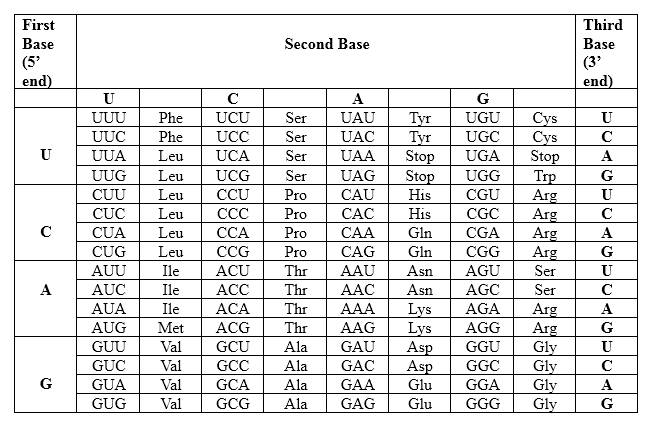
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. CUC triplet is unique for Leucine. CAG triplet is unique for Glutamine. CAC triplet is unique for Histidine. There is a point mutation in the mRNA strand, which CUU in the normal strand converts to CUC in the mutated strand. Though there is a point mutation in the strand, the resulting protein is not different from the un-mutated one.
Therefore, Leu-Gln-His is the amino acid sequence for 5' CUC CAG CAC 3'.
(d)
Interpretation:
Peptide formed from mutated mRNA 5' CUU UAG CAC 3' should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule.
Answer to Problem 22.75P
Amino acid is Leucine and after that amino acid sequence generation is terminated.
Explanation of Solution
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. When mutation happens at a particular position of a DNA molecule, that mutation goes through mRNA and translate a wrong peptide.
Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule. There are three types of mutations which can be classified as follows;
- Point mutations − A substitution of one nucleotide for another nucleotide.
- Deletion mutations − One or more nucleotides is lost from a particular DNA molecule.
- Insertion mutations − One or more nucleotides is added to a DNA molecule.
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
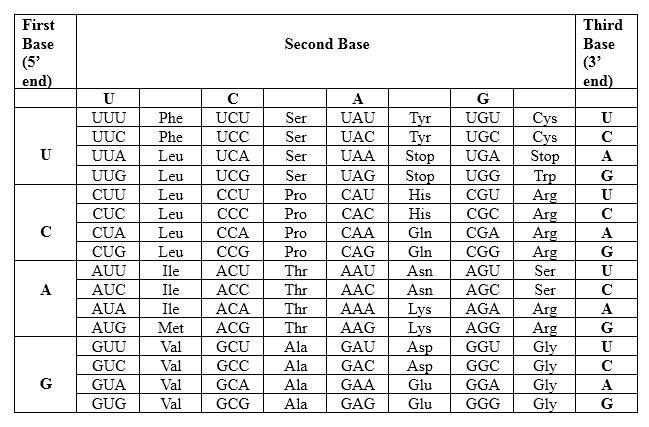
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. CUC triplet is unique for Leucine. UAG triplet is a unique for a stop codon. Hence, after this codon peptide synthesis is terminated. In this case required protein is not synthesized. Hence, the effect of this mutation may be catastrophic to the organism.
Therefore, Leu is the amino acid sequence for 5' CUU UAG CAC 3'
(e)
Interpretation:
Peptide formed from mutated mRNA 5' UCAGCAC 3' should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule.
Answer to Problem 22.75P
Peptide − Ser-Ala
Explanation of Solution
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. When mutation happens at a particular position of a DNA molecule, that mutation goes through mRNA and translate a wrong peptide.
Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule. There are three types of mutations which can be classified as follows;
- Point mutations − A substitution of one nucleotide for another nucleotide.
- Deletion mutations − One or more nucleotides is lost from a particular DNA molecule.
- Insertion mutations − One or more nucleotides is added to a DNA molecule.
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
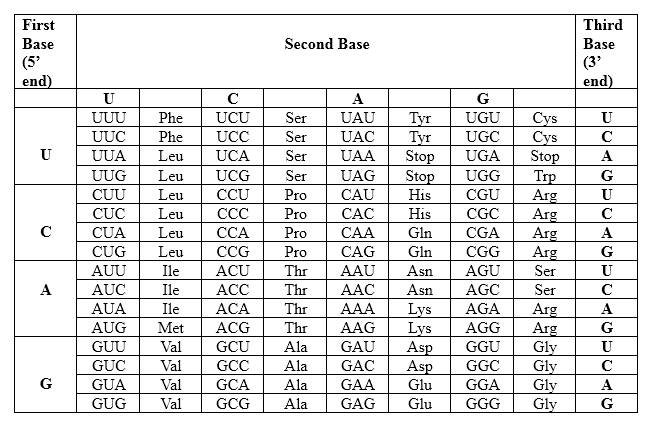
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA and read as triplets, because of the deletion mutation which occurred here because of deletion of CU in the beginning of the mRNA, triplets are read as follows. UCA triplet is unique for Serine and GCA triplet is unique for Alanine. There is an additional A nucleotide, which is not involved into this peptide. Furthermore, this mutation generates totally different peptide and generated peptide is as follows; Ser-Ala is the amino acid sequence for 5' UCAGCAC 3'.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
GENERAL ORGANIC+BIOCHEM (LL)W/CONNECT
- Consider the following mRNA base sequence 5ACCCAC3 a. What dipeptide is coded for by this mRNA? b. What dipeptide is formed if a point mutation converts CAC to AAC? c. What dipeptide is formed if a point mutation converts ACC to ACU? d. What dipeptide is formed if a point mutation converts CAC to AAC and ACC to ACU?arrow_forward3. Which amino acid is selected by the mRNA codon GAA? alanine glutamic acid histidine tyrosinearrow_forwardConsider the following DNA base sequence 3TTAATA5 a. What dipeptide is formed from the transcription and translation of this DNA segment? b. What dipeptide is formed if a DNA point mutation converts ATA to ATG? c. What dipeptide is formed if a DNA point mutation converts ATA to AGA? d. What dipeptide is formed if a DNA point mutation converts TTA to TTT?arrow_forward
- Is the trinucleotide in Problem 22-31 found only in DNA, found only in RNA, or found in both DNA and RNA? Explain the basis for your answer.arrow_forwardThe following is a base sequence for an exon portion of a template strand of a DNA molecule: What is the base sequence of the hnRNA strand synthesized from the DNA template strand? What is the base sequence of the mRNA strand synthesized from the hnRNA strand? What codons are present in the mRNA strand produced from the DNA template strand? What tRNA molecule anticodons are needed to interact with the codons present in the mRNA strand produced from the template DNA strand?arrow_forwardAn hnRNA molecule contains three exons, with the middle one and one other being alternative exons. How many different mRNA molecules can be produced from this hnRNA molecule?arrow_forward
- Give an mRNA sequence that will code for the synthesis of metenkephalin. Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Metarrow_forwardGive an mRNA sequence that will code for the synthesis of angiotensin II. Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro-Phearrow_forwardWhat mRNA base sequence, specified in the 5-to-3 direction, would be obtained from the following portion of a gene?arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





